Abstract
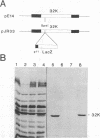
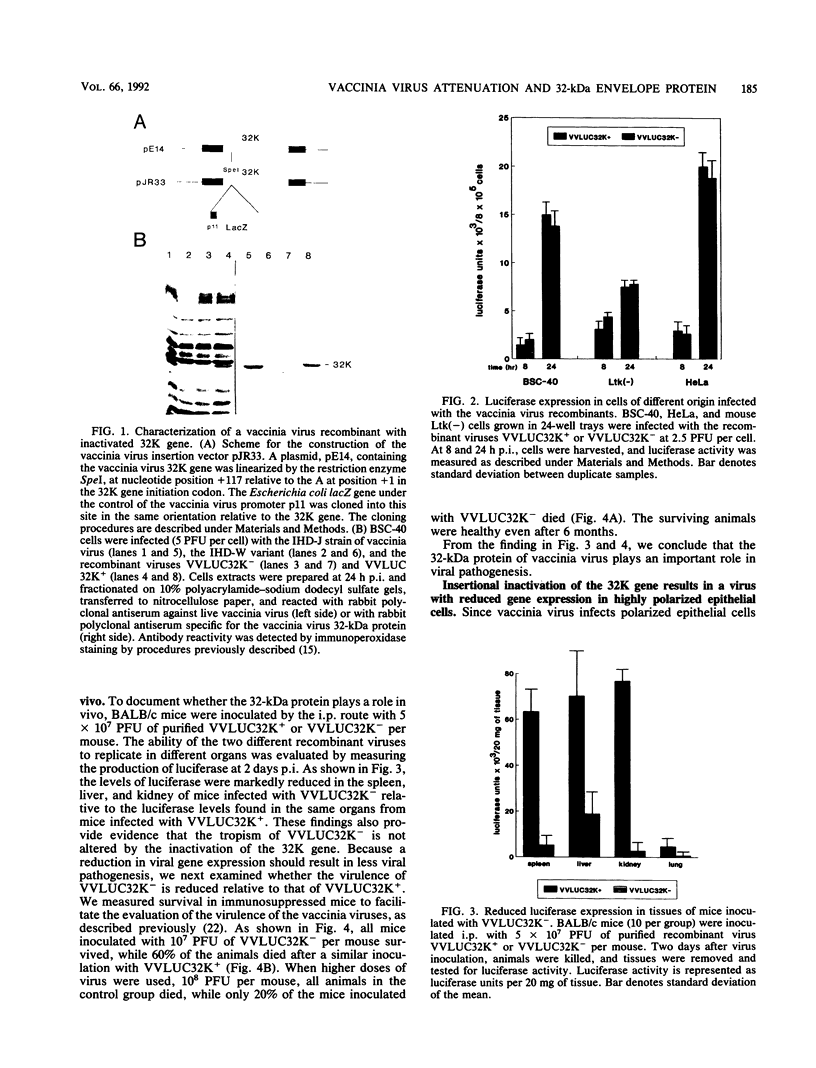
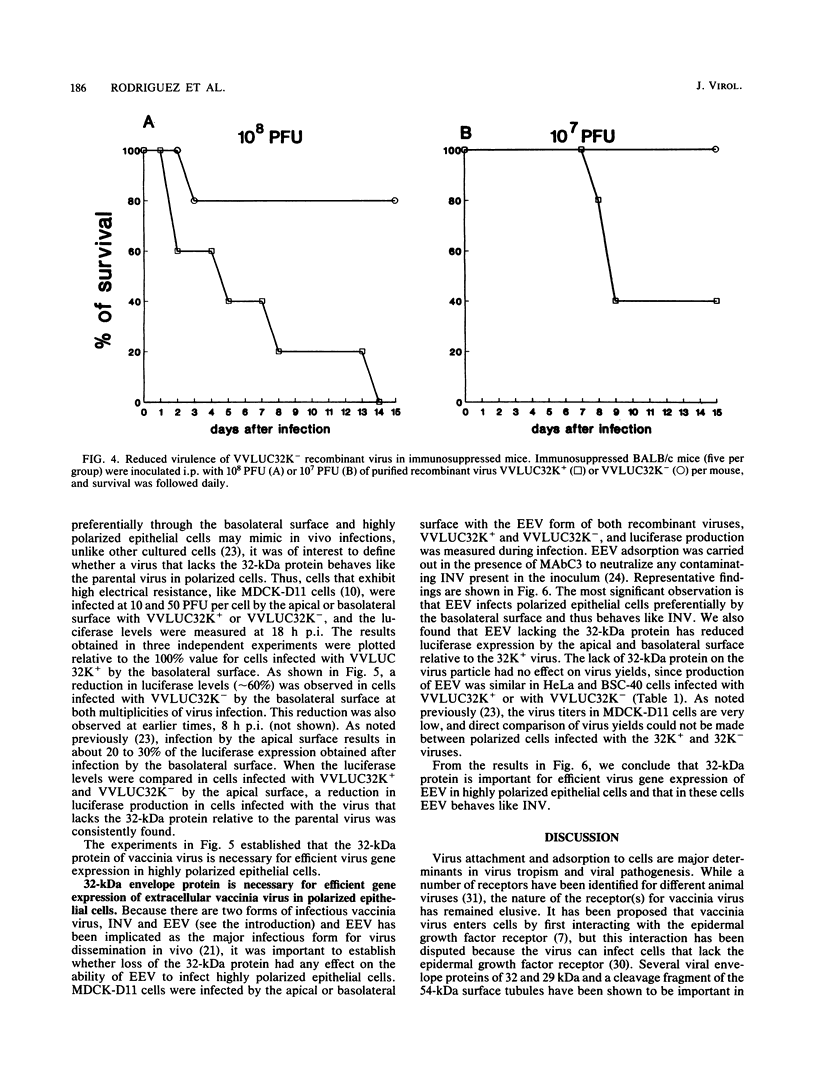
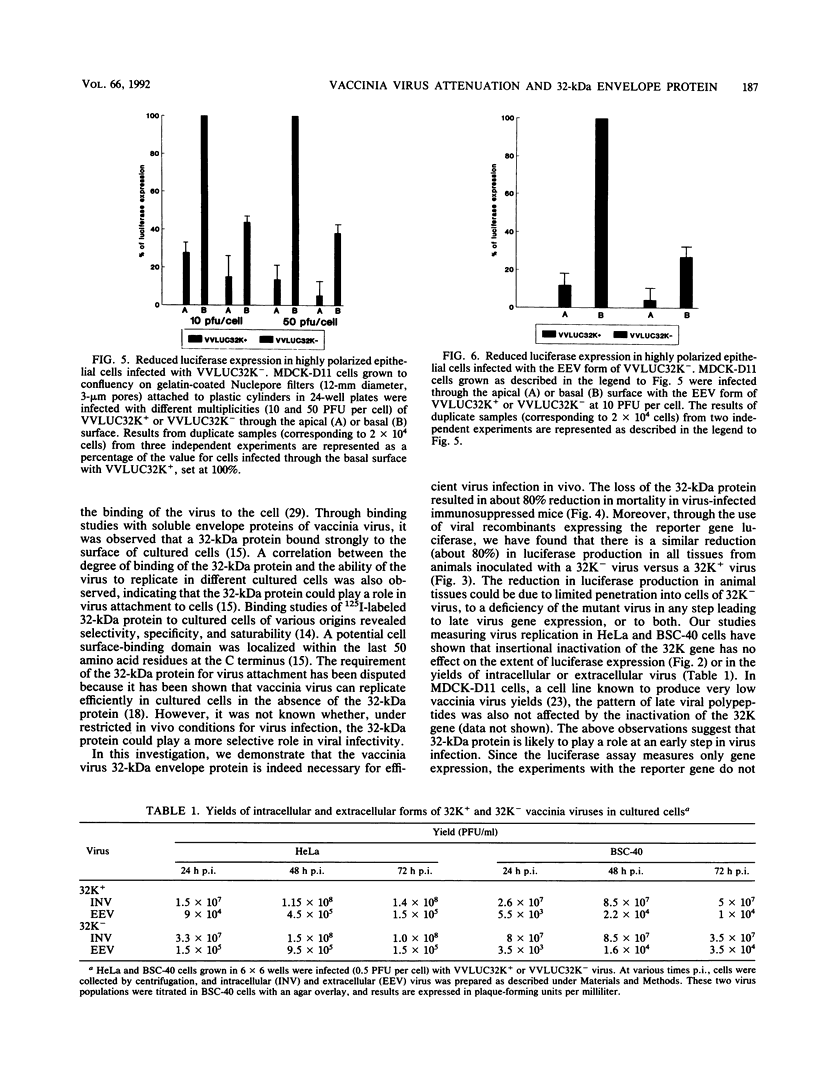
The mechanism of poxvirus attachment to cells is poorly understood. We have identified a 32-kDa envelope protein of vaccinia virus which binds to the surface of cultured cells. This binding is specific and selective (J.-S. Maa, J. F. Rodriguez, and M. Esteban, J. Biol. Chem. 265:22174-22180, 1990; C. Lai, S. Gong, and M. Esteban, J. Virol. 65:499-504, 1991). In this investigation, we studied the effect of inactivating the 32-kDa gene (32K gene) on the biology of vaccinia virus. We show that inactivation of the 32K gene decreases by 80% the mortality of mice infected with 32K- vaccinia virus. This reduction in mortality correlates with diminished viral gene expression in target tissues. In highly polarized epithelial cells, viral gene expression of 32K- virus was reduced (50 to 60%) at both the apical and basolateral surfaces in comparison with a 32K+ virus. Restriction of virus gene expression in polarized cell surfaces occurs for both intracellular and extracellular forms of infectious 32K- vaccinia virus. The two infectious forms of vaccinia virus 32K+ infect polarized cells preferentially by the basolateral surface. Our findings provide evidence of the importance of the 32-kDa protein in viral pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buller R. M., Chakrabarti S., Cooper J. A., Twardzik D. R., Moss B. Deletion of the vaccinia virus growth factor gene reduces virus virulence. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):866–874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.866-874.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. M., Smith G. L., Cremer K., Notkins A. L., Moss B. Decreased virulence of recombinant vaccinia virus expression vectors is associated with a thymidine kinase-negative phenotype. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):813–815. doi: 10.1038/317813a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Brechling K., Moss B. Vaccinia virus expression vector: coexpression of beta-galactosidase provides visual screening of recombinant virus plaques. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3403–3409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Child S. J., Palumbo G. J., Buller R. M., Hruby D. E. Insertional inactivation of the large subunit of ribonucleotide reductase encoded by vaccinia virus is associated with reduced virulence in vivo. Virology. 1990 Feb;174(2):625–629. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90119-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Blumenthal R., Moss B. Fusion of intra- and extracellular forms of vaccinia virus with the cell membrane. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4884–4892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4884-4892.