Abstract
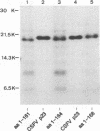
The polyprotein of classical swine fever virus starts with the nonstructural protein p23, which is followed by the nucleocapsid protein p14. Proteolytic cleavage between p23 and p14 was demonstrated in a cell-free transcription-translation system. Successive truncation of the cDNA used for the transcription indicated that the proteolytic activity responsible for the cleavage between p23 and p14 resides within p23. In order to determine the cleavage site between these two proteins, the respective genomic regions were expressed in two different expression systems. N-terminal sequencing of the resulting p14-related proteins revealed that cleavage occurs between Cys-168 and Ser-169. Comparison of the sequence around the cleavage site with sequences of other pestiviruses suggests a conserved processing site between similar proteins.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carrington J. C., Herndon K. L. Characterization of the potyviral HC-pro autoproteolytic cleavage site. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):308–315. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90319-K. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi G. H., Pawlyk D. M., Nuss D. L. The autocatalytic protease p29 encoded by a hypovirulence-associated virus of the chestnut blight fungus resembles the potyvirus-encoded protease HC-Pro. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):747–752. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)91004-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colett M. S., Larson R., Gold C., Strick D., Anderson D. K., Purchio A. F. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the pestivirus bovine viral diarrhea virus. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90672-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Larson R., Belzer S. K., Retzel E. Proteins encoded by bovine viral diarrhea virus: the genomic organization of a pestivirus. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):200–208. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90673-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Wiskerchen M., Welniak E., Belzer S. K. Bovine viral diarrhea virus genomic organization. Arch Virol Suppl. 1991;3:19–27. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9153-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng R., Brock K. V. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of a pestivirus genome, noncytopathic bovine viral diarrhea virus strain SD-1. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):867–869. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90262-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Lai M. M. Putative papain-related thiol proteases of positive-strand RNA viruses. Identification of rubi- and aphthovirus proteases and delineation of a novel conserved domain associated with proteases of rubi-, alpha- and coronaviruses. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 19;288(1-2):201–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81034-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Use of protein A-bearing staphylococci for the immunoprecipitation and isolation of antigens from cells. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):442–459. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers G., Rümenapf T., Thiel H. J. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the genome of hog cholera virus. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):555–567. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90625-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers G., Tautz N., Stark R., Brownlie J., Dubovi E. J., Collett M. S., Thiel H. J. Rearrangement of viral sequences in cytopathogenic pestiviruses. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):368–386. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90199-Y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moormann R. J., Warmerdam P. A., van der Meer B., Schaaper W. M., Wensvoort G., Hulst M. M. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of hog cholera virus strain Brescia and mapping of the genomic region encoding envelope protein E1. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):184–198. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90472-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehe P. M., Woodward M. J., Edwards S. Characterisation of p20 gene sequences from a border disease-like pestivirus isolated from pigs. Vet Microbiol. 1992 Nov;33(1-4):231–238. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(92)90051-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rümenapf T., Meyers G., Stark R., Thiel H. J. Hog cholera virus--characterization of specific antiserum and identification of cDNA clones. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):18–27. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90506-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rümenapf T., Stark R., Meyers G., Thiel H. J. Structural proteins of hog cholera virus expressed by vaccinia virus: further characterization and induction of protective immunity. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):589–597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.589-597.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rümenapf T., Unger G., Strauss J. H., Thiel H. J. Processing of the envelope glycoproteins of pestiviruses. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3288–3294. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3288-3294.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snijder E. J., Wassenaar A. L., Spaan W. J. The 5' end of the equine arteritis virus replicase gene encodes a papainlike cysteine protease. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7040–7048. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7040-7048.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R., Rümenapf T., Meyers G., Thiel H. J. Genomic localization of hog cholera virus glycoproteins. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):286–289. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandström H., Veijalainen P., Moennig V., Hunsmann G., Schwarz H., Schäfer W. C-type particles produced by a permanent cell line from a leukemic pig. I. Origin and properties of the host cells and some evidence for the occurrence of C-type-like particles. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G., De Groot R. J., Levinson R., Strauss J. H. Identification of the active site residues in the nsP2 proteinase of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):932–940. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90268-T. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strebel K., Beck E., Strohmaier K., Schaller H. Characterization of foot-and-mouth disease virus gene products with antisera against bacterially synthesized fusion proteins. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):983–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.983-991.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiel H. J., Stark R., Weiland E., Rümenapf T., Meyers G. Hog cholera virus: molecular composition of virions from a pestivirus. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4705–4712. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4705-4712.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskerchen M., Belzer S. K., Collett M. S. Pestivirus gene expression: the first protein product of the bovine viral diarrhea virus large open reading frame, p20, possesses proteolytic activity. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4508–4514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4508-4514.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskerchen M., Collett M. S. Pestivirus gene expression: protein p80 of bovine viral diarrhea virus is a proteinase involved in polyprotein processing. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):341–350. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90850-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]