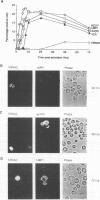
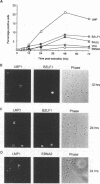
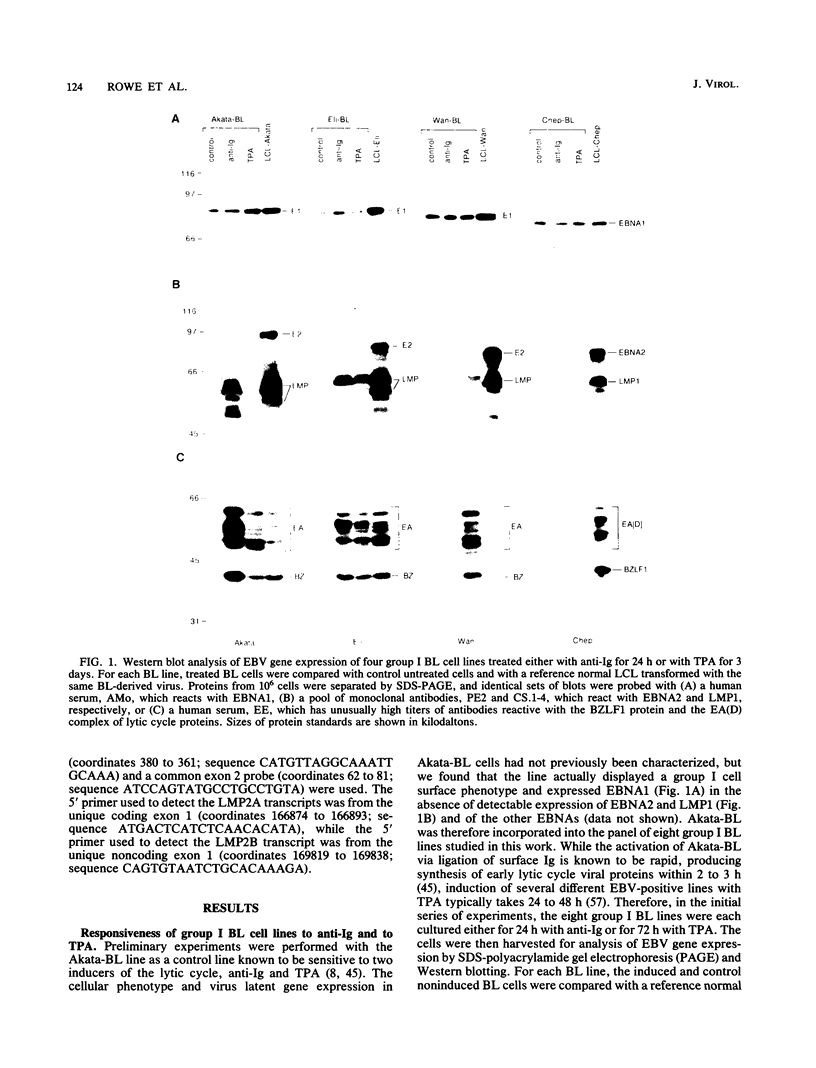
Abstract
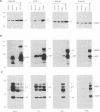
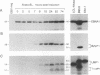
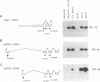
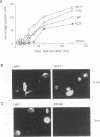
Previous studies on Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive B-cell lines have identified two distinct forms of virus latency. Lymphoblastoid cell lines generated by virus-induced transformation of normal B cells in vitro, express the full spectrum of six EBNAs and three latent membrane proteins (LMP1, LMP2A, and LMP2B); furthermore, these lines often contain a small fraction of cells spontaneously entering the lytic cycle. In contrast, Burkitt's lymphoma-derived cell lines retaining the tumor biopsy cell phenotype express only one of the latent proteins, the nuclear antigen EBNA1; such cells do not enter the lytic cycle spontaneously but may be induced to do so by treatment with such agents as tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate and anti-immunoglobulin. The present study set out to determine whether activation of full virus latent-gene expression was a necessary accompaniment to induction of the lytic cycle in Burkitt's lymphoma lines. Detailed analysis of Burkitt's lymphoma lines responding to anti-immunoglobulin treatment revealed three response pathways of EBV gene activation from EBNA1-positive latency. A first, rapid response pathway involves direct entry of cells into the lytic cycle without broadening of the pattern of latent gene expression; thereafter, the three "latent" LMPs are expressed as early lytic cycle antigens. A second, delayed response pathway in another cell subpopulation involves the activation of full latent gene expression and conversion to a lymphoblastoidlike cell phenotype. A third response pathway in yet another subpopulation involves the selective activation of LMPs, with no induction of the lytic cycle and with EBNA expression still restricted to EBNA1; this type of latent infection in B lymphocytes has hitherto not been described. Interestingly, the EBNA1+ LMP+ cells displayed some but not all of the phenotypic changes normally induced by LMP1 expression in a B-cell environment. These studies highlight the existence of four different types of EBV infection in B cells, including three distinct forms of latency, which we now term latency I, latency II, and latency III.
