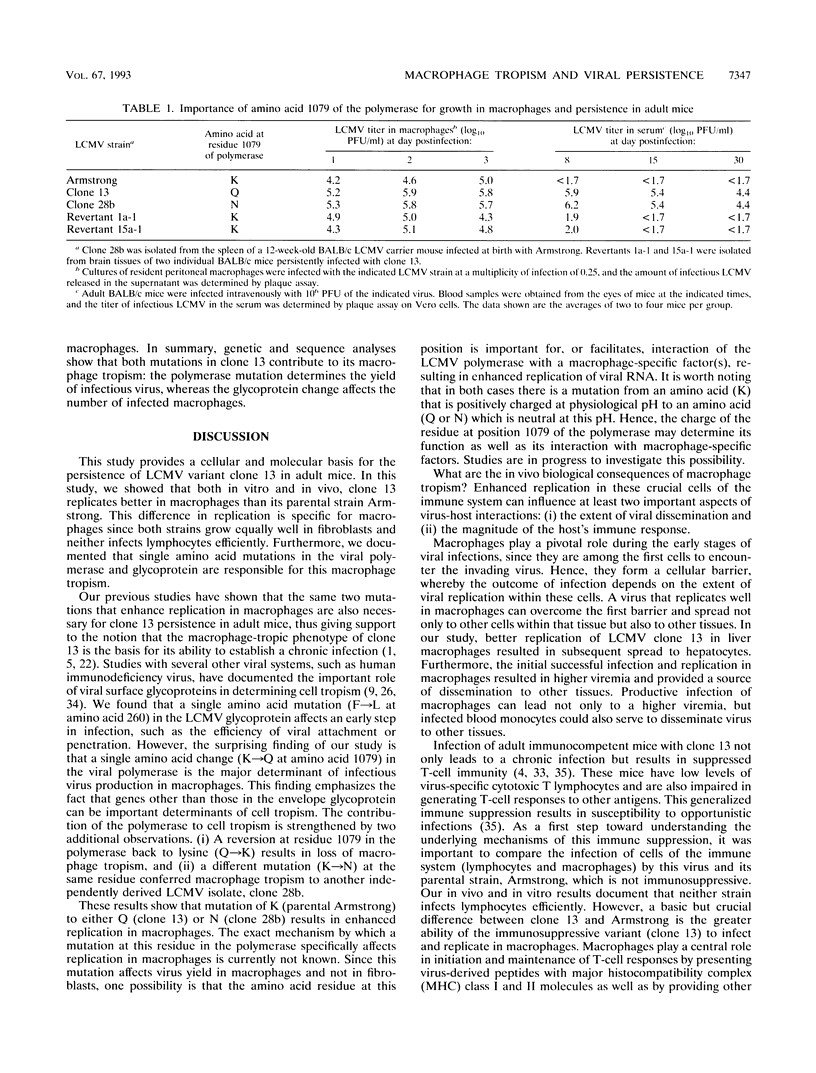
Abstract
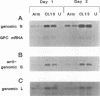
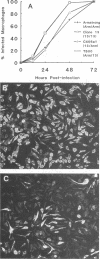
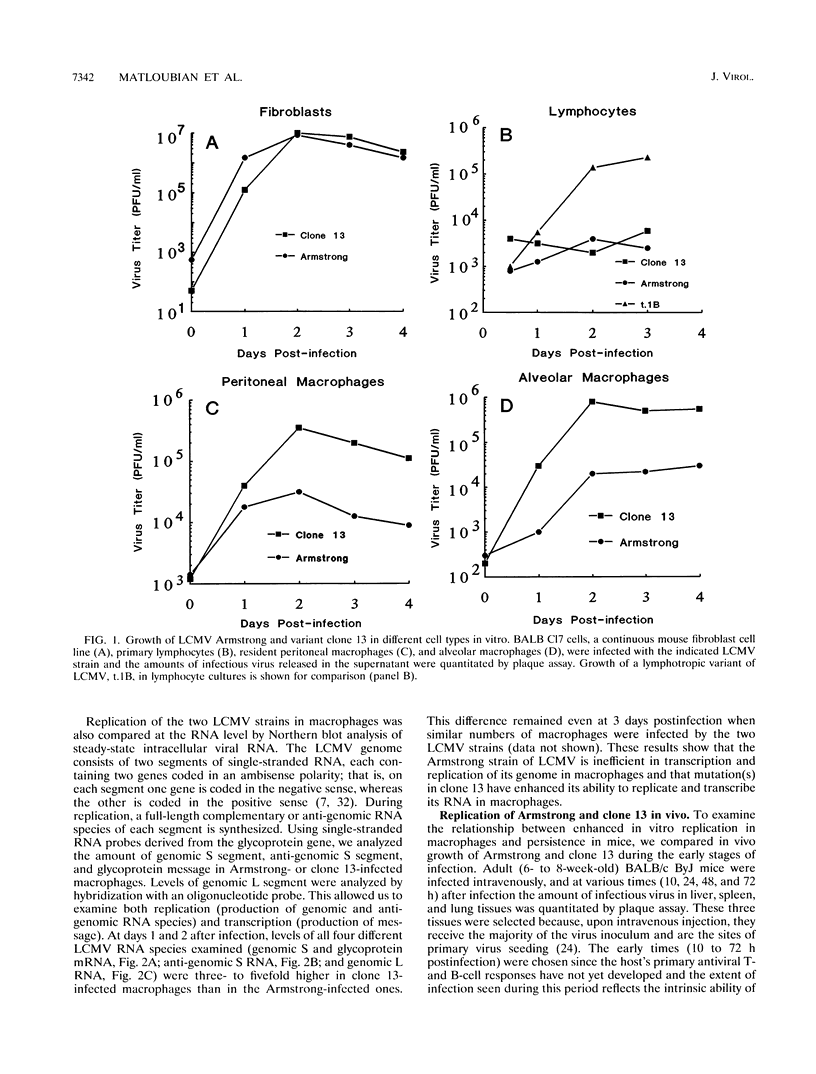
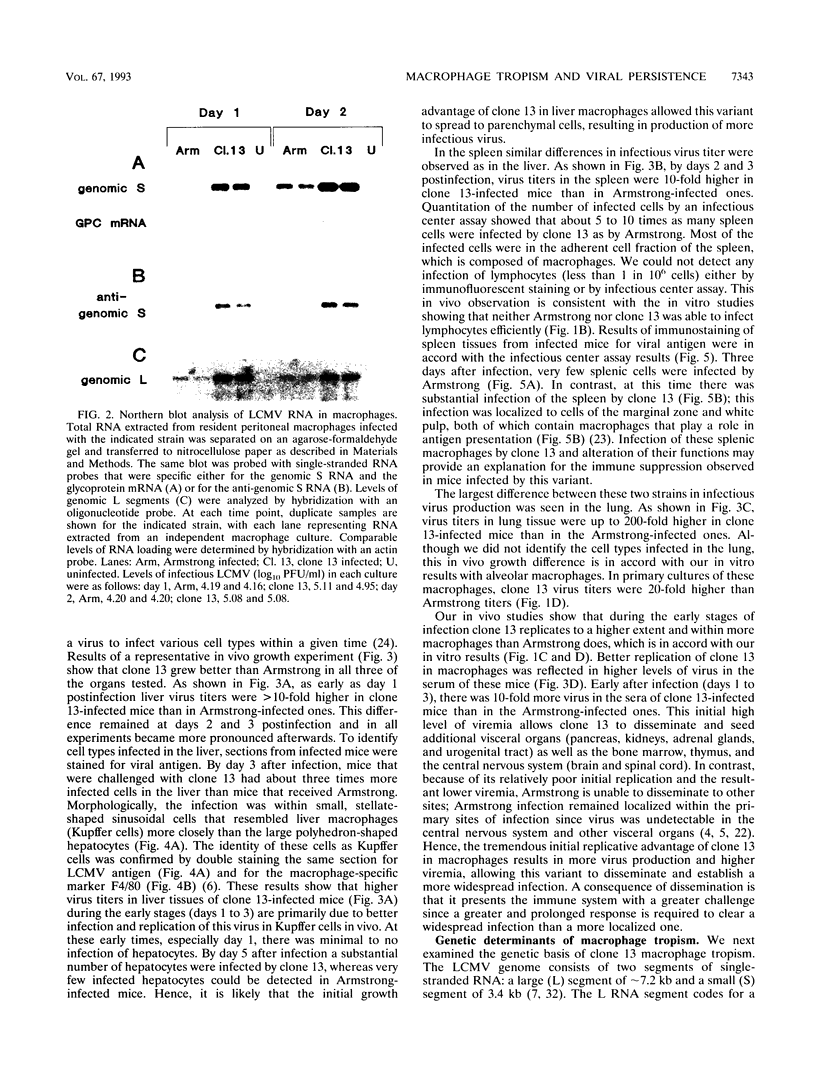
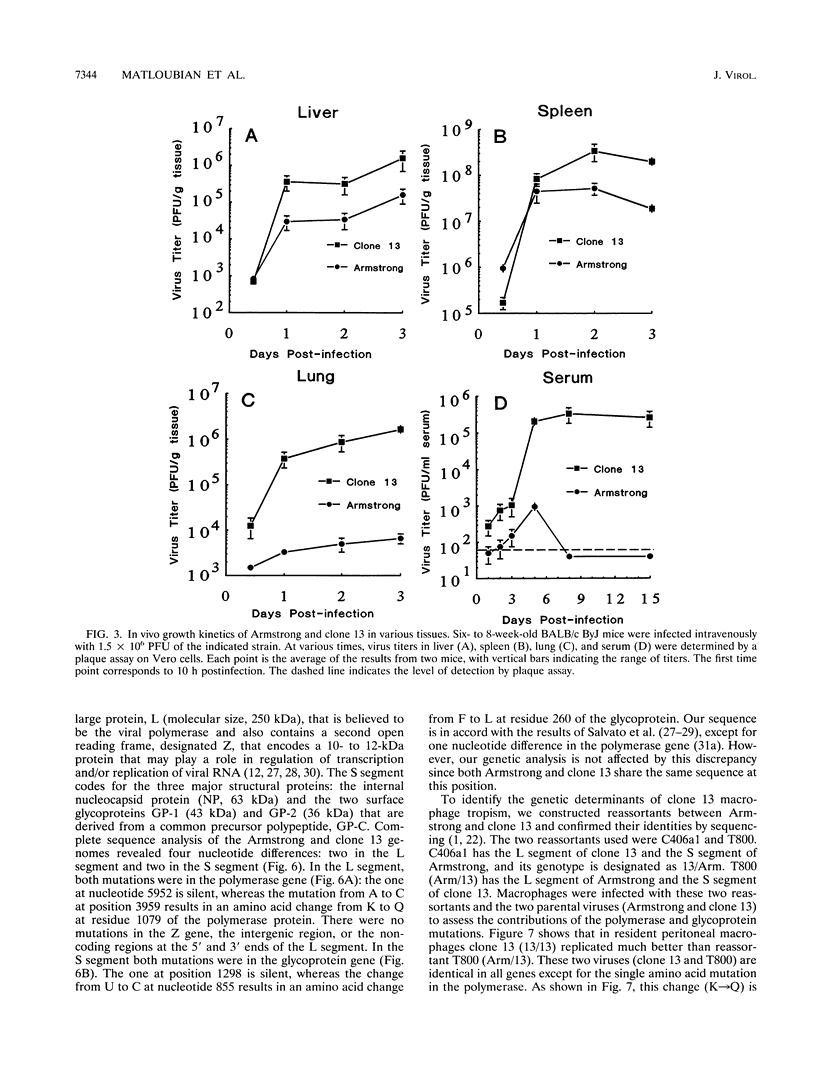
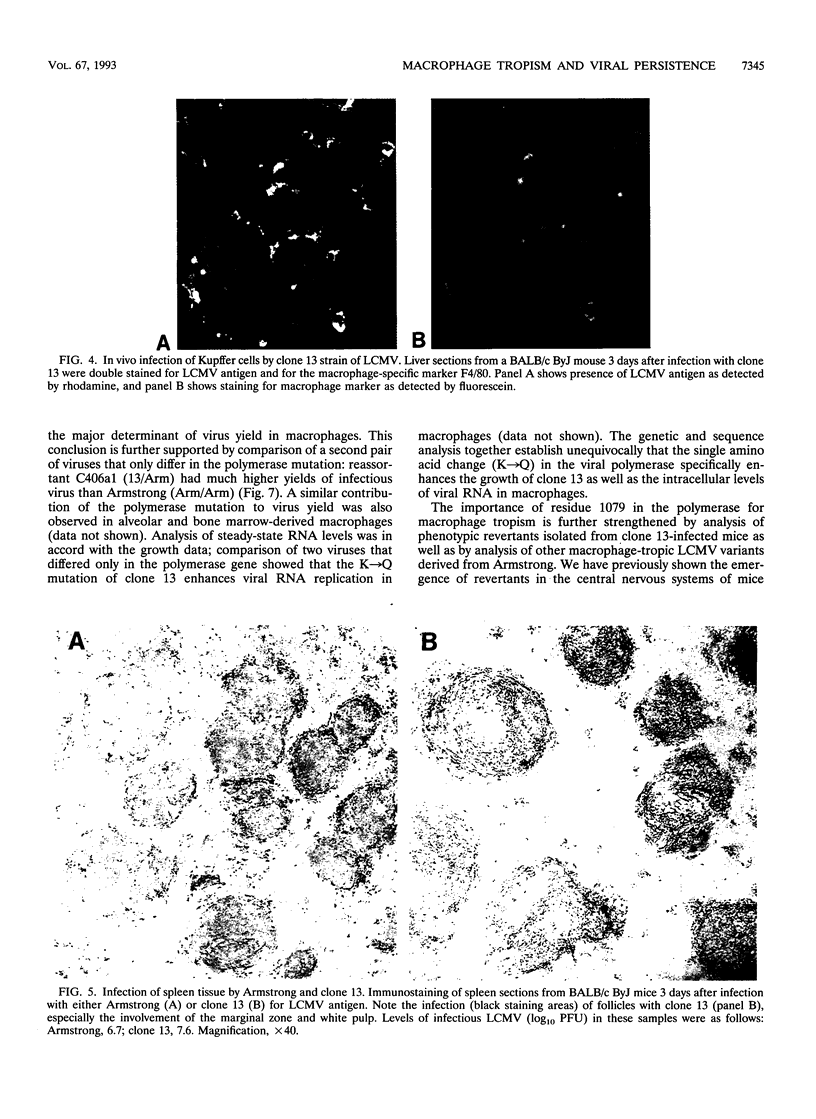
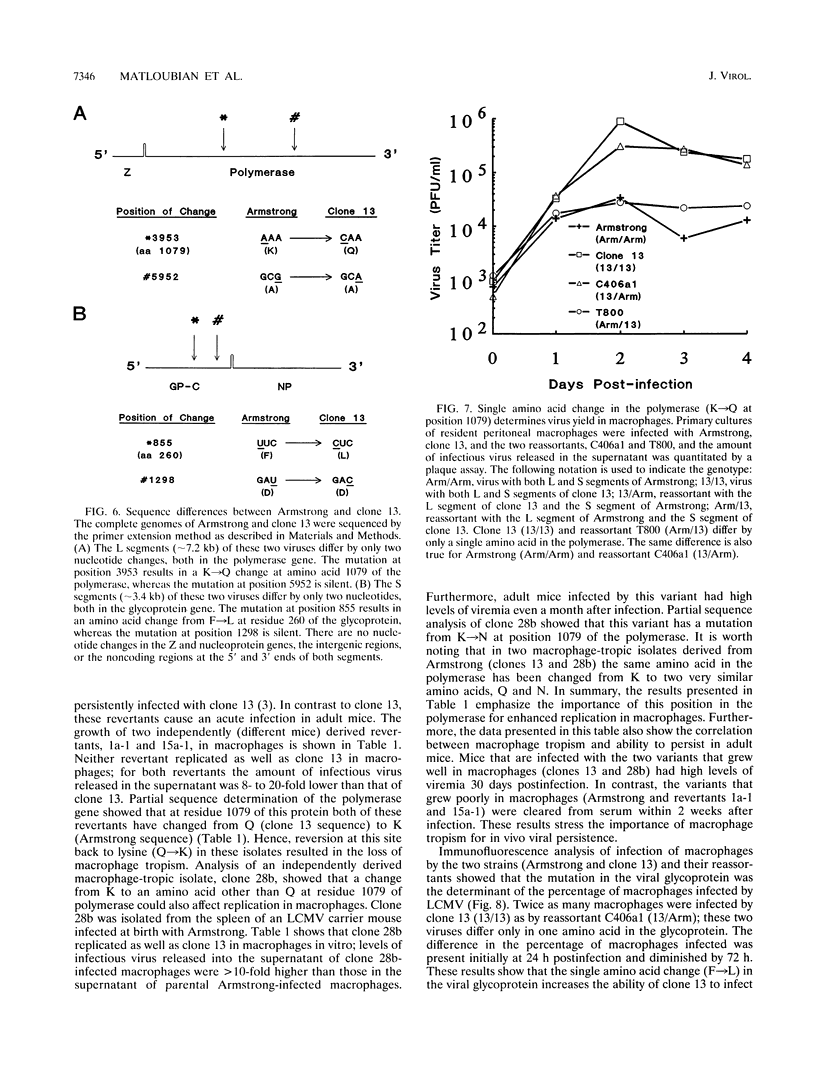
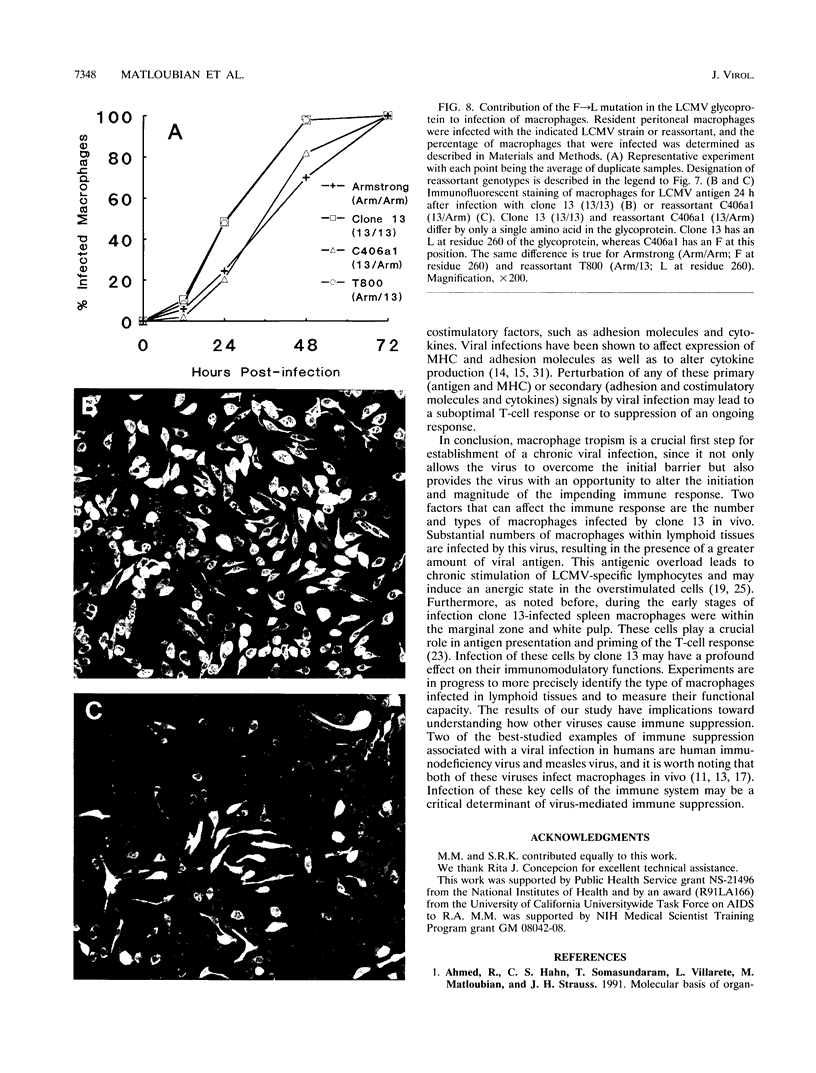
This study documents that the immunosuppressive lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) variant, clone 13, shows a specific predilection for enhanced infection of macrophages both in vitro and in vivo and that single amino acid changes in the viral polymerase and glycoprotein are responsible for macrophage tropism. The growth difference seen between variant clone 13 and the parental Armstrong strain was specific for macrophages, since both clone 13 and Armstrong grew equally well in fibroblasts and neither isolate infected lymphocytes efficiently. Complete sequencing of the clone 13 genome, along with genetic analysis, showed that a single amino acid change in the polymerase (K-->Q at position 1079) was the major determinant of virus yield in macrophages. This was proven unequivocally by comparing the sequences of parental and reassortant viruses, which were identical at all loci except for the single mutation in the polymerase gene. This finding was further strengthened by showing that reversion at this site back to lysine (Q-->K) resulted in loss of macrophage tropism. In addition, an independently derived macrophage-tropic variant of LCMV, clone 28b, had a K-->N mutation at the same position. Thus, these results show that substitution of the positively charged amino acid K with a neutral amino acid (either Q or