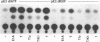Abstract
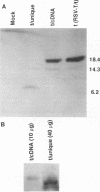
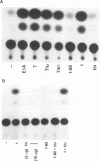
Simian virus 40 (SV40) small t and large T antigens can each trans activate the adenovirus (Ad) E2A and the Ad VA-I promoters. The first 82 amino acids of large T and small t are identical. However, this large T-small t common domain between residues 1 and 82 does not trans activate, suggesting that large T and small t each encode separate trans-activation functions. To determine whether the large T or small t unique domains, which are required for trans activation of the E2A promoter, are sufficient for this activity, we have employed expression plasmids separately encoding the common and unique domains of large T and small t. Cotransfection of a large T unique domain expression plasmid efficiently trans activated the E2A promoter. Optimal trans activation by large T required the motif that binds cellular proteins such as the retinoblastoma gene product, which is located in the large T unique domain, and additional large T structures outside this motif. In contrast, the small t unique domain did not trans activate the E2A promoter. Experiments utilizing E2A promoter mutants containing only the ATF- or EIIF-binding sites demonstrated that trans activation by small t involves only the EIIF transcription factor and that this function requires both the common (residues 1 to 82) and the small t unique domains expressed as a colinear protein. trans activation by large T, in contrast, involves at least three mechanisms. There appear to be at least two mechanisms that involve the EIIF transcription factor, at least one of which does not require the common domain (residues 1 to 82) and one mechanism that involves the ATF factor and does require both the common and the large T unique domains.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Hafiz H. A., Heasley L. E., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Kroll D. J., Johnson G. L., Hoeffler J. P. Activating transcription factor-2 DNA-binding activity is stimulated by phosphorylation catalyzed by p42 and p54 microtubule-associated protein kinases. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Dec;6(12):2079–2089. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.12.1337144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi S., Weinmann R., Raychaudhuri P. The retinoblastoma protein copurifies with E2F-I, an E1A-regulated inhibitor of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1063–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90558-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandara L. R., La Thangue N. B. Adenovirus E1a prevents the retinoblastoma gene product from complexing with a cellular transcription factor. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):494–497. doi: 10.1038/351494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bikel I., Loeken M. R. Involvement of simian virus 40 (SV40) small t antigen in trans activation of SV40 early and late promoters. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1489–1494. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1489-1494.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Bolen J. B., Radonovich M., Salzman N., Khoury G. Stimulation of simian virus 40 late gene expression by simian virus 40 tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2040–2044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellappan S. P., Hiebert S., Mudryj M., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90557-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittenden T., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr The T/E1A-binding domain of the retinoblastoma product can interact selectively with a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1073–1082. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90559-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devoto S. H., Mudryj M., Pines J., Hunter T., Nevins J. R. A cyclin A-protein kinase complex possesses sequence-specific DNA binding activity: p33cdk2 is a component of the E2F-cyclin A complex. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Ludlow J. W., Marsilio E., DeCaprio J. A., Millikan R. C., Cheng S. H., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. An N-terminal transformation-governing sequence of SV40 large T antigen contributes to the binding of both p110Rb and a second cellular protein, p120. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90840-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E. Simian virus 40 large T antigen: the puzzle, the pieces, and the emerging picture. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1289–1293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1289-1293.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Activation of gene expression by adenovirus and herpesvirus regulatory genes acting in trans and by a cis-acting adenovirus enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jog P., Joshi B., Dhamankar V., Imperiale M. J., Rutila J., Rundell K. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 small-t antigen. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2895–2900. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2895-2900.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Smith A. E. In vitro mutagenesis of a putative DNA binding domain of SV40 large-T. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):109–137. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeken M. R., Brady J. The adenovirus EIIA enhancer. Analysis of regulatory sequences and changes in binding activity of ATF and EIIF following adenovirus infection. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6572–6579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeken M. R., Khoury G., Brady J. Stimulation of the adenovirus E2 promoter by simian virus 40 T antigen or E1A occurs by different mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2020–2026. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeken M. R. Simian virus 40 small t antigen trans activates the adenovirus E2A promoter by using mechanisms distinct from those used by adenovirus E1A. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2551–2555. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2551-2555.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeken M., Bikel I., Livingston D. M., Brady J. trans-activation of RNA polymerase II and III promoters by SV40 small t antigen. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1171–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsilio E., Cheng S. H., Schaffhausen B., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. The T/t common region of simian virus 40 large T antigen contains a distinct transformation-governing sequence. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5647–5652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5647-5652.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montano X., Lane D. P. Monoclonal antibody to simian virus 40 small t. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):760–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.760-767.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montano X., Millikan R., Milhaven J. M., Newsom D. A., Ludlow J. W., Arthur A. K., Fanning E., Bikel I., Livingston D. M. Simian virus 40 small tumor antigen and an amino-terminal domain of large tumor antigen share a common transforming function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7448–7452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Devoto S. H., Hiebert S. W., Hunter T., Pines J., Nevins J. R. Cell cycle regulation of the E2F transcription factor involves an interaction with cyclin A. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1243–1253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90019-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Shahrik L. K., Martin B. L., Jaspers S., Miller T. B., Brautigan D. L., Roberts T. M. Polyoma small and middle T antigens and SV40 small t antigen form stable complexes with protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90726-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallas D. C., Weller W., Jaspers S., Miller T. B., Lane W. S., Roberts T. M. The third subunit of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), a 55-kilodalton protein which is apparently substituted for by T antigens in complexes with the 36- and 63-kilodalton PP2A subunits, bears little resemblance to T antigens. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):886–893. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.886-893.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Yee C. L., Münger K., Howley P. M. The human papillomavirus type 16 E7 gene encodes transactivation and transformation functions similar to those of adenovirus E1A. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90570-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Mumby M. C., Rundell K., Walter G. Dephosphorylation of simian virus 40 large-T antigen and p53 protein by protein phosphatase 2A: inhibition by small-t antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1996–2003. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodkar S., Ewen M., DeCaprio J. A., Morgan J., Livingston D. M., Chittenden T. The transcription factor E2F interacts with the retinoblastoma product and a p107-cyclin A complex in a cell cycle-regulated manner. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90214-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan A., Peden K. W., Pipas J. M. The large tumor antigen of simian virus 40 encodes at least two distinct transforming functions. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5459–5463. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5459-5463.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe Y., Seiki M., Fujisawa J., Hoy P., Yokota K., Arai K., Yoshida M., Arai N. SR alpha promoter: an efficient and versatile mammalian cDNA expression system composed of the simian virus 40 early promoter and the R-U5 segment of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):466–472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Ruediger R., Slaughter C., Mumby M. Association of protein phosphatase 2A with polyoma virus medium tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2521–2525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. G., Draetta G., Moran E. E1A induces phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein independently of direct physical association between the E1A and retinoblastoma products. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4253–4265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. I., Lickteig R. L., Estes R., Rundell K., Walter G., Mumby M. C. Control of protein phosphatase 2A by simian virus 40 small-t antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1988–1995. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J. Y., Rice P. W., Chamberlain M., Cole C. N. Mapping the transcriptional transactivation function of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2778–2790. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2778-2790.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]