Full text
PDF


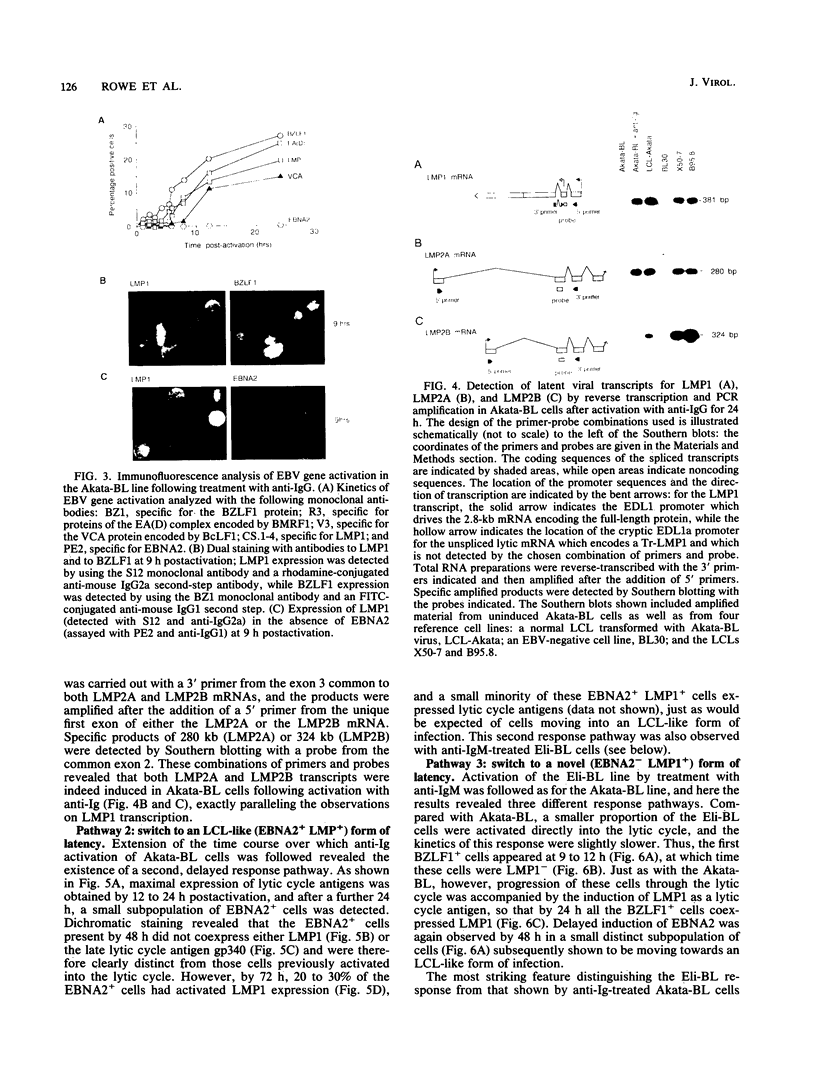
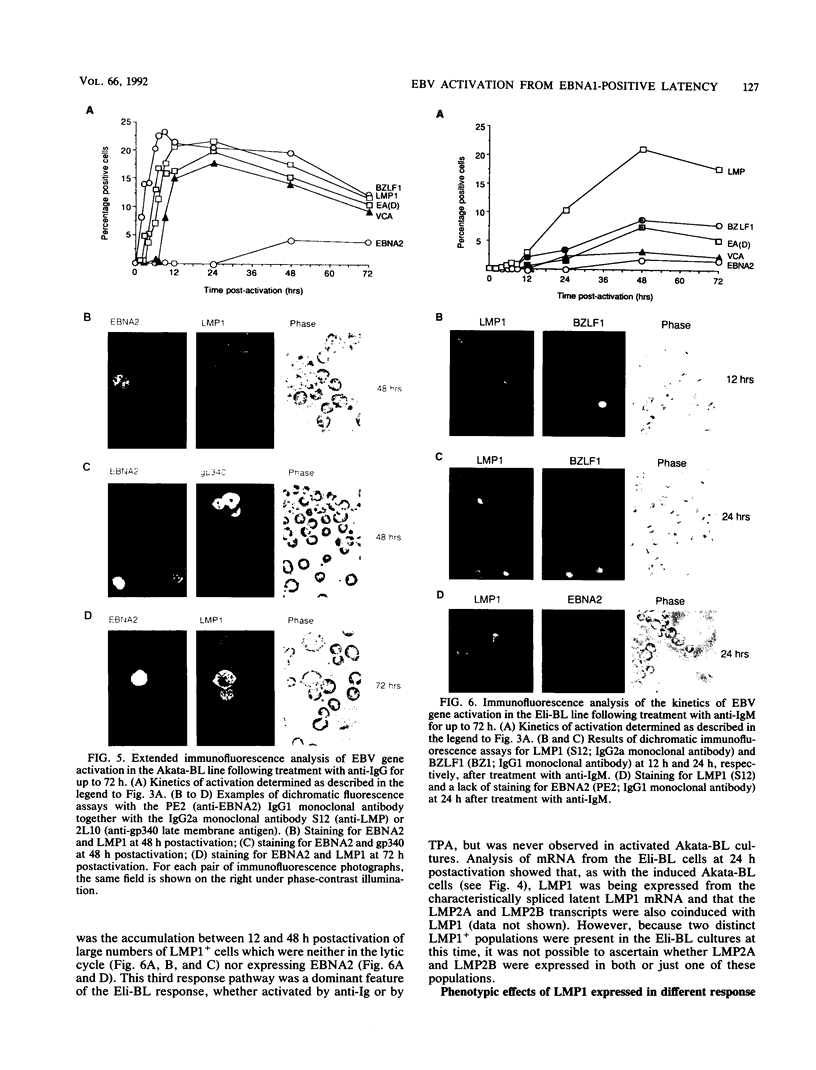
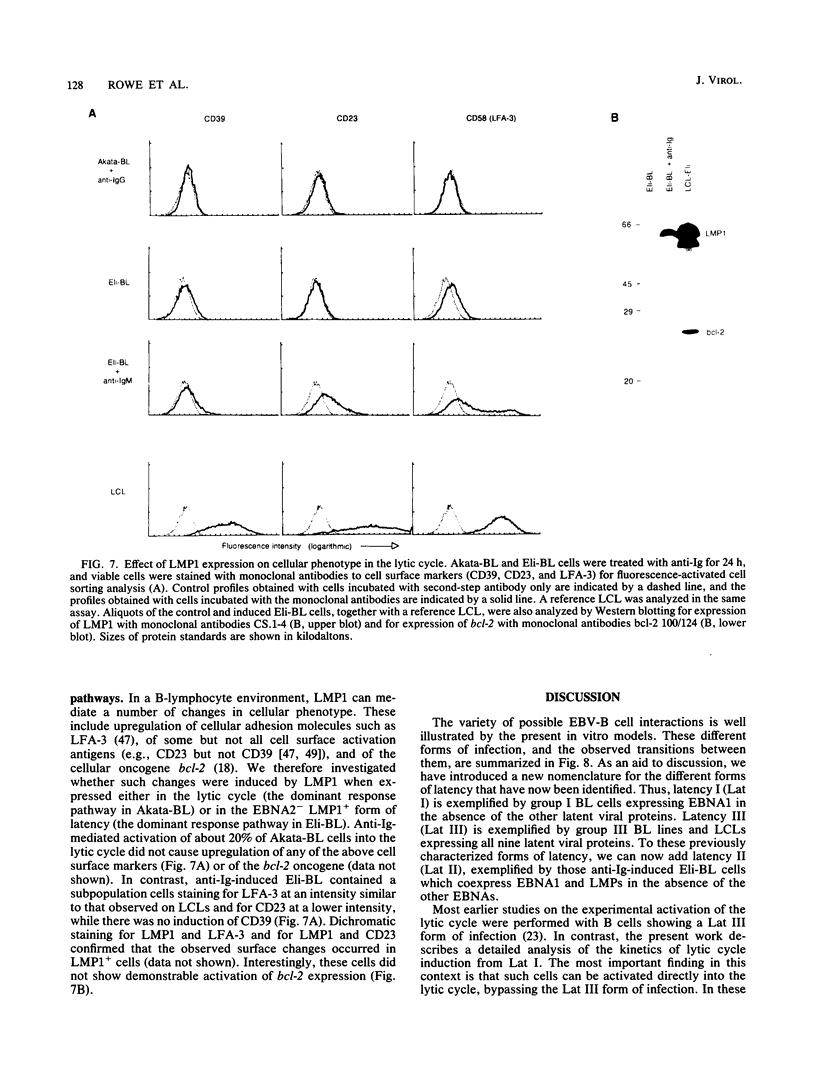
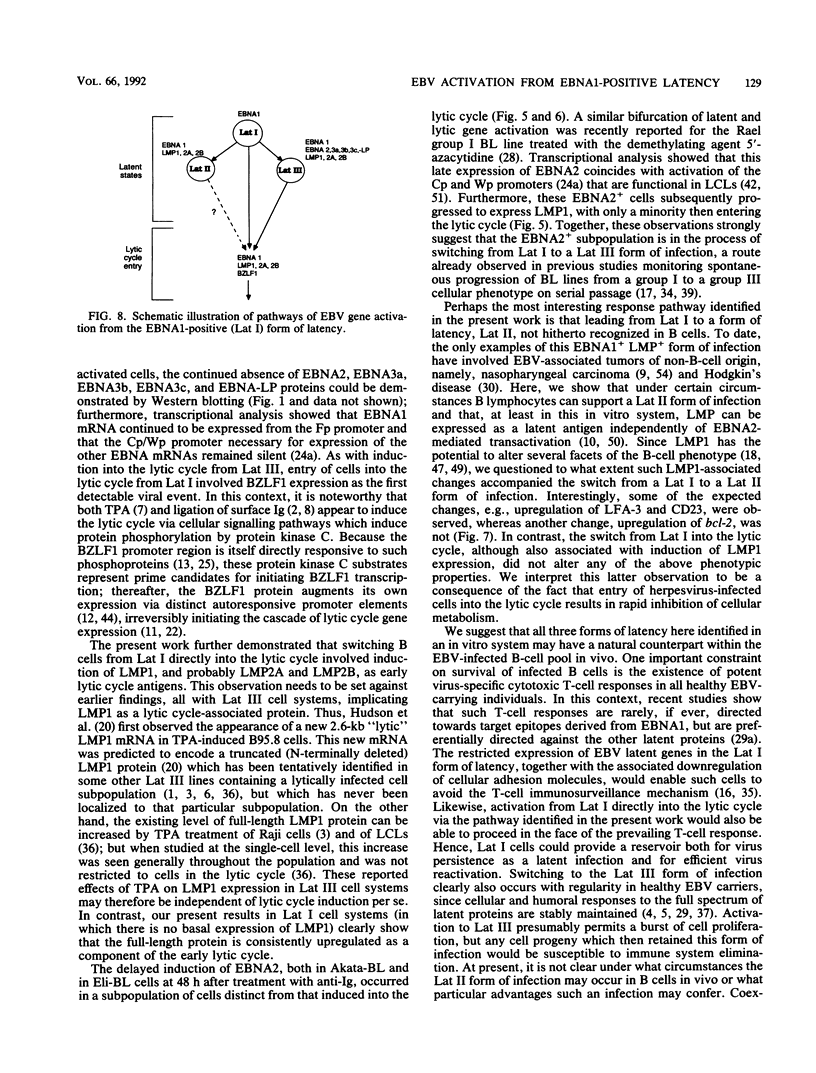


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baichwal V. R., Sugden B. Posttranslational processing of an Epstein-Barr virus-encoded membrane protein expressed in cells transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):866–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.866-875.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boos H., Berger R., Kuklik-Roos C., Iftner T., Mueller-Lantzsch N. Enhancement of Epstein-Barr virus membrane protein (LMP) expression by serum, TPA, or n-butyrate in latently infected Raji cells. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):161–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90360-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows S. R., Misko I. S., Sculley T. B., Schmidt C., Moss D. J. An Epstein-Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T-cell epitope present on A- and B-type transformants. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3974–3976. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3974-3976.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows S. R., Sculley T. B., Misko I. S., Schmidt C., Moss D. J. An Epstein-Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T cell epitope in EBV nuclear antigen 3 (EBNA 3). J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):345–349. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras-Salazar B., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Klein G., Masucci M. G. Up regulation of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded membrane protein LMP in the Burkitt's lymphoma line Daudi after exposure to n-butyrate and after EBV superinfection. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5441–5447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5441-5447.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daibata M., Humphreys R. E., Takada K., Sairenji T. Activation of latent EBV via anti-IgG-triggered, second messenger pathways in the Burkitt's lymphoma cell line Akata. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4788–4793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. H., Grand R. J., Evans F. J., Rickinson A. B. Induction of Epstein-Barr virus lytic cycle by tumor-promoting and non-tumor-promoting phorbol esters requires active protein kinase C. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6838–6844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6838-6844.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Rowe D. T., Rooney C. M., Kouzarides T. Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 trans-activator specifically binds to a consensus AP-1 site and is related to c-fos. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):127–132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Speck S. H. Autoregulation of Epstein-Barr virus putative lytic switch gene BZLF1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1227–1232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1227-1232.