Abstract
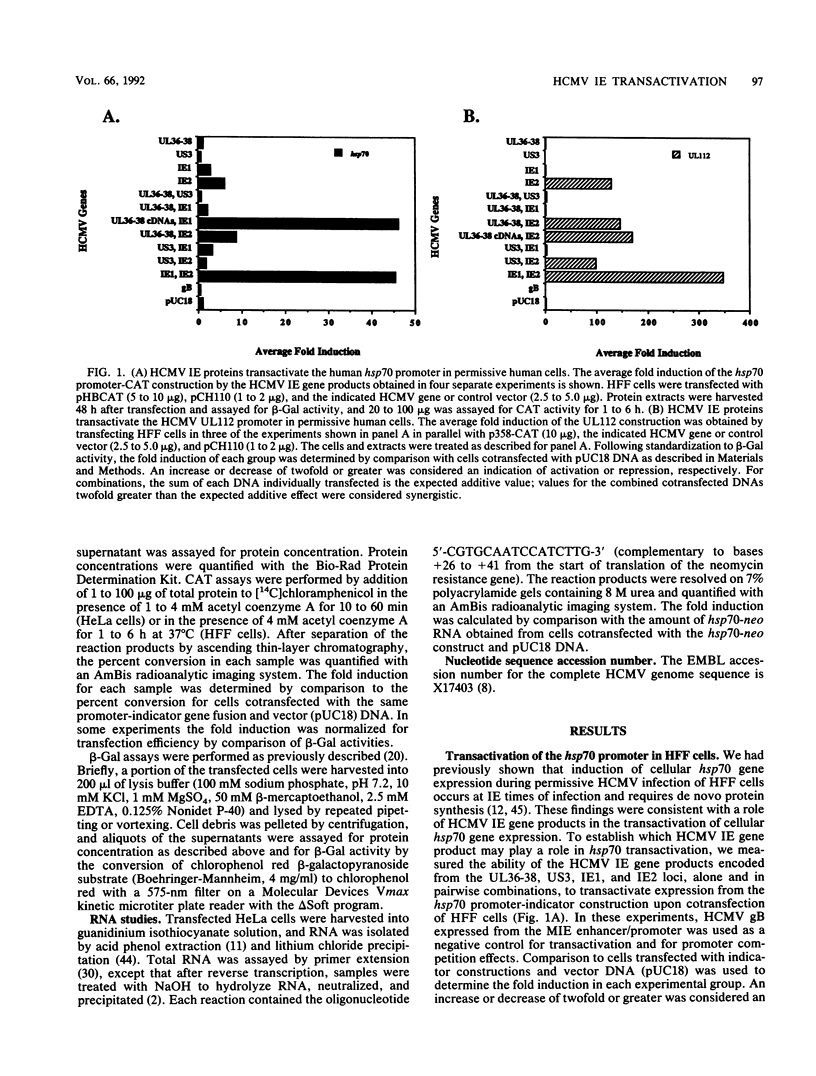
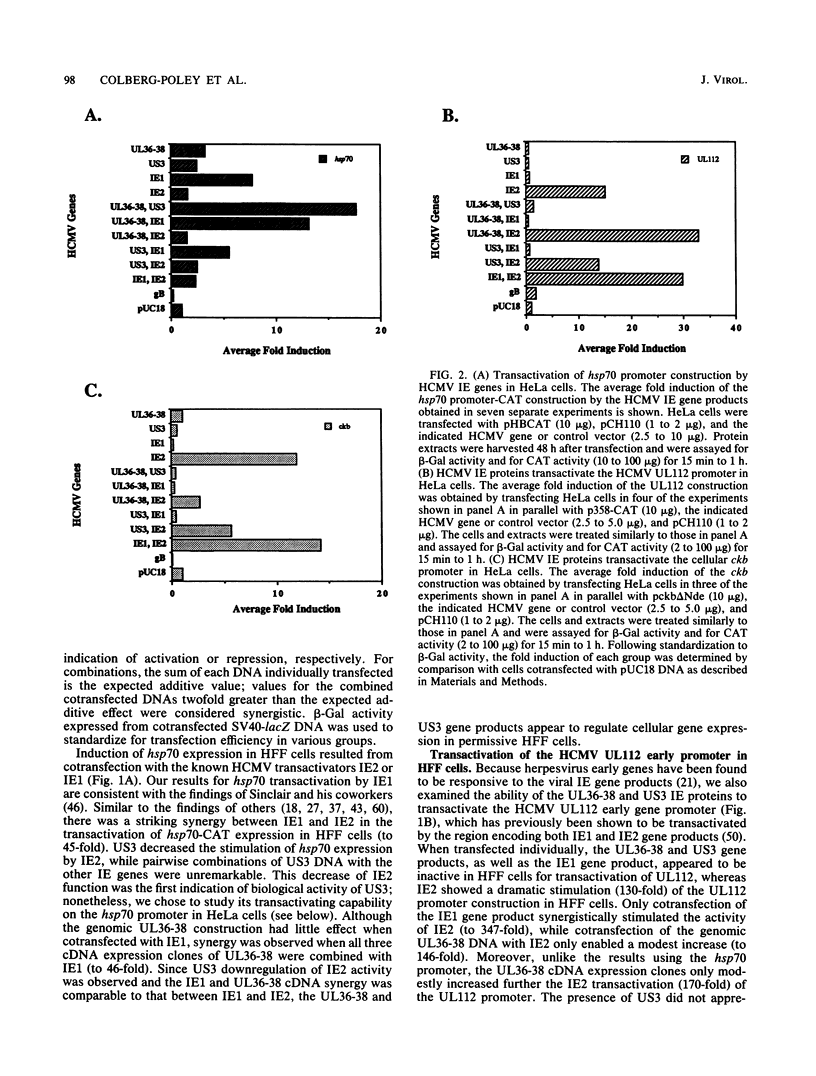
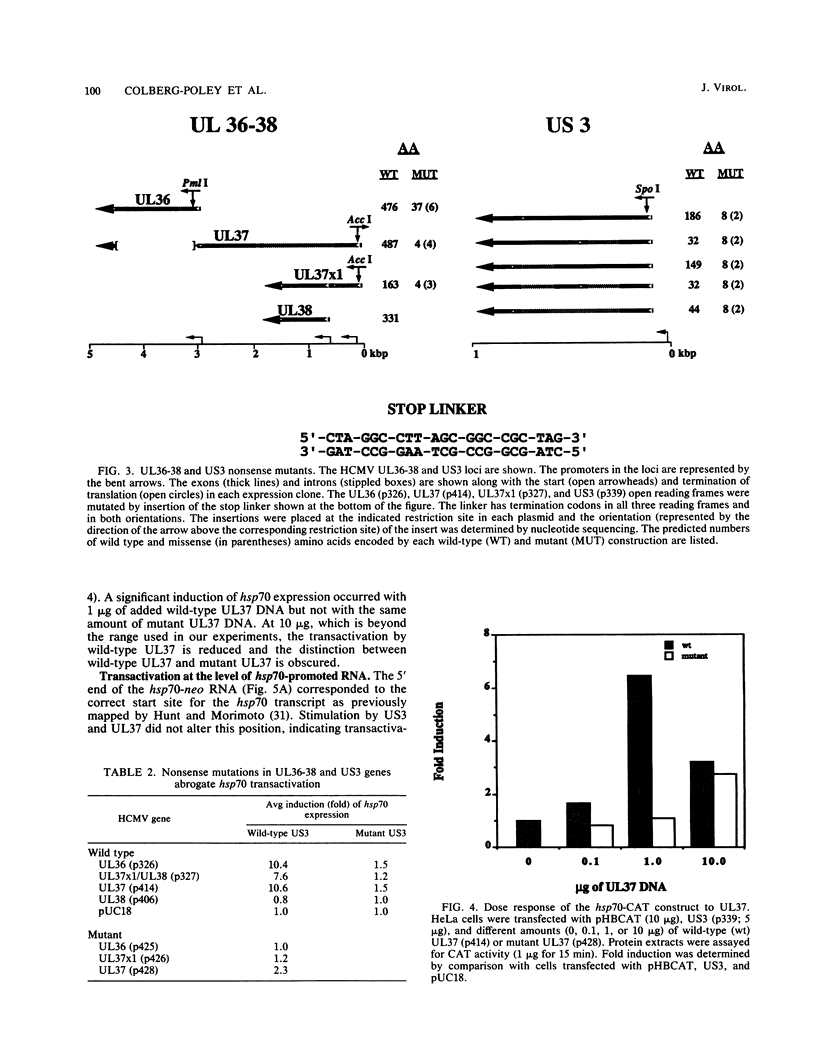
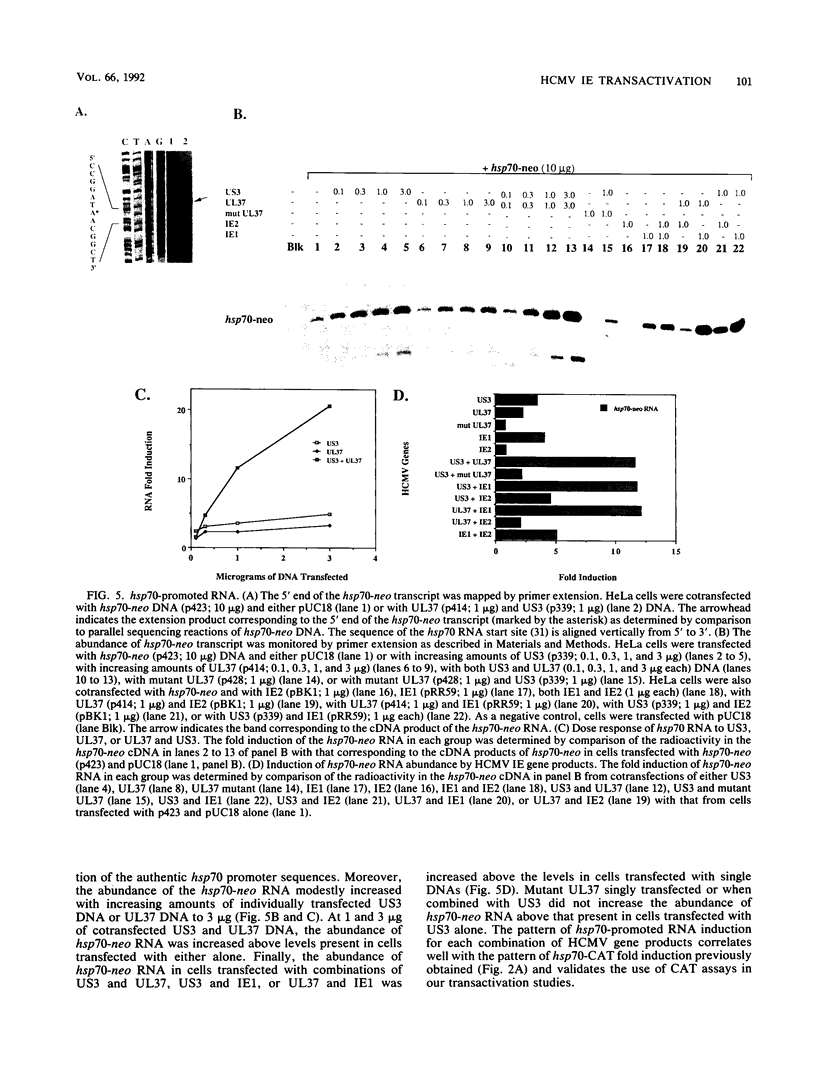
We have established the ability of the human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) UL36-38 and US3 immediate-early (IE) gene products to alter gene expression in human cells by using transient transfection assays. The cellular heat shock protein 70 (hsp70) promoter was transactivated following cotransfection with the HCMV IE regions in nonpermissive HeLa cells by UL36-38, US3, or IE1 and in permissive human diploid fibroblasts (HFF) by IE1 or IE2. Moreover, hsp70 expression was synergistically increased in HeLa cells cotransfected with US3 and UL36, with US3 and UL37, or with US3 and UL37x1. The synergistic transactivation of hsp70 expression by US3 and UL36-38 was not observed in HFF cells. Synergy was also not observed in HeLa cells between US3 and UL38, an early gene product encoded by the UL36-38 IE locus. Synergistic transactivation of hsp70 expression in HeLa cells required the syntheses of UL36-38 and US3 IE proteins, since nonsense mutants were not functional. hsp70 expression increased with increasing amounts of transfected US3 and UL37 DNA and occurred at the level of stable hsp70-promoted RNA. In contrast to the broad hsp70 response, promoters from the HCMV UL112 early gene and another cellular gene, brain creatine kinase, both responded strongly only to singly transfected IE2 in HeLa cells. Nevertheless, IE2 transactivation of the UL112 promoter was further stimulated by cotransfection of IE1 or of UL36-38 in both HeLa and HFF cells. Thus, different patterns of promoter transactivation and interactions between HCMV IE gene products in transactivation were found in HFF cells and in HeLa cells. These results establish the ability of the HCMV US3 and UL36-38 proteins to alter cellular and viral gene expression and are consistent with involvement of cellular transcription factors in HCMV IE regulation of gene expression.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akrigg A., Wilkinson G. W., Oram J. D. The structure of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virus Res. 1985 Mar;2(2):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfield P. A., Graf D., Korolkoff P. N., Hobson G., Pearson M. L. Isolation of four rat creatine kinase genes and identification of multiple potential promoter sequences within the rat brain creatine kinase promoter region. Gene. 1988 Mar 31;63(2):227–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90527-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldogh I., AbuBakar S., Albrecht T. Activation of proto-oncogenes: an immediate early event in human cytomegalovirus infection. Science. 1990 Feb 2;247(4942):561–564. doi: 10.1126/science.1689075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldogh I., AbuBakar S., Deng C. Z., Albrecht T. Transcriptional activation of cellular oncogenes fos, jun, and myc by human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1568–1571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1568-1571.