N) at residue 1079 of the polymerase resulted in enhanced viral replication in macrophages. In addition to the polymerase change, a mutation in the glycoprotein was also associated with macrophage tropism. This single amino acid change in the glycoprotein (F-->L at position 260) did not affect virus yield per macrophage but was critical in determining the number of macrophages infected. Our previous studies have shown that the same two mutations in the polymerase and glycoprotein are essential for establishing a chronic infection in adult mice. Since the same mutations confer macrophage tropism and ability to persist in vivo, these studies provide compelling evidence that infection of macrophages is a critical determinant of viral persistence and immune suppression.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed R., Hahn C. S., Somasundaram T., Villarete L., Matloubian M., Strauss J. H. Molecular basis of organ-specific selection of viral variants during chronic infection. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4242–4247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4242-4247.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed R., Jamieson B. D., Porter D. D. Immune therapy of a persistent and disseminated viral infection. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3920–3929. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3920-3929.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed R., Oldstone M. B. Organ-specific selection of viral variants during chronic infection. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1719–1724. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed R., Salmi A., Butler L. D., Chiller J. M., Oldstone M. B. Selection of genetic variants of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus in spleens of persistently infected mice. Role in suppression of cytotoxic T lymphocyte response and viral persistence. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):521–540. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed R., Simon R. S., Matloubian M., Kolhekar S. R., Southern P. J., Freedman D. M. Genetic analysis of in vivo-selected viral variants causing chronic infection: importance of mutation in the L RNA segment of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3301–3308. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3301-3308.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austyn J. M., Gordon S. F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Oct;11(10):805–815. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830111013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H. Ambisense RNA genomes of arenaviruses and phleboviruses. Adv Virus Res. 1986;31:1–51. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60261-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrow P., Tishon A., Oldstone M. B. Infection of lymphocytes by a virus that aborts cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity and establishes persistent infection. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):203–212. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann A. J., Churcher M. J., Boyd M., O'Brien W., Zhao J. Q., Zack J., Chen I. S. The region of the envelope gene of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 responsible for determination of cell tropism. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):305–309. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.305-309.