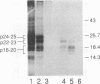
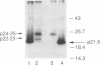
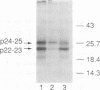
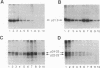
Abstract
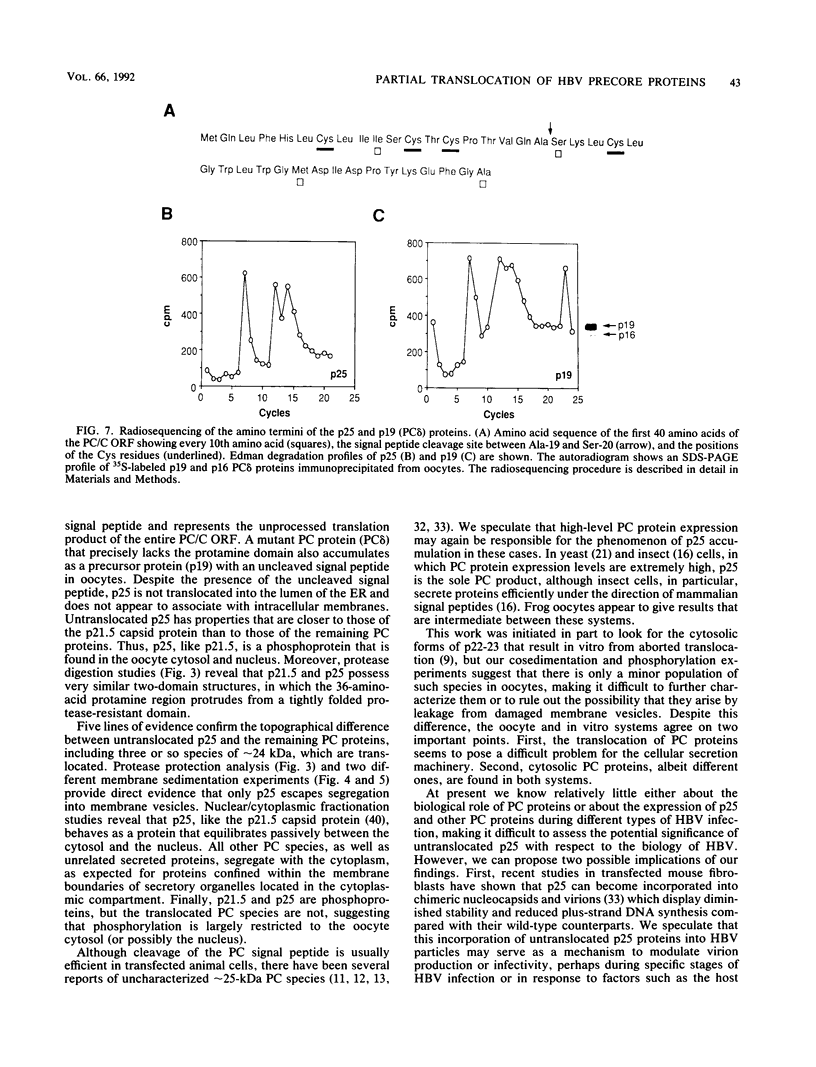
We have analyzed the translocation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) precore (PC) proteins by using Xenopus oocytes injected with a synthetic PC mRNA. The PC region is a 29-amino-acid sequence that precedes the 21.5-kDa HBV capsid or core (C) protein (p21.5) and directs the secretion of core-related proteins. The first 19 PC amino acids provide a signal peptide that is cleaved with the resultant translocation of a 22.5-kDa species (p22.5), in which the last 10 PC residues precede the complete p21.5 C polypeptide. Most p22.5 is matured to 16-20 kDa species by carboxyl-terminal proteolytic cleavage prior to secretion. Here we show that some four unexpected PC proteins of 24 to 25 kDa are produced in addition to the secretion products described above. Protease protection and membrane cosedimentation experiments reveal that all PC proteins behave as expected for proteins that are translocated into the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum except for the single largest PC protein (p25), which is not translocated. Like p21.5, p25 is a phosphoprotein that localizes to the oocyte cytosol and nucleus, and protease digestion studies suggest that the two molecules have similar two-domain structures. Radiosequencing of immobilized p25 demonstrates that it contains the intact PC signal peptide and represents the unprocessed translation product of the entire PC/C locus. Thus, while many HBV PC protein molecules are correctly targeted to intracellular membranes and translocated, a significant fraction of these molecules can evade translocation and processing.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruss V., Gerlich W. H. Formation of transmembraneous hepatitis B e-antigen by cotranslational in vitro processing of the viral precore protein. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):268–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90266-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büscher M., Reiser W., Will H., Schaller H. Transcripts and the putative RNA pregenome of duck hepatitis B virus: implications for reverse transcription. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):717–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Enders G., Sprengel R., Peters N., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Expression of the precore region of an avian hepatitis B virus is not required for viral replication. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3322–3325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3322-3325.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C. M., Liaw Y. F. Intrahepatic distribution of hepatitis B surface and core antigens in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatocyte with cytoplasmic/membranous hepatitis B core antigen as a possible target for immune hepatocytolysis. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jan;92(1):220–225. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90863-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt S. G., Milich D. R., McLachlan A. Hepatitis B virus core antigen has two nuclear localization sequences in the arginine-rich carboxyl terminus. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):575–582. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.575-582.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders G. H., Ganem D., Varmus H. Mapping the major transcripts of ground squirrel hepatitis virus: the presumptive template for reverse transcriptase is terminally redundant. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):297–308. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia P. D., Ou J. H., Rutter W. J., Walter P. Targeting of the hepatitis B virus precore protein to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane: after signal peptide cleavage translocation can be aborted and the product released into the cytoplasm. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1093–1104. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Wickens M. P. The use of Xenopus oocytes for the expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:370–386. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean-Jean O., Salhi S., Carlier D., Elie C., De Recondo A. M., Rossignol J. M. Biosynthesis of hepatitis B virus e antigen: directed mutagenesis of the putative aspartyl protease site. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5497–5500. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5497-5500.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junker M., Galle P., Schaller H. Expression and replication of the hepatitis B virus genome under foreign promoter control. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10117–10132. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima T., Bloemen J., Desmet V. J. Immune electron microscopic demonstration of hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg) in liver cell plasma membranes. Liver. 1987 Aug;7(4):191–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1987.tb00342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Notvall L. Expression of hepatitis B virus core and precore antigens in insect cells and characterization of a core-associated kinase activity. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):222–233. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90247-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnius L. O., Espmark J. A. New specificities in Australia antigen positive sera distinct from the Le Bouvier determinants. J Immunol. 1972 Nov;109(5):1017–1021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A., Milich D. R., Raney A. K., Riggs M. G., Hughes J. L., Sorge J., Chisari F. V. Expression of hepatitis B virus surface and core antigens: influences of pre-S and precore sequences. