Abstract
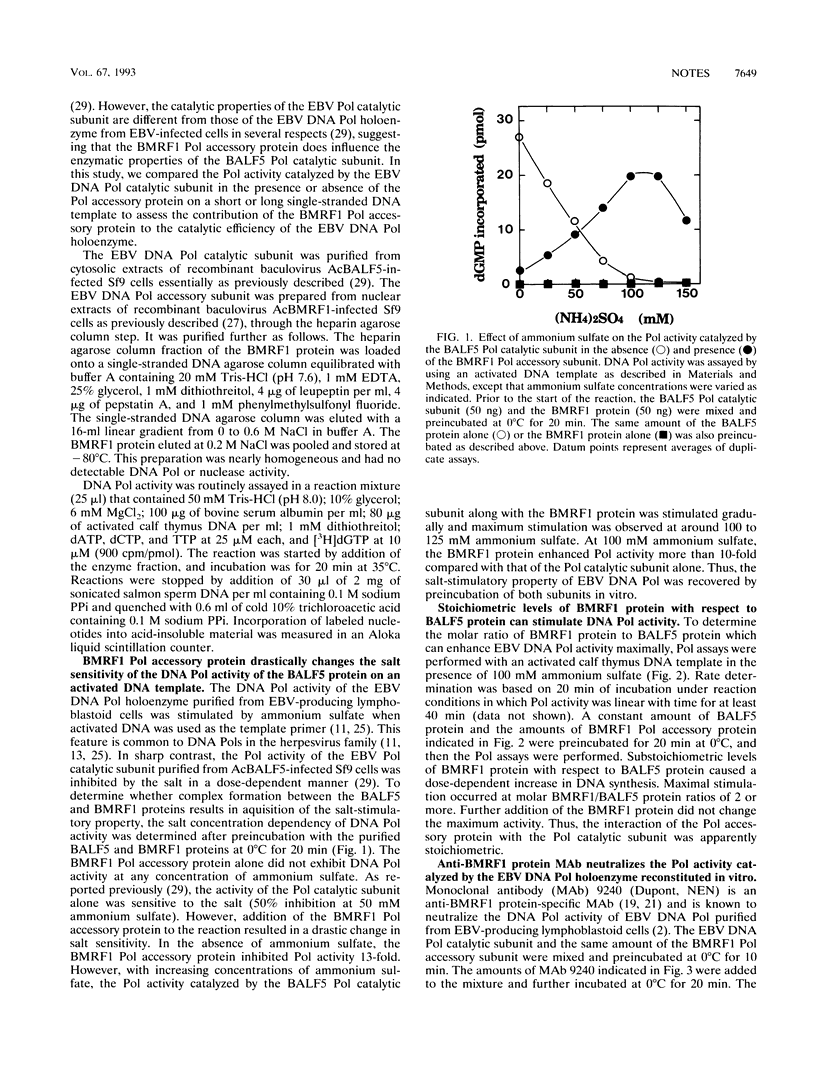
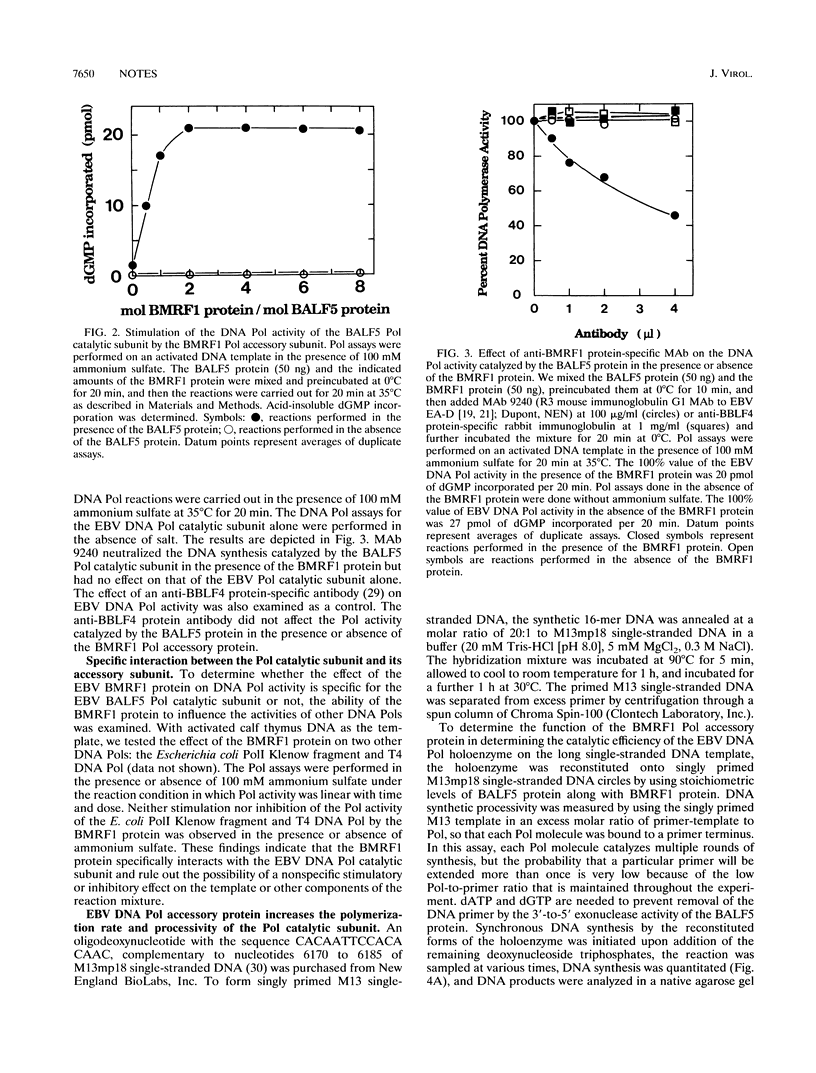
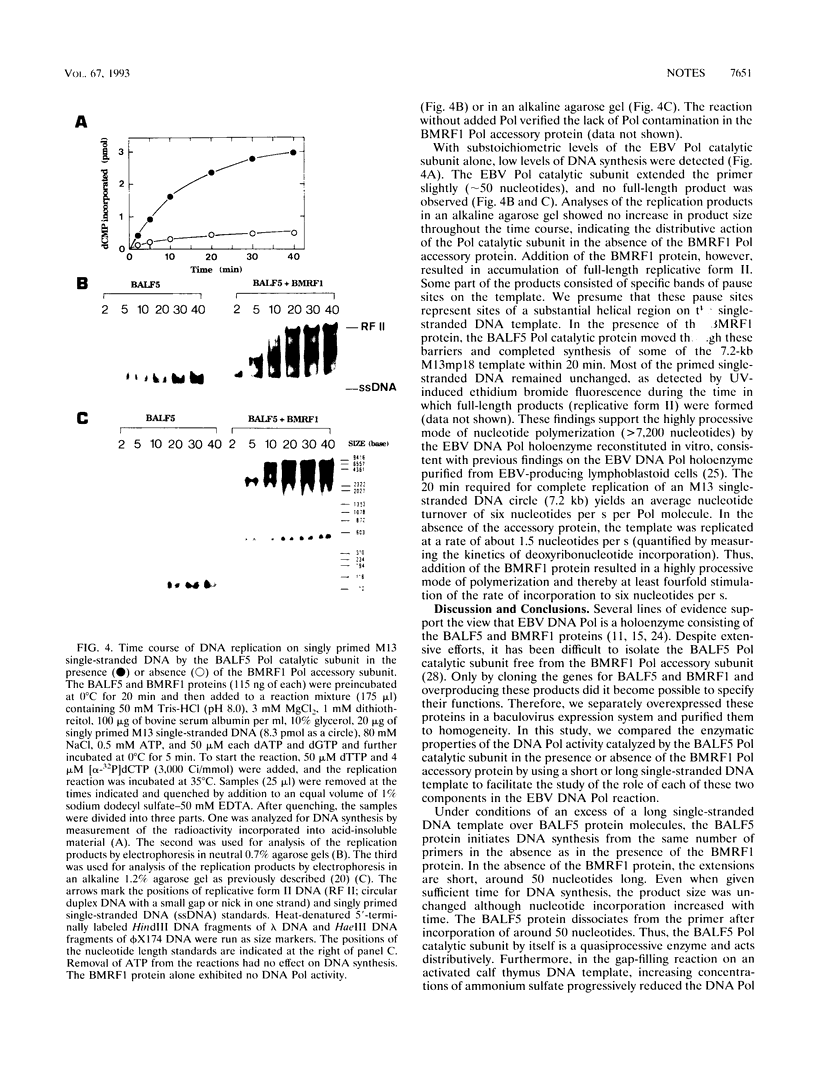
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA polymerase catalytic subunit (BALF5 protein) and its accessory subunit (BMRF1 protein) have been independently overexpressed and purified (T. Tsurumi, A. Kobayashi, K. Tamai, T. Daikoku, R. Kurachi, and Y. Nishiyama, J. Virol. 67:4651-4658, 1993; T. Tsurumi, J. Virol. 67:1681-1687, 1993). In an investigation of the molecular basis of protein-protein interactions between the subunits of the EBV DNA polymerase holoenzyme, we compared the DNA polymerase activity catalyzed by the BALF5 protein in the presence or absence of the BMRF1 polymerase accessory subunit in vitro. The DNA polymerase activity of the BALF5 polymerase catalytic subunit alone was sensitive to high ionic strength on an activated DNA template (80% inhibition at 100 mM ammonium sulfate). Addition of the polymerase accessory subunit to the reaction greatly enhanced DNA polymerase activity in the presence of high concentrations of ammonium sulfate (10-fold stimulation at 100 mM ammonium sulfate). Optimal stimulation was obtained when the molar ratio of BMRF1 protein to BALF5 protein was 2 or more. The DNA polymerase activity of the BALF5 protein along with the BMRF1 protein was neutralized by a monoclonal antibody to the BMRF1 protein, whereas that of the BALF5 protein alone was not, suggesting a specific interaction between the BALF5 protein and the BMRF1 protein in the reaction. The processivity of nucleotide polymerization of the BALF5 polymerase catalytic subunit on singly primed M13 single-stranded DNA circles was low (approximately 50 nucleotides). Addition of the BMRF1 polymerase accessory subunit resulted in a strikingly high processive mode of deoxynucleotide polymerization (> 7,200 nucleotides). These findings strongly suggest that the BMRF1 polymerase accessory subunit stabilizes interaction between the EBV DNA polymerase and primer template and functions as a sliding clamp at the growing 3'-OH end of the primer terminus to increase the processivity of polymerization.