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Speck S. H. Identification of phorbol ester response elements in the promoter of Epstein-Barr virus putative lytic switch gene BZLF1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1217–1226. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1217-1226.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frech B., Zimber-Strobl U., Suentzenich K. O., Pavlish O., Lenoir G. M., Bornkamm G. W., Mueller-Lantzsch N. Identification of Epstein-Barr virus terminal protein 1 (TP1) in extracts of four lymphoid cell lines, expression in insect cells, and detection of antibodies in human sera. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2759–2767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2759-2767.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fåhraeus R., Fu H. L., Ernberg I., Finke J., Rowe M., Klein G., Falk K., Nilsson E., Yadav M., Busson P. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded proteins in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1988 Sep 15;42(3):329–338. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fåhraeus R., Jansson A., Ricksten A., Sjöblom A., Rymo L. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen 2 activates the viral latent membrane protein promoter by modulating the activity of a negative regulatory element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7390–7394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratama J. W., Oosterveer M. A., Zwaan F. E., Lepoutre J., Klein G., Ernberg I. Eradication of Epstein-Barr virus by allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: implications for sites of viral latency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8693–8696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory C. D., Murray R. J., Edwards C. F., Rickinson A. B. Downregulation of cell adhesion molecules LFA-3 and ICAM-1 in Epstein-Barr virus-positive Burkitt's lymphoma underlies tumor cell escape from virus-specific T cell surveillance. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1811–1824. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B. Different Epstein-Barr virus-B cell interactions in phenotypically distinct clones of a Burkitt's lymphoma cell line. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jul;71(Pt 7):1481–1495. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-7-1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Rowe M., Gregory C., Croom-Carter D., Wang F., Longnecker R., Kieff E., Rickinson A. Induction of bcl-2 expression by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 protects infected B cells from programmed cell death. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1107–1115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90007-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman G. J., Lazarowitz S. G., Hayward S. D. Monoclonal antibody against a 250,000-dalton glycoprotein of Epstein-Barr virus identifies a membrane antigen and a neutralizing antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2979–2983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson G. S., Farrell P. J., Barrell B. G. Two related but differentially expressed potential membrane proteins encoded by the EcoRI Dhet region of Epstein-Barr virus B95-8. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):528–535. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.528-535.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. A., Blomfield P. I., Bevan I. S., Woodman C. B., Young L. S. Analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 E6-E7 transcription in cervical carcinomas and normal cervical epithelium using the polymerase chain reaction. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jul;71(Pt 7):1473–1479. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-7-1473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Holley-Guthrie E., Mar E. C., Smith M. The Epstein-Barr virus BMLF1 promoter contains an enhancer element that is responsive to the BZLF1 and BRLF1 transactivators. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3878–3883. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3878-3883.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A spliced Epstein-Barr virus gene expressed in immortalized lymphocytes is created by circularization of the linear viral genome. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):769–774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Hardwick J. M., Sample J., Hayward G. S., Hayward S. D. The zta transactivator involved in induction of lytic cycle gene expression in Epstein-Barr virus-infected lymphocytes binds to both AP-1 and ZRE sites in target promoter and enhancer regions. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1143–1155. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1143-1155.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Kieff E. A second Epstein-Barr virus membrane protein (LMP2) is expressed in latent infection and colocalizes with LMP1. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2319–2326. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2319-2326.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. P., Staunton D., Thorley-Lawson D. A. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded protein found in plasma membranes of transformed cells. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):710–720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.710-720.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masucci M. G., Contreras-Salazar B., Ragnar E., Falk K., Minarovits J., Ernberg I., Klein G. 5-Azacytidine up regulates the expression of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA-2) through EBNA-6 and latent membrane protein in the Burkitt's lymphoma line rael. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3135–3141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3135-3141.