Abstract
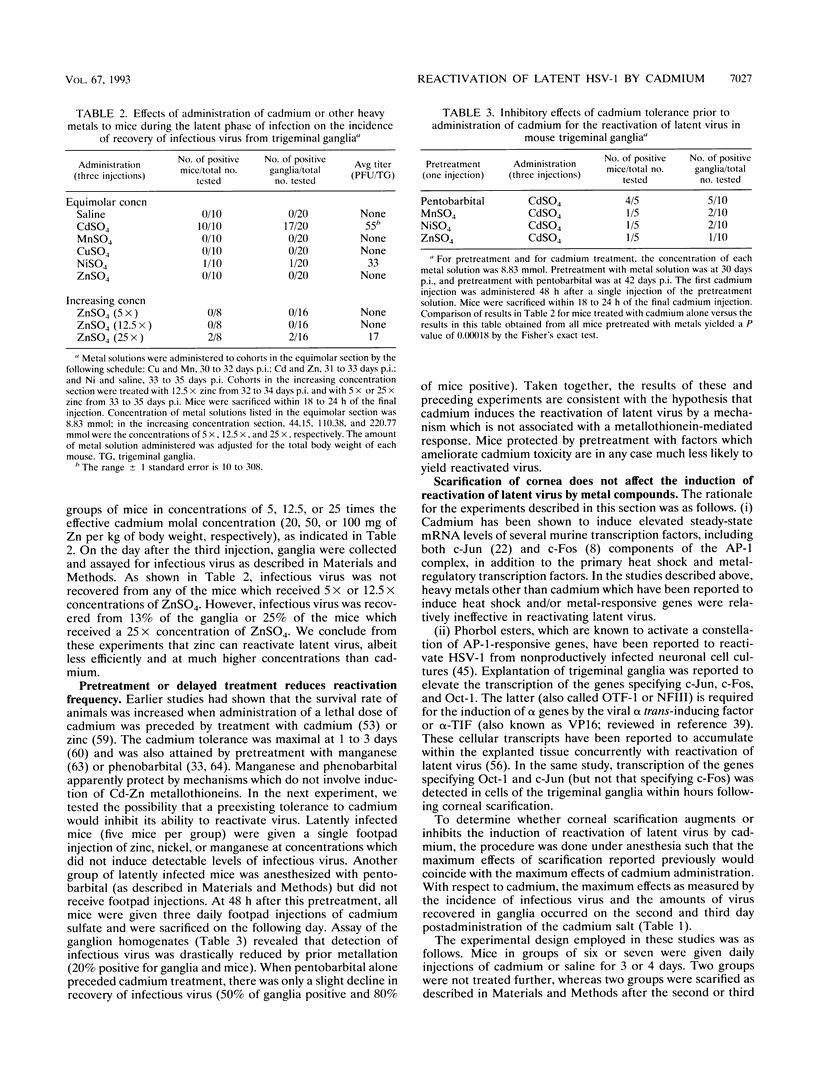
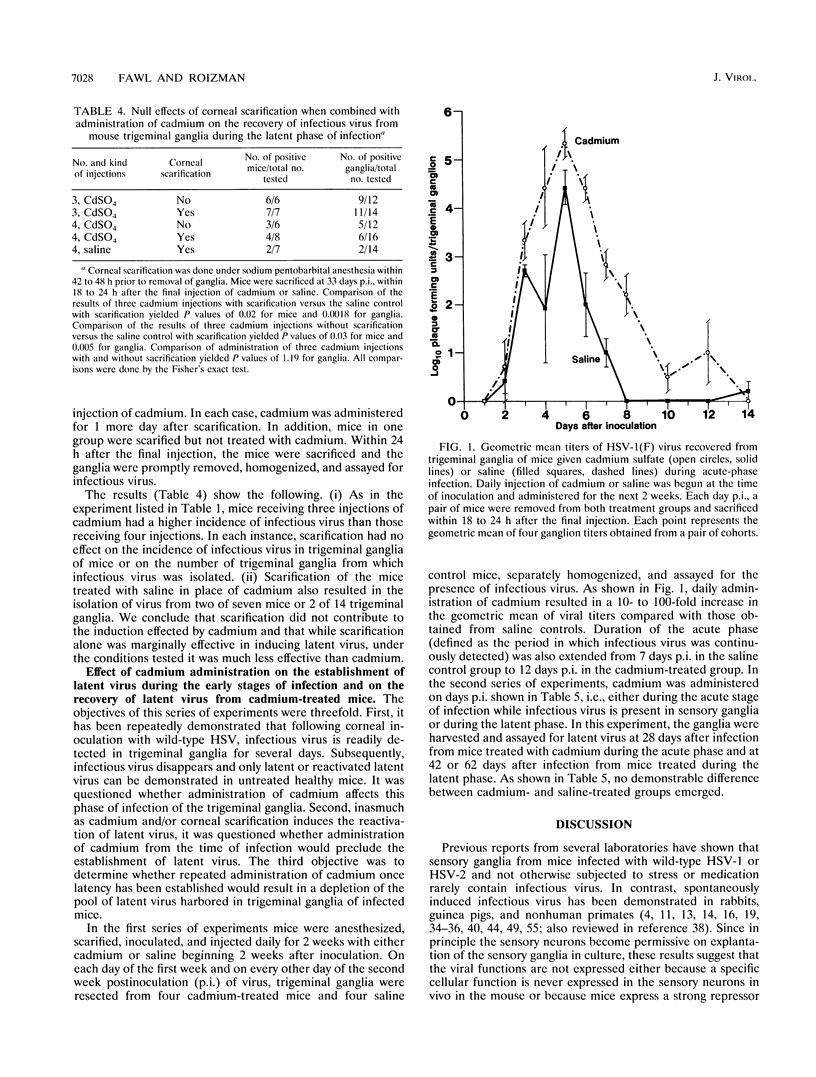
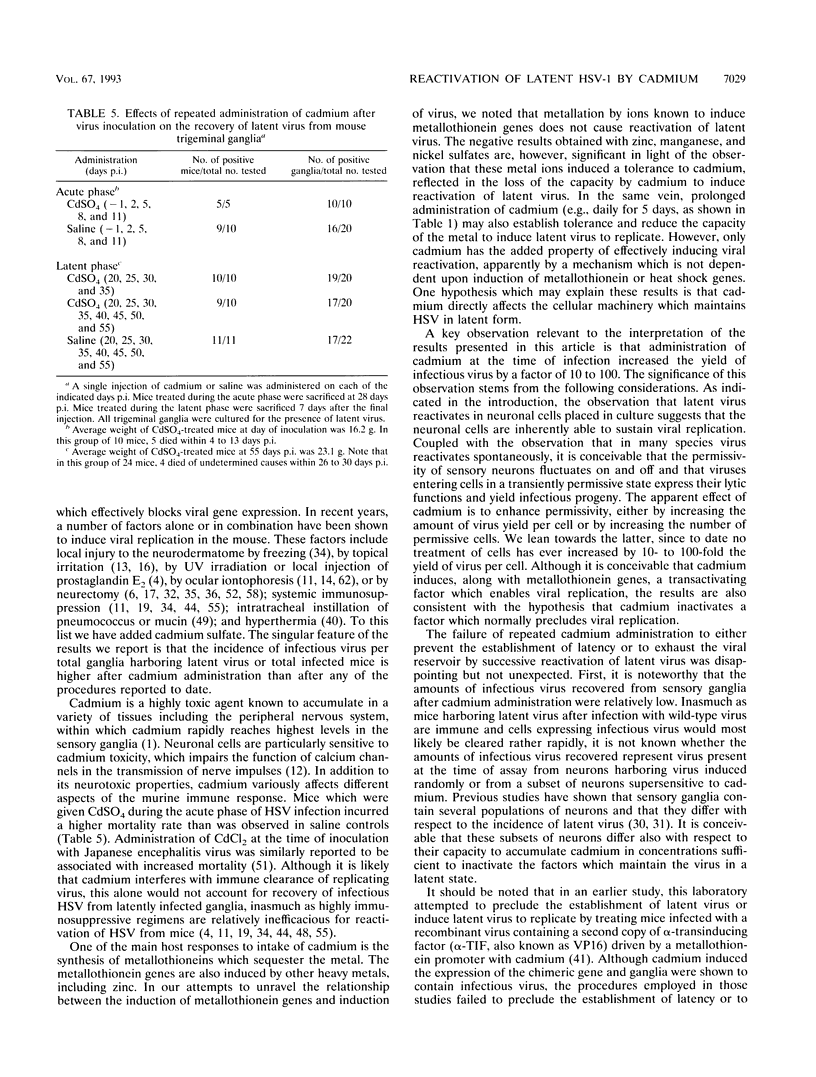
Herpes simplex viruses maintained in a latent state in sensory neurons in mice do not reactivate spontaneously, and therefore the factors or procedures which cause the virus to reactivate serve as a clue to the mechanisms by which the virus is maintained in a latent state. We report that cadmium sulfate induces latent virus to reactivate in 75 to 100% of mice tested. The following specific findings are reported. (i) The highest frequency of induction was observed after two to four daily administrations of 100 micrograms of cadmium sulfate. (ii) Zinc, copper, manganese, or nickel sulfate administered in equimolar amounts under the same regimen did not induce viral reactivation; however, zinc sulfate in molar ratios 25-fold greater than those of cadmium induced viral replication in 2 of 16 ganglia tested. (iii) Administration of zinc, nickel, or manganese prior to the cadmium sulfate reduced the incidence of ganglia containing infectious virus. (iv) Administration of cadmium daily during the first week after infection and at 2-day intervals to 13 days after infection resulted in the recovery from ganglia of infectious virus in titers 10- to 100-fold higher than those obtained from animals given saline. Moreover, infectious virus was recovered as late as 11 days after infection compared with 6 days in mice administered saline. (v) Administration of cadmium immediately after infection or repeatedly after establishment of latency did not exhaust the latent virus harbored by sensory neurons, inasmuch as the fraction of ganglia of mice administered cadmium and yielding infectious virus was similar to that observed in mice treated with saline. We conclude that induction of cadmium tolerance precludes reactivation of latent virus. If the induction of metallothionein genes was the sole factor required to cause reactivation of latent virus, it would have been expected that all metals which induce metallothioneins would also induce reactivation, which was not observed. The results therefore raise the possibility that in addition to inducing the metallothionein genes, cadmium inactivates the factors which maintain the virus in latent state.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvidson B., Tjälve H. Distribution of 109Cd in the nervous system of rats after intravenous injection. Acta Neuropathol. 1986;69(1-2):111–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00687046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block T. M., Deshmane S., Masonis J., Maggioncalda J., Valyi-Nagi T., Fraser N. W. An HSV LAT null mutant reactivates slowly from latent infection and makes small plaques on CV-1 monolayers. Virology. 1993 Feb;192(2):618–630. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block T. M., Spivack J. G., Steiner I., Deshmane S., McIntosh M. T., Lirette R. P., Fraser N. W. A herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcript mutant reactivates with normal kinetics from latent infection. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3417–3426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3417-3426.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blyth W. A., Hill T. J., Field H. J., Harbour D. A. Reactivation of herpes simplex virus infection by ultraviolet light and possible involvement of prostaglandins. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):547–550. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the mouse metallothionein-I gene by heavy metals. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5712–5716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecob-Prince M. S., Rixon F. J., Preston C. M., Hassan K., Kennedy P. G. Reactivation in vivo and in vitro of herpes simplex virus from mouse dorsal root ganglia which contain different levels of latency-associated transcripts. J Gen Virol. 1993 Jun;74(Pt 6):995–1002. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-6-995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epner D. E., Herschman H. R. Heavy metals induce expression of the TPA-inducible sequence (TIS) genes. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Jul;148(1):68–74. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041480109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser N. W., Spivack J. G., Wroblewska Z., Block T., Deshmane S. L., Valyi-Nagy T., Natarajan R., Gesser R. M. A review of the molecular mechanism of HSV-1 latency. Curr Eye Res. 1991;10 (Suppl):1–13. doi: 10.3109/02713689109020352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon Y. J., Araullo-Cruz T. P., Romanowski E., Ruziczka L., Balouris C., Oren J., Cheng K. P., Kim S. The development of an improved murine iontophoresis reactivation model for the study of HSV-1 latency. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1986 Aug;27(8):1230–1234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbour D. A., Hill T. J., Blyth W. A. Recurrent herpes simplex in the mouse: inflammation in the skin and activation of virus in the ganglia following peripheral stimulation. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jul;64(Pt 7):1491–1498. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-7-1491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwick J., Romanowski E., Araullo-Cruz T., Gordon Y. J. Timolol promotes reactivation of latent HSV-1 in the mouse iontophoresis model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987 Mar;28(3):580–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. J., Blyth W. A., Harbour D. A. Recurrence of herpes simplex in the mouse requires an intact nerve supply to the skin. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2763–2765. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. J., Blyth W. A., Harbour D. A. Trauma to the skin causes recurrence of herpes simplex in the mouse. J Gen Virol. 1978 Apr;39(1):21–28. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-39-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. Y., Mocarski E. S. Herpes simplex virus latent RNA (LAT) is not required for latent infection in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7596–7600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurd J., Robinson T. W. Herpes virus reactivation in a mouse model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Mar;3 (Suppl A):99–106. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.suppl_a.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi K. M., McKelvey A. M., Devi-Rao G., Wagner E. K., Stevens J. G. Molecular and biological characterization of a type 1 herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) specifically deleted for expression of the latency-associated transcript (LAT). Microb Pathog. 1989 Aug;7(2):121–134. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javier R. T., Stevens J. G., Dissette V. B., Wagner E. K. A herpes simplex virus transcript abundant in latently infected neurons is dispensable for establishment of the latent state. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):254–257. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin P., Ringertz N. R. Cadmium induces transcription of proto-oncogenes c-jun and c-myc in rat L6 myoblasts. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14061–14064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J. P., Bodin E. T., Coen D. M. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of herpes simplex virus DNA in ganglia of mice infected with replication-incompetent mutants. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4288–4295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4288-4295.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp L. M., Dent C. L., Latchman D. S. Octamer motif mediates transcriptional repression of HSV immediate-early genes and octamer-containing cellular promoters in neuronal cells. Neuron. 1990 Feb;4(2):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latchman D. S. Current status review: molecular biology of herpes simplex virus latency. J Exp Pathol (Oxford) 1990 Feb;71(1):133–141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leib D. A., Bogard C. L., Kosz-Vnenchak M., Hicks K. A., Coen D. M., Knipe D. M., Schaffer P. A. A deletion mutant of the latency-associated transcript of herpes simplex virus type 1 reactivates from the latent state with reduced frequency. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2893–2900. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2893-2900.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leib D. A., Nadeau K. C., Rundle S. A., Schaffer P. A. The promoter of the latency-associated transcripts of herpes simplex virus type 1 contains a functional cAMP-response element: role of the latency-associated transcripts and cAMP in reactivation of viral latency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):48–52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson W., Oppermann H., Jackson J. Transition series metals and sulfhydryl reagents induce the synthesis of four proteins in eukaryotic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;606(1):170–180. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillycrop K. A., Dent C. L., Wheatley S. C., Beech M. N., Ninkina N. N., Wood J. N., Latchman D. S. The octamer-binding protein Oct-2 represses HSV immediate-early genes in cell lines derived from latently infectable sensory neurons. Neuron. 1991 Sep;7(3):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90290-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis T. P., Dawson C. R., LaVail J. H. Herpes simplex viral infection of the mouse trigeminal ganglion. Immunohistochemical analysis of cell populations. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992 Feb;33(2):259–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis T. P., Sedarati F., Dobson A. T., Feldman L. T., Stevens J. G. Pathways of viral gene expression during acute neuronal infection with HSV-1. Virology. 1992 Jul;189(1):150–160. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90690-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan J. L., Darby G. Herpes simplex virus latency: the cellular location of virus in dorsal root ganglia and the fate of the infected cell following virus activation. J Gen Virol. 1980 Dec;51(Pt 2):233–243. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-51-2-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Openshaw H., Asher L. V., Wohlenberg C., Sekizawa T., Notkins A. L. Acute and latent infection of sensory ganglia with herpes simplex virus: immune control and virus reactivation. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jul;44(1):205–215. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-1-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Schmitz J. Reactivation of latent herpes simplex virus infection of the autonomic nervous system by postganglionic neurectomy. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):523–532. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.523-532.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Schmitz J. Route of infection, systemic host resistance, and integrity of ganglionic axons influence acute and latent herpes simplex virus infection of the superior cervical ganglion. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):373–383. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.373-383.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROIZMAN B., ROANE P. R., Jr A physical difference between two strains of herpes simplex virus apparent on sedimentation in cesium chloride. Virology. 1961 Sep;15:75–79. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Sears A. E. An inquiry into the mechanisms of herpes simplex virus latency. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:543–571. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawtell N. M., Thompson R. L. Rapid in vivo reactivation of herpes simplex virus in latently infected murine ganglionic neurons after transient hyperthermia. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2150–2156. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2150-2156.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears A. E., Hukkanen V., Labow M. A., Levine A. J., Roizman B. Expression of the herpes simplex virus 1 alpha transinducing factor (VP16) does not induce reactivation of latent virus or prevent the establishment of latency in mice. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2929–2935. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2929-2935.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears A. E., Meignier B., Roizman B. Establishment of latency in mice by herpes simplex virus 1 recombinants that carry insertions affecting regulation of the thymidine kinase gene. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):410–416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.410-416.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedarati F., Izumi K. M., Wagner E. K., Stevens J. G. Herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcription plays no role in establishment or maintenance of a latent infection in murine sensory neurons. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4455–4458. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4455-4458.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimeld C., Hill T. J., Blyth W. A., Easty D. L. Reactivation of latent infection and induction of recurrent herpetic eye disease in mice. J Gen Virol. 1990 Feb;71(Pt 2):397–404. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-2-397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Pizer L. I., Johnson E. M., Jr, Wilcox C. L. Activation of second-messenger pathways reactivates latent herpes simplex virus in neuronal cultures. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90760-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner I., Spivack J. G., Lirette R. P., Brown S. M., MacLean A. R., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Fraser N. W. Herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcripts are evidently not essential for latent infection. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):505–511. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03404.