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiou J. F., Li J. K., Cheng Y. C. Demonstration of a stimulatory protein for virus-specified DNA polymerase in phorbol ester-treated Epstein-Barr virus-carrying cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5728–5731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., LaDuca R. J., Johanson K. O., McHenry C. S., Bambara R. A. Excess beta subunit can bypass the ATP requirement for highly processive synthesis by the Escherichia coli DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11344–11349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., Lehman I. R. Herpes simplex-1 DNA polymerase. Identification of an intrinsic 5'----3' exonuclease with ribonuclease H activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19266–19270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay P. J., Johanson K. O., McHenry C. S., Bambara R. A. Size classes of products synthesized processively by two subassemblies of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5692–5699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fixman E. D., Hayward G. S., Hayward S. D. trans-acting requirements for replication of Epstein-Barr virus ori-Lyt. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5030–5039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5030-5039.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb J., Marcy A. I., Coen D. M., Challberg M. D. The herpes simplex virus type 1 UL42 gene product: a subunit of DNA polymerase that functions to increase processivity. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5976–5987. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5976-5987.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Identification and characterization of oriLyt, a lytic origin of DNA replication of Epstein-Barr virus. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez T. R., Lehman I. R. Functional interaction between the herpes simplex-1 DNA polymerase and UL42 protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11227–11232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis T. C., Paul L. S., Hockensmith J. W., von Hippel P. H. Structural and enzymatic studies of the T4 DNA replication system. II. ATPase properties of the polymerase accessory protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12717–12729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallin B., Sternås L., Saemundssen A. K., Luka J., Jörnvall H., Eriksson B., Tao P. Z., Nilsson M. T., Klein G. Purification of Epstein-Barr virus DNA polymerase from P3HR-1 cells. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):561–568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.561-568.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehl A., Dorsky D. I. Cooperation of EBV DNA polymerase and EA-D(BMRF1) in vitro and colocalization in nuclei of infected cells. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):330–340. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90849-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf K. W. Properties of herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase and characterization of its associated exonuclease activity. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):231–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. S., Zhou B. S., Dutschman G. E., Grill S. P., Tan R. S., Cheng Y. C. Association of Epstein-Barr virus early antigen diffuse component and virus-specified DNA polymerase activity. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2947–2949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2947-2949.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. C., Sista N. D., Besençon F., Kamine J., Pagano J. S. Identification and functional characterization of Epstein-Barr virus DNA polymerase by in vitro transcription-translation of a cloned gene. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2728–2731. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2728-2731.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcy A. I., Olivo P. D., Challberg M. D., Coen D. M. Enzymatic activities of overexpressed herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase purified from recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1207–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell M., Studwell P. S. Total reconstitution of DNA polymerase III holoenzyme reveals dual accessory protein clamps. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):1179–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., Vroman B., Chase B., Sculley T., Hummel M., Kieff E. Identification of polypeptide components of the Epstein-Barr virus early antigen complex with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):193–201. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.193-201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi S., Takada K., Sairenji T. Formation of intranuclear replication compartments of Epstein-Barr virus with redistribution of BZLF1 and BMRF1 gene products. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90778-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Functions of replication factor C and proliferating-cell nuclear antigen: functional similarity of DNA polymerase accessory proteins from human cells and bacteriophage T4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1023–1027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Replication factors required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. I. DNA structure-specific recognition of a primer-template junction by eukaryotic DNA polymerases and their accessory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1950–1960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurumi T. Characterization of 3'-to 5'-exonuclease activity associated with Epstein-Barr virus DNA polymerase. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):376–381. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90685-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurumi T., Kobayashi A., Tamai K., Daikoku T., Kurachi R., Nishiyama Y. Functional expression and characterization of the Epstein-Barr virus DNA polymerase catalytic subunit. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4651–4658. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4651-4658.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurumi T. Primer terminus recognition and highly processive replication by Epstein-Barr virus DNA polymerase. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 15;280(Pt 3):703–708. doi: 10.1042/bj2800703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurumi T. Purification and characterization of the DNA-binding activity of the Epstein-Barr virus DNA polymerase accessory protein BMRF1 gene products, as expressed in insect cells by using the baculovirus system. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1681–1687. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1681-1687.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurumi T. Selective inhibition of the 3'-to-5' exonuclease activity associated with Epstein-Barr virus DNA polymerase by ribonucleoside 5'-monophosphates. Virology. 1992 Aug;189(2):803–807. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90611-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J., Warren N., Reisman D., Sugden B. A cis-acting element from the Epstein-Barr viral genome that permits stable replication of recombinant plasmids in latently infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. C., Reddy M. K., von Hippel P. H. Structure and function of the bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase holoenzyme. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 22;31(37):8675–8690. doi: 10.1021/bi00152a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]