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond-Matthews B., Davidson N. Transcription from each of the Drosophila act5C leader exons is driven by a separate functional promoter. Gene. 1988;62(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90566-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. P., Malone C. L., Stinski M. F. A human cytomegalovirus early gene has three inducible promoters that are regulated differentially at various times after infection. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):281–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.281-290.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Bankier A. T., Beck S., Bohni R., Brown C. M., Cerny R., Horsnell T., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Kouzarides T., Martignetti J. A. Analysis of the protein-coding content of the sequence of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:125–169. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington J. M., Khoury E. L., Mocarski E. S. Human cytomegalovirus ie2 negatively regulates alpha gene expression via a short target sequence near the transcription start site. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):887–896. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.887-896.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington J. M., Mocarski E. S. Human cytomegalovirus ie1 transactivates the alpha promoter-enhancer via an 18-base-pair repeat element. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1435–1440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1435-1440.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Santomenna L. D. Selective induction of chromosomal gene expression by human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. G., Kenney S. C., Kamine J., Pagano J. S., Huang E. S. Immediate-early gene region of human cytomegalovirus trans-activates the promoter of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8642–8646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarchi J. M. Post-transcriptional control of human cytomegalovirus gene expression. Virology. 1983 Jan 30;124(2):390–402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depto A. S., Stenberg R. M. Regulated expression of the human cytomegalovirus pp65 gene: octamer sequence in the promoter is required for activation by viral gene products. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1232–1238. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1232-1238.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudding L., Haskill S., Clark B. D., Auron P. E., Sporn S., Huang E. S. Cytomegalovirus infection stimulates expression of monocyte-associated mediator genes. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3343–3352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermiston T. W., Malone C. L., Stinski M. F. Human cytomegalovirus immediate-early two protein region involved in negative regulation of the major immediate-early promoter. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3532–3536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3532-3536.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermiston T. W., Malone C. L., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Identification and characterization of the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 gene that stimulates gene expression from an inducible promoter. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3214–3221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3214-3221.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson G. M., Molloy G. R., Benfield P. A. Identification of cis-acting regulatory elements in the promoter region of the rat brain creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6533–6543. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horlick R. A., Hobson G. M., Patterson J. H., Mitchell M. T., Benfield P. A. Brain and muscle creatine kinase genes contain common TA-rich recognition protein-binding regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4826–4836. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C., Morimoto R. I. Conserved features of eukaryotic hsp70 genes revealed by comparison with the nucleotide sequence of human hsp70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6455–6459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Cooperation between oncogenes. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):249–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90637-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto G. K., Monick M. M., Clark B. D., Auron P. E., Stinski M. F., Hunninghake G. W. Modulation of interleukin 1 beta gene expression by the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1853–1857. doi: 10.1172/JCI114645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn G., Knust E., Schmolla H., Sarre T., Nelson J. A., McDougall J. K., Fleckenstein B. Predominant immediate-early transcripts of human cytomegalovirus AD 169. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):363–370. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.363-370.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Bankier A. T., Satchwell S. C., Preddy E., Barrell B. G. An immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus encodes a potential membrane glycoprotein. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):151–164. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90668-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Hermiston T. W., Stinski M. F. A cis-acting element in the major immediate-early (IE) promoter of human cytomegalovirus is required for negative regulation by IE2. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):897–903. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.897-903.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone C. L., Vesole D. H., Stinski M. F. Transactivation of a human cytomegalovirus early promoter by gene products from the immediate-early gene IE2 and augmentation by IE1: mutational analysis of the viral proteins. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1498–1506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1498-1506.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall G. S., Ricciardi R. P., Rando R. F., Puck J., Ge R. W., Plotkin S. A., Gönczöl E. An adenovirus recombinant that expresses the human cytomegalovirus major envelope glycoprotein and induces neutralizing antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1177–1181. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough S. H., Spector D. H. Transcription in human fibroblasts permissively infected by human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):31–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., Hayward G. S. The IE2 gene products of human cytomegalovirus specifically down-regulate expression from the major immediate-early promoter through a target sequence located near the cap site. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6154–6165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6154-6165.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., Mullen M. A., Chang Y. N., Hayward G. S. The functionally active IE2 immediate-early regulatory protein of human cytomegalovirus is an 80-kilodalton polypeptide that contains two distinct activator domains and a duplicated nuclear localization signal. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3839–3852. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3839-3852.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., O'Hare P., Sha L., LaFemina R. L., Hayward G. S. trans-activation and autoregulation of gene expression by the immediate-early region 2 gene products of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1167–1179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1167-1179.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santomenna L. D., Colberg-Poley A. M. Induction of cellular hsp70 expression by human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2033–2040. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2033-2040.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Klucher K. M., Rabert D. K., Wright D. A. Human cytomegalovirus early gene expression. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:21–45. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. J., Tevethia M. J. Identification of a human cytomegalovirus virus DNA segment that complements an adenovirus 5 immediate early mutant. Virology. 1986 Jun;151(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamminger T., Puchtler E., Fleckenstein B. Discordant expression of the immediate-early 1 and 2 gene regions of human cytomegalovirus at early times after infection involves posttranscriptional processing events. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2273–2282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2273-2282.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staprans S. I., Rabert D. K., Spector D. H. Identification of sequence requirements and trans-acting functions necessary for regulated expression of a human cytomegalovirus early gene. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3463–3473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3463-3473.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Depto A. S., Fortney J., Nelson J. A. Regulated expression of early and late RNAs and proteins from the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene region. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2699–2708. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2699-2708.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Fortney J., Barlow S. W., Magrane B. P., Nelson J. A., Ghazal P. Promoter-specific trans activation and repression by human cytomegalovirus immediate-early proteins involves common and unique protein domains. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1556–1565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1556-1565.