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esolen L. M., Ward B. J., Moench T. R., Griffin D. E. Infection of monocytes during measles. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jul;168(1):47–52. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcin D., Rochat S., Kolakofsky D. The Tacaribe arenavirus small zinc finger protein is required for both mRNA synthesis and genome replication. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):807–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.807-812.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Markovits P., Markovitz D. M., Kaplan M. H., Gallo R. C., Popovic M. The role of mononuclear phagocytes in HTLV-III/LAV infection. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):215–219. doi: 10.1126/science.3014648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooding L. R. Virus proteins that counteract host immune defenses. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):5–7. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90259-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory C. D., Murray R. J., Edwards C. F., Rickinson A. B. Downregulation of cell adhesion molecules LFA-3 and ICAM-1 in Epstein-Barr virus-positive Burkitt's lymphoma underlies tumor cell escape from virus-specific T cell surveillance. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1811–1824. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOTCHIN J. The biology of lymphocytic choriomeningitis infection: virus-induced immune disease. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:479–499. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlyn P. H., Gait M. J., Milstein C. Complete sequence of an immunoglobulin mRNA using specific priming and the dideoxynucleotide method of RNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 25;9(18):4485–4494. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.18.4485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Rota T. R., Hirsch M. S. Infection of monocyte/macrophages by human T lymphotropic virus type III. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1712–1715. doi: 10.1172/JCI112491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt P. G. Alveolar macrophages. I. A simple technique for the preparation of high numbers of viable alveolar macrophages from small laboratory animals. J Immunol Methods. 1979;27(2):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson B. D., Butler L. D., Ahmed R. Effective clearance of a persistent viral infection requires cooperation between virus-specific Lyt2+ T cells and nonspecific bone marrow-derived cells. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3930–3937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3930-3937.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. C., de Fries R., Kolhekar S. R., Ahmed R. In vivo selection of lymphocyte-tropic and macrophage-tropic variants of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus during persistent infection. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5611–5616. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5611-5616.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matloubian M., Somasundaram T., Kolhekar S. R., Selvakumar R., Ahmed R. Genetic basis of viral persistence: single amino acid change in the viral glycoprotein affects ability of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus to persist in adult mice. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1043–1048. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metlay J. P., Witmer-Pack M. D., Agger R., Crowley M. T., Lawless D., Steinman R. M. The distinct leukocyte integrins of mouse spleen dendritic cells as identified with new hamster monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1753–1771. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskophidis D., Lechner F., Pircher H., Zinkernagel R. M. Virus persistence in acutely infected immunocompetent mice by exhaustion of antiviral cytotoxic effector T cells. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):758–761. doi: 10.1038/362758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien W. A., Koyanagi Y., Namazie A., Zhao J. Q., Diagne A., Idler K., Zack J. A., Chen I. S. HIV-1 tropism for mononuclear phagocytes can be determined by regions of gp120 outside the CD4-binding domain. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):69–73. doi: 10.1038/348069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvato M. S., Schweighofer K. J., Burns J., Shimomaye E. M. Biochemical and immunological evidence that the 11 kDa zinc-binding protein of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus is a structural component of the virus. Virus Res. 1992 Mar;22(3):185–198. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90050-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvato M. S., Shimomaye E. M. The completed sequence of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus reveals a unique RNA structure and a gene for a zinc finger protein. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90216-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvato M., Shimomaye E., Oldstone M. B. The primary structure of the lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus L gene encodes a putative RNA polymerase. Virology. 1989 Apr;169(2):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90163-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvato M., Shimomaye E., Southern P., Oldstone M. B. Virus-lymphocyte interactions. IV. Molecular characterization of LCMV Armstrong (CTL+) small genomic segment and that of its variant, Clone 13 (CTL-). Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):517–522. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90566-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier P. I., Bernards R., Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Expression of class I major histocompatibility antigens switched off by highly oncogenic adenovirus 12 in transformed rat cells. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):771–775. doi: 10.1038/305771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Singh M. K., Riviere Y., Jacoby D. R., Buchmeier M. J., Oldstone M. B. Molecular characterization of the genomic S RNA segment from lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90323-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tishon A., Borrow P., Evans C., Oldstone M. B. Virus-induced immunosuppression. 1. Age at infection relates to a selective or generalized defect. Virology. 1993 Aug;195(2):397–405. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu-Hsieh B., Howard D. H., Ahmed R. Virus-induced immunosuppression: a murine model of susceptibility to opportunistic infection. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):232–235. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]