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):683–692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.683-692.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., Jones J. E., Hughes J. L., Price J., Raney A. K., McLachlan A. Is a function of the secreted hepatitis B e antigen to induce immunologic tolerance in utero? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6599–6603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyanohara A., Imamura T., Araki M., Sugawara K., Ohtomo N., Matsubara K. Expression of hepatitis B virus core antigen gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: synthesis of two polypeptides translated from different initiation codons. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):176–180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.176-180.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondelli M., Vergani G. M., Alberti A., Vergani D., Portmann B., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Specificity of T lymphocyte cytotoxicity to autologous hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: evidence that T cells are directed against HBV core antigen expressed on hepatocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2773–2778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Laub O., Rutter W. J. Hepatitis B virus gene function: the precore region targets the core antigen to cellular membranes and causes the secretion of the e antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1578–1582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou J. H., Yeh C. T., Yen T. S. Transport of hepatitis B virus precore protein into the nucleus after cleavage of its signal peptide. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5238–5243. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5238-5243.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignatelli M., Waters J., Lever A., Iwarson S., Gerety R., Thomas H. C. Cytotoxic T-cell responses to the nucleocapsid proteins of HBV in chronic hepatitis. Evidence that antibody modulation may cause protracted infection. J Hepatol. 1987 Feb;4(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(87)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roossinck M. J., Jameel S., Loukin S. H., Siddiqui A. Expression of hepatitis B viral core region in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1393–1400. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roossinck M. J., Siddiqui A. In vivo phosphorylation and protein analysis of hepatitis B virus core antigen. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):955–961. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.955-961.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salfeld J., Pfaff E., Noah M., Schaller H. Antigenic determinants and functional domains in core antigen and e antigen from hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):798–808. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.798-808.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Salfeld J., Schaller H. The duck hepatitis B virus pre-C region encodes a signal sequence which is essential for synthesis and secretion of processed core proteins but not for virus formation. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3701–3709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3701-3709.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Schaller H. The secretory core protein of human hepatitis B virus is expressed on the cell surface. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5399–5404. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5399-5404.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifer M., Heermann K. H., Gerlich W. H. Expression pattern of the hepatitis B virus genome in transfected mouse fibroblasts. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):287–299. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90297-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifer M., Heermann K. H., Gerlich W. H. Replication of hepatitis B virus in transfected nonhepatic cells. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):300–311. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90298-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Ou J. H., Masiarz F. R., Rutter W. J. A signal peptide encoded within the precore region of hepatitis B virus directs the secretion of a heterogeneous population of e antigens in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8405–8409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Ou J. H., Rutter W. J. Assembly of viral particles in Xenopus oocytes: pre-surface-antigens regulate secretion of the hepatitis B viral surface envelope particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9338–9342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Machida A., Funatsu G., Nomura M., Usuda S., Aoyagi S., Tachibana K., Miyamoto H., Imai M., Nakamura T. Immunochemical structure of hepatitis B e antigen in the serum. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2903–2907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimer T., Salfeld J., Will H. Expression of the hepatitis B virus core gene in vitro and in vivo. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3109–3113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3109-3113.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh C. T., Liaw Y. F., Ou J. H. The arginine-rich domain of hepatitis B virus precore and core proteins contains a signal for nuclear transport. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6141–6147. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6141-6147.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou S. L., Standring D. N. Production of hepatitis B virus nucleocapsidlike core particles in Xenopus oocytes: assembly occurs mainly in the cytoplasm and does not require the nucleus. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5457–5464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5457-5464.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]