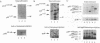Abstract
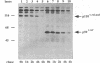
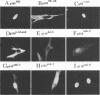
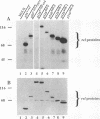
Members of the NF-kappa B/rel family of transcription factors are regulated through a trans association with members of a family of inhibitor proteins, collectively known as I kappa B proteins, that contain five to eight copies of a 33-amino-acid repeat sequence (ankyrin repeat). Certain NF-kappa B/rel proteins are also regulated by cis-acting ankyrin repeat-containing domains. The C terminus of p105NF-kappa B, the precursor of the 50-kDa subunit of NF-kappa B, contains a series of ankyrin repeats; proteolytic removal of this ankyrin domain is necessary for the manifestation of sequence-specific DNA binding and nuclear translocation of the N-terminal product. To investigate the structural requirements important for regulation of different NF-kappa B/rel family members by polypeptides containing ankyrin repeat domains, we have constructed a p59v-rel:p105NF-kappa B chimeric protein (p110v-rel-ank). The presence of C-terminal p105NF-kappa B-derived sequences in p110v-rel-ank inhibited nuclear translocation, sequence-specific DNA binding, pp40I kappa B-alpha association, and oncogenic transformation. Sequential truncation of the C-terminal ankyrin domain of p110v-rel-ank resulted in the restoration of nuclear translocation, DNA binding, and pp40I kappa B-alpha association but did not restore the oncogenic properties of p59v-rel. The presence of 67 C-terminal p105NF-kappa B-derived amino acids was sufficient to inhibit both transcriptional activation and oncogenic transformation by p59v-rel. These results support a model in which activation of gene expression by p59v-rel is required for its ability to induce oncogenic transformation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Sista P., Molitor J. A., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene encodes a kappa B enhancer binding protein that inhibits NF-kappa B function. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):803–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank V., Kourilsky P., Israël A. Cytoplasmic retention, DNA binding and processing of the NF-kappa B p50 precursor are controlled by a small region in its C-terminus. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4159–4167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04994.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bours V., Villalobos J., Burd P. R., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. Cloning of a mitogen-inducible gene encoding a kappa B DNA-binding protein with homology to the rel oncogene and to cell-cycle motifs. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):76–80. doi: 10.1038/348076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capobianco A. J., Chang D., Mosialos G., Gilmore T. D. p105, the NF-kappa B p50 precursor protein, is one of the cellular proteins complexed with the v-Rel oncoprotein in transformed chicken spleen cells. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3758–3767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3758-3767.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N., Bargmann W., Lim M. Y., Bose H., Jr Avian reticuloendotheliosis virus-transformed lymphoid cells contain multiple pp59v-rel complexes. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):584–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.584-591.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N., Ghosh S., Simmons D. L., Tempst P., Liou H. C., Baltimore D., Bose H. R., Jr Rel-associated pp40: an inhibitor of the rel family of transcription factors. Science. 1991 Sep 13;253(5025):1268–1271. doi: 10.1126/science.1891714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl J. A., McKinsey T. A., Hannink M. Differential pp40I kappa B-beta inhibition of DNA binding by rel proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1769–1778. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty J. P., Temin H. M. High mutation rate of a spleen necrosis virus-based retrovirus vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4387–4395. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. Generation of p50 subunit of NF-kappa B by processing of p105 through an ATP-dependent pathway. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):395–398. doi: 10.1038/354395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garson K., Percival H., Kang C. Y. The N-terminal env-derived amino acids of v-rel are required for full transforming activity. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90464-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D., Temin H. M. Different localization of the product of the v-rel oncogene in chicken fibroblasts and spleen cells correlates with transformation by REV-T. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):791–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90845-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskill S., Beg A. A., Tompkins S. M., Morris J. S., Yurochko A. D., Sampson-Johannes A., Mondal K., Ralph P., Baldwin A. S., Jr Characterization of an immediate-early gene induced in adherent monocytes that encodes I kappa B-like activity. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1281–1289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90022-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkel T., Zabel U., van Zee K., Müller J. M., Fanning E., Baeuerle P. A. Intramolecular masking of the nuclear location signal and dimerization domain in the precursor for the p50 NF-kappa B subunit. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1121–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90083-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Kerr L. D., Kakizuka A., Verma I. M. I kappa B gamma, a 70 kd protein identical to the C-terminal half of p110 NF-kappa B: a new member of the I kappa B family. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1109–1120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90082-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Kerr L. D., Rashid D., Davis N., Bose H. R., Jr, Verma I. M. Direct association of pp40/I kappa B beta with rel/NF-kappa B transcription factors: role of ankyrin repeats in the inhibition of DNA binding activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4333–4337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabrun N., Hodgson J. W., Doemer M., Mak G., Franza B. R., Jr, Enrietto P. J. Interaction of the v-rel protein with an NF-kappa B DNA binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1783–1787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Nishizawa M. New procedure for DNA transfection with polycation and dimethyl sulfoxide. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1172–1174. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Duckett C. S., Wamsley P., Zhang Q., Chiao P., Nabel G., McKeithan T. W., Baeuerle P. A., Verma I. M. The proto-oncogene bcl-3 encodes an I kappa B protein. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2352–2363. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Inoue J., Davis N., Link E., Baeuerle P. A., Bose H. R., Jr, Verma I. M. The rel-associated pp40 protein prevents DNA binding of Rel and NF-kappa B: relationship with I kappa B beta and regulation by phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1464–1476. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M., Bennett V. Analysis of cDNA for human erythrocyte ankyrin indicates a repeated structure with homology to tissue-differentiation and cell-cycle control proteins. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):36–42. doi: 10.1038/344036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R., Hatada E. N., Hohmann H. P., Haiker M., Bartsch C., Röthlisberger U., Lahm H. W., Schlaeger E. J., van Loon A. P., Scheidereit C. Cloning of the DNA-binding subunit of human nuclear factor kappa B: the level of its mRNA is strongly regulated by phorbol ester or tumor necrosis factor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):966–970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin P. J., Gilmore T. D. The C terminus of the NF-kappa B p50 precursor and an I kappa B isoform contain transcription activation domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 25;20(10):2453–2458. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.10.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison L. E., Boehmelt G., Enrietto P. J. Mutations in the rel-homology domain alter the biochemical properties of v-rel and render it transformation defective in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1992 Jun;7(6):1137–1147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison L. E., Kabrun N., Mudri S., Hayman M. J., Enrietto P. J. Viral rel and cellular rel associate with cellular proteins in transformed and normal cells. Oncogene. 1989 Jun;4(6):677–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosialos G., Gilmore T. D. v-Rel and c-Rel are differentially affected by mutations at a consensus protein kinase recognition sequence. Oncogene. 1993 Mar;8(3):721–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Gilmore T. D. Transformation by the vRel oncoprotein requires sequences carboxy-terminal to the Rel homology domain. Oncogene. 1993 Aug;8(8):2245–2252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simek S., Rice N. R. p59v-rel, the transforming protein of reticuloendotheliosis virus, is complexed with at least four other proteins in transformed chicken lymphoid cells. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4730–4736. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4730-4736.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. C., Brown T. A., McKnight S. L. Convergence of Ets- and notch-related structural motifs in a heteromeric DNA binding complex. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):762–768. doi: 10.1126/science.1876833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. H., Stein B., Ganchi P. A., Hoffman J. A., Kaufman P. A., Ballard D. W., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene: insights into the mechanism of transcriptional activation, repression, and transformation. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5018–5029. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5018-5029.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen K. C., Eggleton K., Temin H. M. Nucleic acid sequences of the oncogene v-rel in reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T and its cellular homolog, the proto-oncogene c-rel. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):172–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.172-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]