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. J., Kurilla M. G., Griffin H. M., Brooks J. M., Mackett M., Arrand J. R., Rowe M., Burrows S. R., Moss D. J., Kieff E. Human cytotoxic T-cell responses against Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens demonstrated by using recombinant vaccinia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2906–2910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., Vroman B., Chase B., Sculley T., Hummel M., Kieff E. Identification of polypeptide components of the Epstein-Barr virus early antigen complex with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):193–201. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.193-201.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella F., Tse A. G., Cordell J. L., Pulford K. A., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. Expression of the bcl-2 oncogene protein is not specific for the 14;18 chromosomal translocation. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):225–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qualtiere L. F., Chase R., Vroman B., Pearson G. R. Identification of Epstein-Barr virus strain differences with monoclonal antibody to a membrane glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):616–620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C. M., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Finerty S., Edwards C., Rupani H., Rickinson A. B. Endemic Burkitt's lymphoma: phenotypic analysis of tumor biopsy cells and of derived tumor cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Sep;77(3):681–687. doi: 10.1093/jnci/77.3.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Rowe M., Evan G. I., Wallace L. E., Farrell P. J., Rickinson A. B. Restricted expression of EBV latent genes and T-lymphocyte-detected membrane antigen in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2599–2607. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Evans H. S., Young L. S., Hennessy K., Kieff E., Rickinson A. B. Monoclonal antibodies to the latent membrane protein of Epstein-Barr virus reveal heterogeneity of the protein and inducible expression in virus-transformed cells. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jun;68(Pt 6):1575–1586. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-6-1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Finke J., Szigeti R., Klein G. Characterization of the serological response in man to the latent membrane protein and the six nuclear antigens encoded by Epstein-Barr virus. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jun;69(Pt 6):1217–1228. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-6-1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Hildreth J. E., Rickinson A. B., Epstein M. A. Monoclonal antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus-induced, transformation-associated cell surface antigens: binding patterns and effect upon virus-specific T-cell cytotoxicity. Int J Cancer. 