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flexner C., Hügin A., Moss B. Prevention of vaccinia virus infection in immunodeficient mice by vector-directed IL-2 expression. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):259–262. doi: 10.1038/330259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel S. J., Johnson G. P., Perkus M. E., Davis S. W., Winslow J. P., Paoletti E. The complete DNA sequence of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):247-66, 517-63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz R. E., Ojakian G. K. Differential targeting of an epithelial plasma membrane glycoprotein in polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4605–4612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihashi Y., Oie M. Adsorption and penetration of the trypsinized vaccinia virion. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):50–60. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90482-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K. The preparation and characteristics of highly purified radioactively labelled poxvirus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 20;61:290–301. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotwal G. J., Hügin A. W., Moss B. Mapping and insertional mutagenesis of a vaccinia virus gene encoding a 13,800-Da secreted protein. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90627-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. F., Gong S. C., Esteban M. The 32-kilodalton envelope protein of vaccinia virus synthesized in Escherichia coli binds with specificity to cell surfaces. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):499–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.499-504.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maa J. S., Rodriguez J. F., Esteban M. Structural and functional characterization of a cell surface binding protein of vaccinia virus. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1569–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Flexner C. Vaccinia virus expression vectors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:305–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles E. G., Seto J. Vaccinia virus gene D8 encodes a virion transmembrane protein. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3772–3778. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3772-3778.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panicali D., Paoletti E. Construction of poxviruses as cloning vectors: insertion of the thymidine kinase gene from herpes simplex virus into the DNA of infectious vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne L. G. Identification of the vaccinia hemagglutinin polypeptide from a cell system yielding large amounts of extracellular enveloped virus. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):147–155. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.147-155.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne L. G. Significance of extracellular enveloped virus in the in vitro and in vivo dissemination of vaccinia. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):89–100. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez D., Rodriguez J. R., Ojakian G. K., Esteban M. Vaccinia virus preferentially enters polarized epithelial cells through the basolateral surface. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):494–498. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.494-498.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez D., Rodriguez J. R., Rodriguez J. F., Trauber D., Esteban M. Highly attenuated vaccinia virus mutants for the generation of safe recombinant viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1287–1291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Janeczko R., Esteban M. Isolation and characterization of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):482–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.482-488.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Paez E., Esteban M. A 14,000-Mr envelope protein of vaccinia virus is involved in cell fusion and forms covalently linked trimers. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):395–404. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.395-404.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Rodriguez D., Rodriguez J. R., McGowan E. B., Esteban M. Expression of the firefly luciferase gene in vaccinia virus: a highly sensitive gene marker to follow virus dissemination in tissues of infected animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1667–1671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Smith G. L. Inducible gene expression from vaccinia virus vectors. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):239–250. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90477-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shida H., Hinuma Y., Hatanaka M., Morita M., Kidokoro M., Suzuki K., Maruyama T., Takahashi-Nishimaki F., Sugimoto M., Kitamura R. Effects and virulences of recombinant vaccinia viruses derived from attenuated strains that express the human T-cell leukemia virus type I envelope gene. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4474–4480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4474-4480.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern W., Dales S. Biogenesis of vaccinia: relationship of the envelope to virus assembly. Virology. 1976 Nov;75(1):242–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroobant P., Rice A. P., Gullick W. J., Cheng D. J., Kerr I. M., Waterfield M. D. Purification and characterization of vaccinia virus growth factor. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):383–393. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M., Littman D. R. Viral receptors of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):725–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90674-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]