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Stinski M. F. Autoregulation of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early gene. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):676–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.676-682.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Structural analysis of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.190-199.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Multiple spliced and unspliced transcripts from human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 and evidence for a common initiation site within immediate-early region 1. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):665–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.665-675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goldstein L. C. Organization and expression of the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):1–14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.1-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenney D. J., Colberg-Poley A. M. Expression of the human cytomegalovirus UL36-38 immediate early region during permissive infection. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):199–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90663-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenney D. J., Colberg-Poley A. M. Human cytomegalovirus UL36-38 and US3 immediate-early genes: temporally regulated expression of nuclear, cytoplasmic, and polysome-associated transcripts during infection. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6724–6734. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6724-6734.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenney D. J., Colberg-Poley A. M. RNA analysis and isolation of cDNAs derived from the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region at 0.24 map units. Intervirology. 1990;31(2-4):203–214. doi: 10.1159/000150155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia M. J., Spector D. J., Leisure K. M., Stinski M. F. Participation of two human cytomegalovirus immediate early gene regions in transcriptional activation of adenovirus promoters. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):276–285. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Stinski M. F. Temporal patterns of human cytomegalovirus transcription: mapping the viral RNAs synthesized at immediate early, early, and late times after infection. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):462–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.462-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K. An enhancer element in the short unique region of human cytomegalovirus regulates the production of a group of abundant immediate early transcripts. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):406–416. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90481-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson G. W., Akrigg A., Greenaway P. J. Transcription of the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virus Res. 1984;1(2):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B., Hunt C., Morimoto R. Structure and expression of the human gene encoding major heat shock protein HSP70. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):330–341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