1982 Apr 15;29(4):373–381. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910290403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Rowe D. T., Gregory C. D., Young L. S., Farrell P. J., Rupani H., Rickinson A. B. Differences in B cell growth phenotype reflect novel patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2743–2751. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Young L. S., Cadwallader K., Petti L., Kieff E., Rickinson A. B. Distinction between Epstein-Barr virus type A (EBNA 2A) and type B (EBNA 2B) isolates extends to the EBNA 3 family of nuclear proteins. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1031–1039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1031-1039.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Young L. S., Crocker J., Stokes H., Henderson S., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated lymphoproliferative disease in the SCID mouse model: implications for the pathogenesis of EBV-positive lymphomas in man. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):147–158. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Brooks L., Sample C., Young L., Rowe M., Gregory C., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Restricted Epstein-Barr virus protein expression in Burkitt lymphoma is due to a different Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6343–6347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Madrid F., Krensky A. M., Ware C. F., Robbins E., Strominger J. L., Burakoff S. J., Springer T. A. Three distinct antigens associated with human T-lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis: LFA-1, LFA-2, and LFA-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7489–7493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair A. J., Brimmell M., Shanahan F., Farrell P. J. Pathways of activation of the Epstein-Barr virus productive cycle. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2237–2244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2237-2244.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Ono Y. Synchronous and sequential activation of latently infected Epstein-Barr virus genomes. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):445–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.445-449.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vroman B., Luka J., Rodriguez M., Pearson G. R. Characterization of a major protein with a molecular weight of 160,000 associated with the viral capsid of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.107-113.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Wang F., Gregory C., Rickinson A., Larson R., Springer T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein alters the human B-lymphocyte phenotype: deletion of the amino terminus abolishes activity. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4173–4184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4173-4184.