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Cook M. L., Jordan M. C. Reactivation of latent Herpes simplex virus after pneumococcal pneumonia in mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):635–639. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.635-639.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G. Human herpesviruses: a consideration of the latent state. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):318–332. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.318-332.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K., Devi-Rao G. B., Cook M. L., Feldman L. T. RNA complementary to a herpesvirus alpha gene mRNA is prominent in latently infected neurons. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2434993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Simizu B., Yabe S., Oya A., Seto H. Effect of cadmium on Japanese encephalitis virus infection in mice. 1. Acute and single-dose exposure experiment. Toxicol Lett. 1981 Nov;9(3):231–235. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(81)90155-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenser R. B., Edris W. A., Hay K. A. Herpes simplex virus latent infection: reactivation and elimination of latency after neurectomy. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):302–305. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trousdale M. D., Steiner I., Spivack J. G., Deshmane S. L., Brown S. M., MacLean A. R., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Fraser N. W. In vivo and in vitro reactivation impairment of a herpes simplex virus type 1 latency-associated transcript variant in a rabbit eye model. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6989–6993. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6989-6993.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood G. E., Weed S. D. Recurrent cutaneous herpes simplex in hairless mice. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):471–474. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.471-474.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valyi-Nagy T., Deshmane S., Dillner A., Fraser N. W. Induction of cellular transcription factors in trigeminal ganglia of mice by corneal scarification, herpes simplex virus type 1 infection, and explantation of trigeminal ganglia. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4142–4152. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4142-4152.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz M. A., Price R. W., Notkins A. L. Latent ganglionic infection with herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2: viral reactivation in vivo after neurectomy. Science. 1974 Jun 14;184(4142):1185–1187. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4142.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb M., Verschoyle R. D. An investigation of the role of metallothioneins in protection against the acute toxicity of the cadmium ion. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Mar 15;25(6):673–679. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. L., Johnson E. M., Jr Nerve growth factor deprivation results in the reactivation of latent herpes simplex virus in vitro. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2311–2315. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2311-2315.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey D. E., Trousdale M. D., Nesburn A. B. Reactivation of murine latent HSV infection by epinephrine iontophoresis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1984 Aug;25(8):945–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


