Abstract
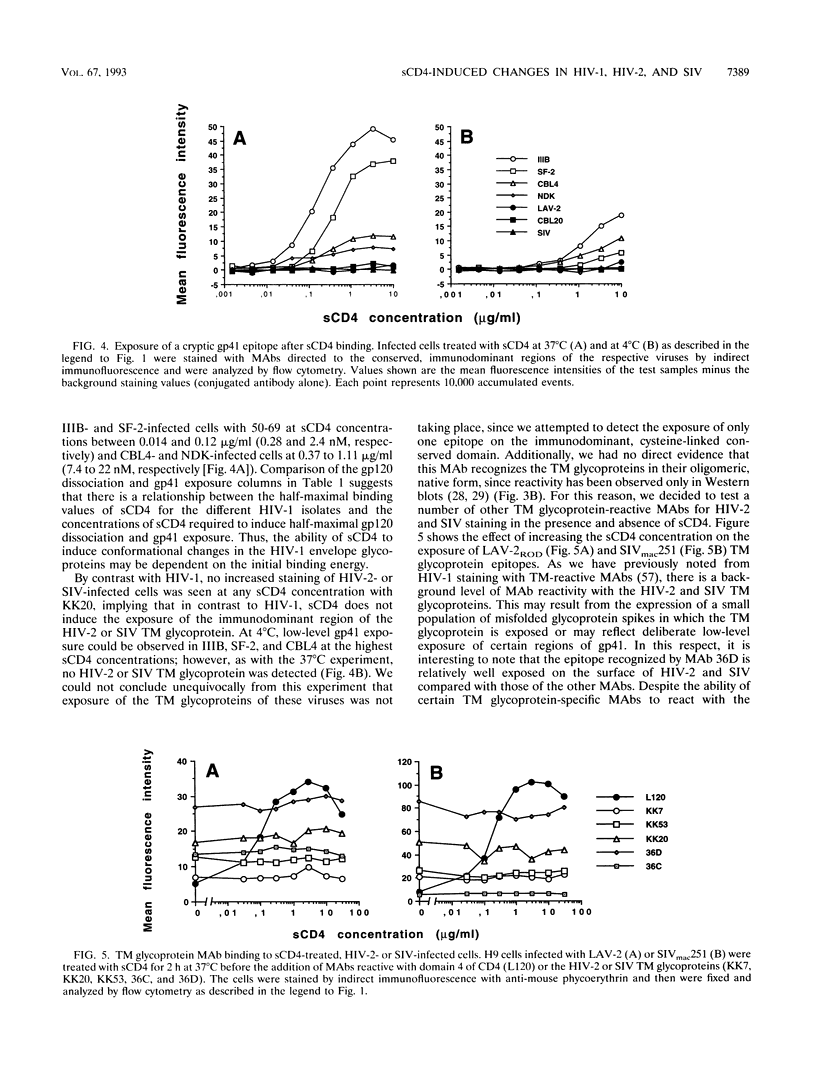
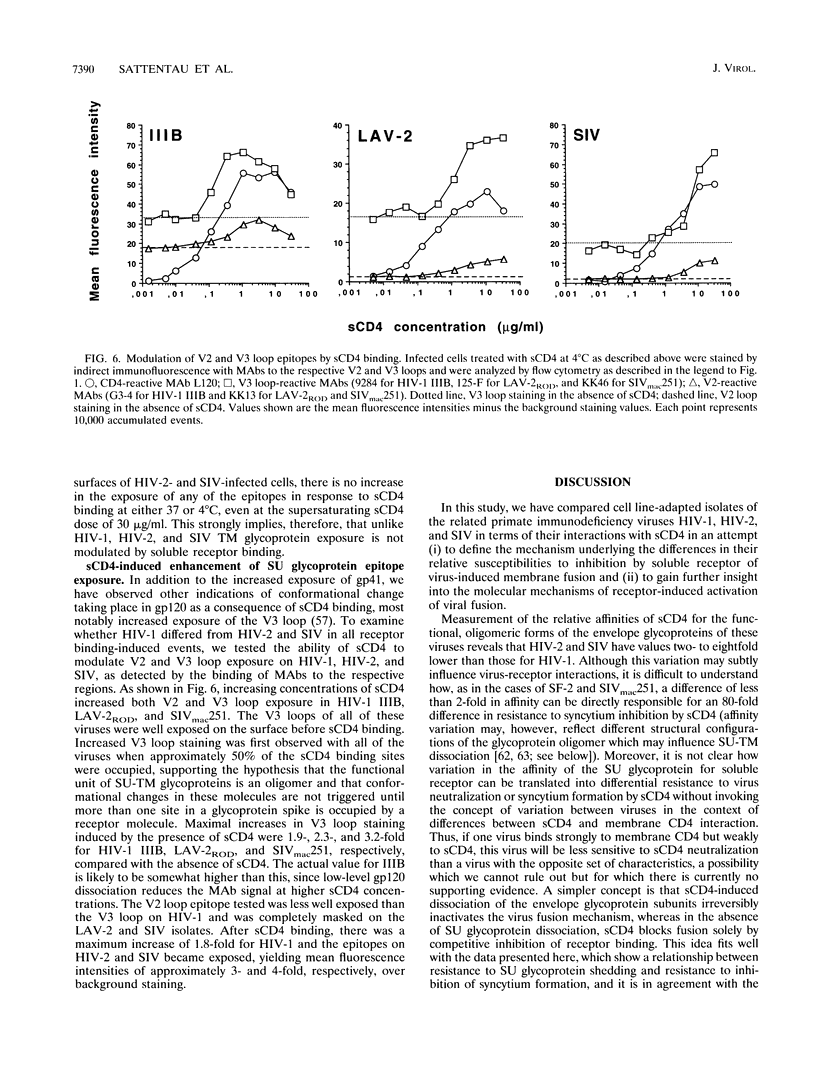
We have investigated the molecular basis of biological differences observed among cell line-adapted isolates of the human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 (HIV-1 and HIV-2) and the simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) in response to receptor binding by using a soluble form of CD4 (sCD4) as a receptor mimic. We find that sCD4 binds to the envelope glycoproteins of all of the HIV-1 isolates tested with affinities within a threefold range, whereas those of the HIV-2 and SIV isolates have relative affinities for sCD4 two- to eightfold lower than those of HIV-1. Treatment of infected cells with sCD4 induced the dissociation of gp120 from gp41 and increased the exposure of a cryptic gp41 epitope on all of the HIV-1 isolates. By contrast, neither dissociation of the outer envelope glycoprotein nor increased exposure of the transmembrane glycoprotein was observed when sCD4 bound to HIV-2- or SIV-infected cells. Moreover, immunoprecipitation with sCD4 resulted in the coprecipitation of the surface and transmembrane glycoproteins from virions of the HIV-2 and SIV isolates, whereas the surface envelope glycoprotein alone was precipitated from HIV-1. However, treatment of HIV-1-, HIV-2-, and SIV-infected cells with sCD4 did result in an increase in exposure of their V2 and V3 loops, as detected by enhanced antibody reactivity. This demonstrates that receptor binding to the outer envelope glycoprotein induces certain conformational changes which are common to all of these viruses and others which are restricted to cell line-passaged isolates of HIV-1.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J. S. Receptor-mediated activation of immunodeficiency viruses in viral fusion. Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1322–1323. doi: 10.1126/science.1925547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan J. S. Receptor-mediated activation of immunodeficiency viruses in viral fusion. Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1322–1323. doi: 10.1126/science.1925547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan J. S., Strauss J., Buck D. W. Enhancement of SIV infection with soluble receptor molecules. Science. 1990 Mar 2;247(4946):1084–1088. doi: 10.1126/science.2309120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan J. S., Whitehead E. M., Strout K., Short M., Kanda P., Hart T. K., Bugelski P. J. Strong association of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIVagm) envelope glycoprotein heterodimers: possible role in receptor-mediated activation. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Dec;8(12):2011–2020. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashkenazi A., Smith D. H., Marsters S. A., Riddle L., Gregory T. J., Ho D. D., Capon D. J. Resistance of primary isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to soluble CD4 is independent of CD4-rgp120 binding affinity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7056–7060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahraoui E., Benjouad A., Guetard D., Kolbe H., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. Study of the interaction of HIV-1 and HIV-2 envelope glycoproteins with the CD4 receptor and role of N-glycans. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 May;8(5):565–573. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A., Lifson J. D., Eiden L. E. Stimulation of glycoprotein gp120 dissociation from the envelope glycoprotein complex of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by soluble CD4 and CD4 peptide derivatives: implications for the role of the complementarity-determining region 3-like region in membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8082–8086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Mizukami T., Franchini G., Moss B. Synthesis, oligomerization, and biological activity of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2 envelope glycoprotein expressed by a recombinant vaccinia virus. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):134–142. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham P. R., Blanc D., Weiss R. A. Specific cell surface requirements for the infection of CD4-positive cells by human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 and by Simian immunodeficiency virus. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):703–715. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90904-P. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham P. R., McKnight A., Weiss R. A. Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 infection and fusion of CD4-negative human cell lines: induction and enhancement by soluble CD4. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3531–3537. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3531-3537.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham P. R., Weber J. N., Whitby D., McIntosh K., Dalgleish A. G., Maddon P. J., Deen K. C., Sweet R. W., Weiss R. A. Soluble CD4 blocks the infectivity of diverse strains of HIV and SIV for T cells and monocytes but not for brain and muscle cells. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):368–370. doi: 10.1038/337368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen K. C., McDougal J. S., Inacker R., Folena-Wasserman G., Arthos J., Rosenberg J., Maddon P. J., Axel R., Sweet R. W. A soluble form of CD4 (T4) protein inhibits AIDS virus infection. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):82–84. doi: 10.1038/331082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. S., Hillman K., Manischewitz J., Blumenthal R., Golding H. Kinetics of soluble CD4 binding to cells expressing human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):132–138. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.132-138.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Earl P. L., Chakrabarti S., Moss B. Human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 and simian immunodeficiency virus env proteins possess a functionally conserved assembly domain. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3537–3540. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3537-3540.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earl P. L., Doms R. W., Moss B. Oligomeric structure of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorny M. K., Gianakakos V., Sharpe S., Zolla-Pazner S. Generation of human monoclonal antibodies to human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyader M., Emerman M., Sonigo P., Clavel F., Montagnier L., Alizon M. Genome organization and transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):662–669. doi: 10.1038/326662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart T. K., Kirsh R., Ellens H., Sweet R. W., Lambert D. M., Petteway S. R., Jr, Leary J., Bugelski P. J. Binding of soluble CD4 proteins to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and infected cells induces release of envelope glycoprotein gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2189–2193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Fung M. S., Cao Y. Z., Li X. L., Sun C., Chang T. W., Sun N. C. Another discontinuous epitope on glycoprotein gp120 that is important in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralization is identified by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8949–8952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockley D. J., Wood R. D., Jacobs J. P., Garrett A. J. Electron microscopy of human immunodeficiency virus. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2455–2469. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoxie J. A., Brass L. F., Pletcher C. H., Haggarty B. S., Hahn B. H. Cytopathic variants of an attenuated isolate of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 exhibit increased affinity for CD4. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):5096–5101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.5096-5101.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoxie J. A. Hypothetical assignment of intrachain disulfide bonds for HIV-2 and SIV envelope glycoproteins. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Jun;7(6):495–499. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivey-Hoyle M., Culp J. S., Chaikin M. A., Hellmig B. D., Matthews T. J., Sweet R. W., Rosenberg M. Envelope glycoproteins from biologically diverse isolates of immunodeficiency viruses have widely different affinities for CD4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):512–516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent K. A., Gritz L., Stallard G., Cranage M. P., Collignon C., Thiriart C., Corcoran T., Silvera P., Stott E. J. Production and of monoclonal antibodies to simian immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoproteins. AIDS. 1991 Jul;5(7):829–836. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199107000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent K. A., Rud E., Corcoran T., Powell C., Thiriart C., Collignon C., Stott E. J. Identification of two neutralizing and 8 non-neutralizing epitopes on simian immunodeficiency virus envelope using monoclonal antibodies. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Jun;8(6):1147–1151. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klasse P. J., Moore J. P. Kinetics of the HIV-CD4 interactions and virus-cell fusion. AIDS. 1992 Mar;6(3):325–327. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199203000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Nakamura G., Smith D. H., Fennie C., Shimasaki C., Patzer E., Berman P., Gregory T., Capon D. J. Delineation of a region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 glycoprotein critical for interaction with the CD4 receptor. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90524-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layne S. P., Merges M. J., Dembo M., Spouge J. L., Nara P. L. HIV requires multiple gp120 molecules for CD4-mediated infection. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):277–279. doi: 10.1038/346277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard C. K., Spellman M. W., Riddle L., Harris R. J., Thomas J. N., Gregory T. J. Assignment of intrachain disulfide bonds and characterization of potential glycosylation sites of the type 1 recombinant human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein (gp120) expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10373–10382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney D. J., Hayashi S., Nicklas M., Redfield R. R., Broder S., Wong-Staal F., Mitsuya H. Differences in the interaction of HIV-1 and HIV-2 with CD4. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(7):649–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Kennedy M. S., Sligh J. M., Cort S. P., Mawle A., Nicholson J. K. Binding of HTLV-III/LAV to T4+ T cells by a complex of the 110K viral protein and the T4 molecule. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):382–385. doi: 10.1126/science.3001934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeating J. A., McKnight A., Moore J. P. Differential loss of envelope glycoprotein gp120 from virions of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates: effects on infectivity and neutralization. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):852–860. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.852-860.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