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C., Sample C., Rowe M., Liebowitz D., Murray R., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein (LMP1) and nuclear proteins 2 and 3C are effectors of phenotypic changes in B lymphocytes: EBNA-2 and LMP1 cooperatively induce CD23. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2309–2318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2309-2318.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Tsang S. F., Kurilla M. G., Cohen J. I., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 transactivates latent membrane protein LMP1. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3407–3416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3407-3416.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisetschlaeger M., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Mutually exclusive use of viral promoters in Epstein-Barr virus latently infected lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6498–6502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Q. Y., Ogan P., Rowe M., Wood M., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells persist in the circulation of acyclovir-treated virus carriers. Int J Cancer. 1989 Jan 15;43(1):67–71. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Dawson C. W., Clark D., Rupani H., Busson P., Tursz T., Johnson A., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Gen Virol. 1988 May;69(Pt 5):1051–1065. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-5-1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Lau R., Rowe M., Niedobitek G., Packham G., Shanahan F., Rowe D. T., Greenspan D., Greenspan J. S., Rickinson A. B. Differentiation-associated expression of the Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 transactivator protein in oral hairy leukoplakia. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2868–2874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2868-2874.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L., Alfieri C., Hennessy K., Evans H., O'Hara C., Anderson K. C., Ritz J., Shapiro R. S., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus transformation-associated genes in tissues of patients with EBV lymphoproliferative disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 19;321(16):1080–1085. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910193211604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimber-Strobl U., Suentzenich K. O., Laux G., Eick D., Cordier M., Calender A., Billaud M., Lenoir G. M., Bornkamm G. W. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 activates transcription of the terminal protein gene. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):415–423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.415-423.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., O'Neill F. J., Freese U. K., Hecker E. Persisting oncogenic herpesvirus induced by the tumour promotor TPA. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):373–375. doi: 10.1038/272373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]