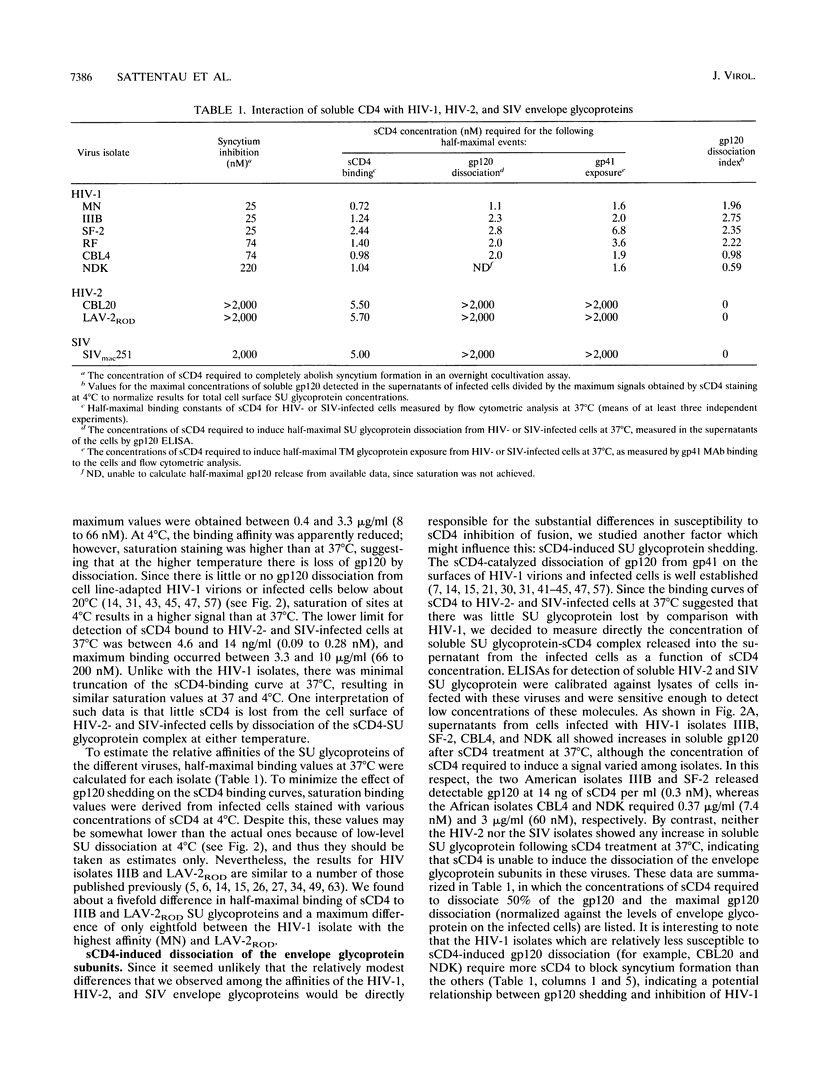
- Moore J. P., Burkly L. C., Connor R. I., Cao Y., Tizard R., Ho D. D., Fisher R. A. Adaptation of two primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates to growth in transformed T cell lines correlates with alterations in the responses of their envelope glycoproteins to soluble CD4. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 Jun;9(6):529–539. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., Klasse P. J. Thermodynamic and kinetic analysis of sCD4 binding to HIV-1 virions and of gp120 dissociation. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Apr;8(4):443–450. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., McKeating J. A., Huang Y. X., Ashkenazi A., Ho D. D. Virions of primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates resistant to soluble CD4 (sCD4) neutralization differ in sCD4 binding and glycoprotein gp120 retention from sCD4-sensitive isolates. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):235–243. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.235-243.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., McKeating J. A., Norton W. A., Sattentau Q. J. Direct measurement of soluble CD4 binding to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions: gp120 dissociation and its implications for virus-cell binding and fusion reactions and their neutralization by soluble CD4. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1133-1140.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., McKeating J. A., Weiss R. A., Sattentau Q. J. Dissociation of gp120 from HIV-1 virions induced by soluble CD4. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1139–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.2251501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
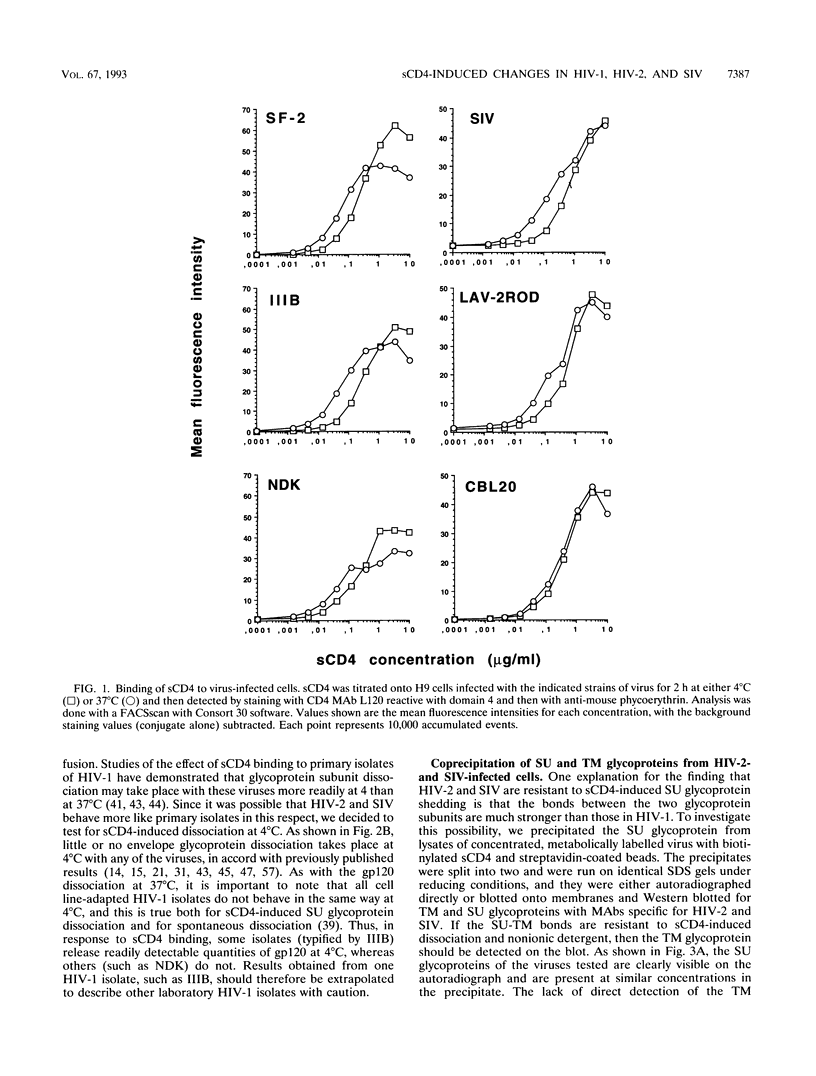
- Moore J. P., Morikawa Y., Jones I. M. Binding of recombinant HIV-1 and HIV-2 SU glycoproteins to sCD4. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(4):442–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
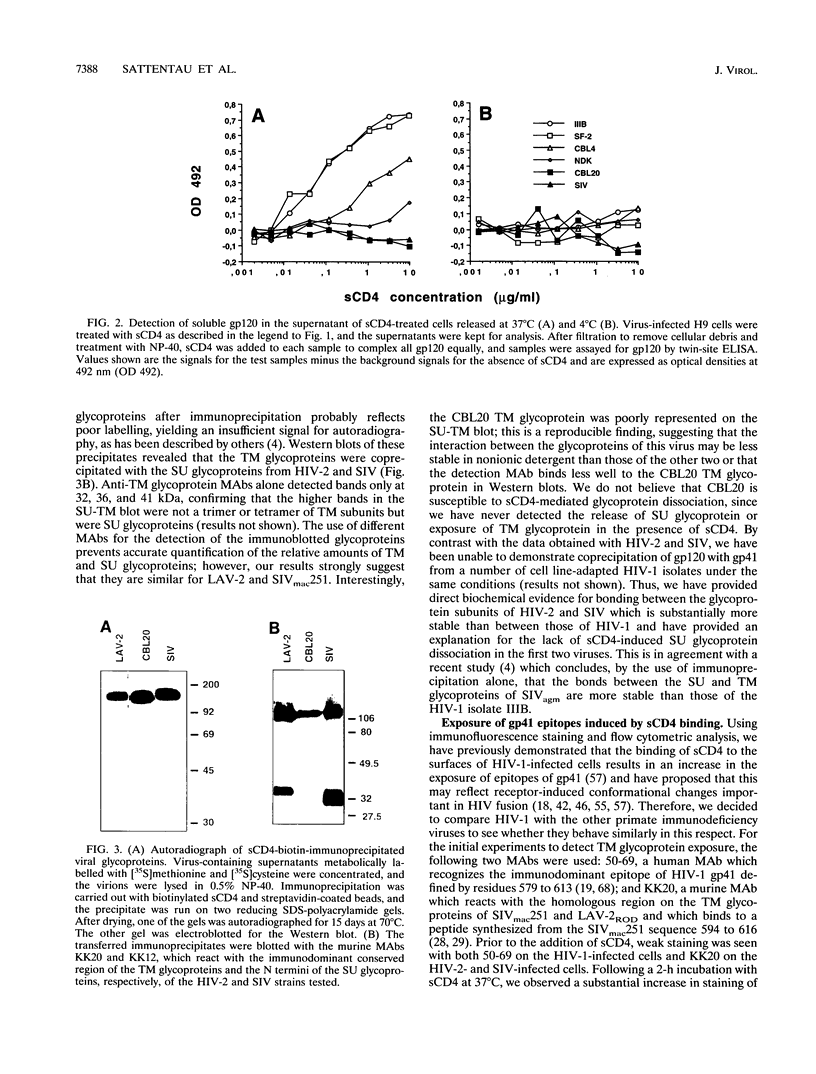
- Moore J. P. Simple methods for monitoring HIV-1 and HIV-2 gp120 binding to soluble CD4 by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: HIV-2 has a 25-fold lower affinity than HIV-1 for soluble CD4. AIDS. 1990 Apr;4(4):297–305. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199004000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. J., Ritter G. D., Jr, Chaikin M. A., Yamshchikov G. V., Kumar P., Hahn B. H., Sweet R. W., Compans R. W. Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 envelope glycoprotein: differential CD4 interactions of soluble gp120 versus the assembled envelope complex. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):233–241. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90311-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozel M., Pauli G., Gelderblom H. R. The organization of the envelope projections on the surface of HIV. Arch Virol. 1988;100(3-4):255–266. doi: 10.1007/BF01487688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E., Martin M. L., Goldsmith C., Switzer W. Ultrastructure of human immunodeficiency virus type 2. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jun;69(Pt 6):1425–1429. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-6-1425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parekh B. S., Pau C. P., Granade T. C., Rayfield M., De Cock K. M., Gayle H., Schochetman G., George J. R. Oligomeric nature of transmembrane glycoproteins of HIV-2: procedures for their efficient dissociation and preparation of Western blots for diagnosis. AIDS. 1991 Aug;5(8):1009–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter A., Honnen W. J., Tilley S. A., Bona C., Zaghouani H., Gorny M. K., Zolla-Pazner S. Oligomeric structure of gp41, the transmembrane protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2674–2679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2674-2679.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey M. A., Laurent A. G., McClure J., Krust B., Montagnier L., Hovanessian A. G. Transmembrane envelope glycoproteins of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 and simian immunodeficiency virus SIV-mac exist as homodimers. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):922–926. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.922-926.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau Q. J. CD4 activation of HIV fusion. Int J Cell Cloning. 1992 Nov;10(6):323–332. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530100603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau Q. J., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Beverley P. C., Montagnier L., Alhalabi M. F., Gluckmann J. C., Klatzmann D. The human and simian immunodeficiency viruses HIV-1, HIV-2 and SIV interact with similar epitopes on their cellular receptor, the CD4 molecule. AIDS. 1988 Apr;2(2):101–105. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198804000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau Q. J., Moore J. P. Conformational changes induced in the human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein by soluble CD4 binding. J Exp Med. 1991 Aug 1;174(2):407–415. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schawaller M., Smith G. E., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Studies with crosslinking reagents on the oligomeric structure of the env glycoprotein of HIV. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):367–369. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz T. F., Jameson B. A., Lopalco L., Siccardi A. G., Weiss R. A., Moore J. P. Conserved structural features in the interaction between retroviral surface and transmembrane glycoproteins? AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Sep;8(9):1571–1580. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekigawa I., Chamow S. M., Groopman J. E., Byrn R. A. CD4 immunoadhesin, but not recombinant soluble CD4, blocks syncytium formation by human immunodeficiency virus type 2-infected lymphoid cells. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5194–5198. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5194-5198.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Bayley P. M., Brown E. B., Martin S. R., Waterfield M. D., White J. M., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. Changes in the conformation of influenza virus hemagglutinin at the pH optimum of virus-mediated membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thali M., Olshevsky U., Furman C., Gabuzda D., Li J., Sodroski J. Effects of changes in gp120-CD4 binding affinity on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein function and soluble CD4 sensitivity. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):5007–5012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.5007-5012.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner S., Tizard R., DeMarinis J., Pepinsky R. B., Zullo J., Schooley R., Fisher R. Resistance of primary isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to neutralization by soluble CD4 is not due to lower affinity with the viral envelope glycoprotein gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1335–1339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss C. D., Levy J. A., White J. M. Oligomeric organization of gp120 on infectious human immunodeficiency virus type 1 particles. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5674–5677. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5674-5677.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner A., Winskowsky G., Kurth R. Soluble CD4 enhances simian immunodeficiency virus SIVagm infection. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6252–6256. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6252-6256.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M., Wilson I. A. Anti-peptide antibodies detect steps in a protein conformational change: low-pH activation of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 2):2887–2896. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu J. Y., Gorny M. K., Palker T., Karwowska S., Zolla-Pazner S. Epitope mapping of two immunodominant domains of gp41, the transmembrane protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, using ten human monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4832–4838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4832-4838.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]