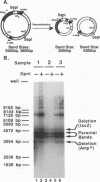
Abstract
During the course of infection, elements of the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) genome undergo inversion, a process that is believed to occur through the viral a sequences. To investigate the mechanism of this recombinational event, we have developed an assay that detects the deletion of DNA segments flanked by directly repeated a sequences in plasmids transiently maintained in Vero cells. With this assay, we have observed a high frequency of recombination (approximately 8%) in plasmids that undergo replication in HSV-1-infected cells. We also found a low level of recombination between a sequences in plasmids introduced into uninfected cells and in unreplicated plasmids in HSV-1-infected cells. In replicating plasmids, recombination between a sequences occurs at twice the frequency seen with directly repeated copies of a different sequence of similar size. Recombination between a sequences appears to occur at approximately the same time as replication, suggesting that the processes of replication and recombination are closely linked.
Full text
PDF


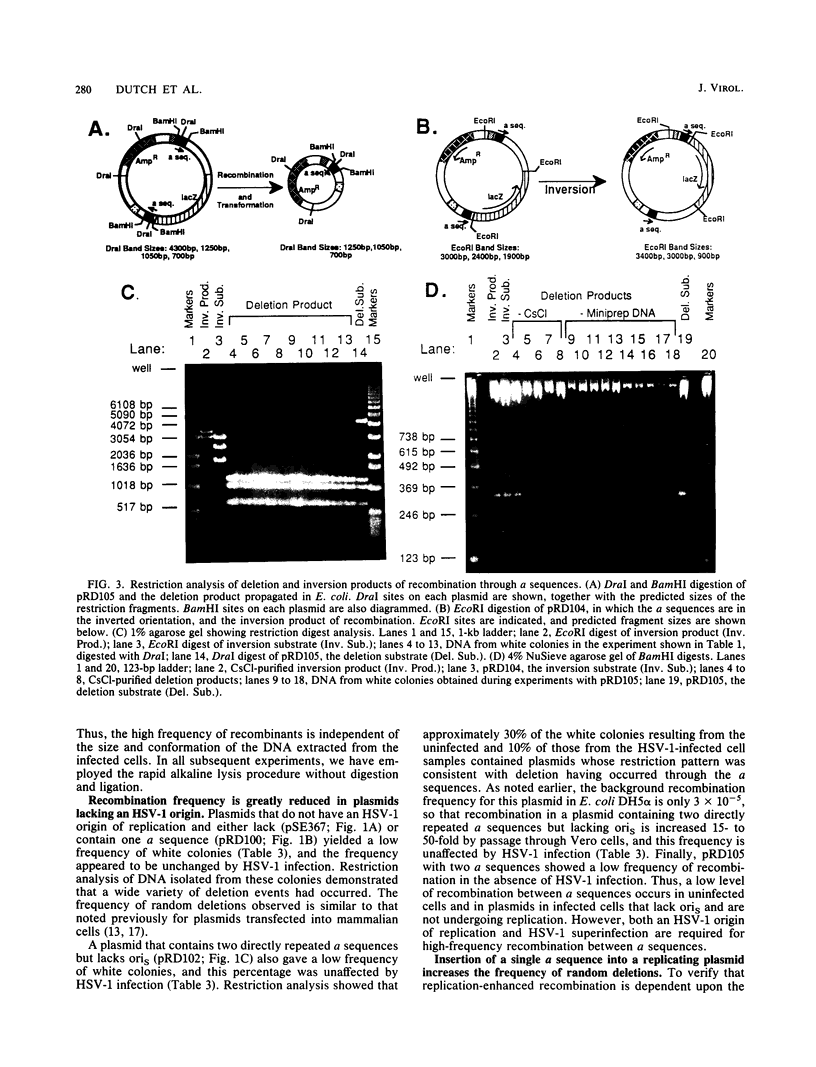
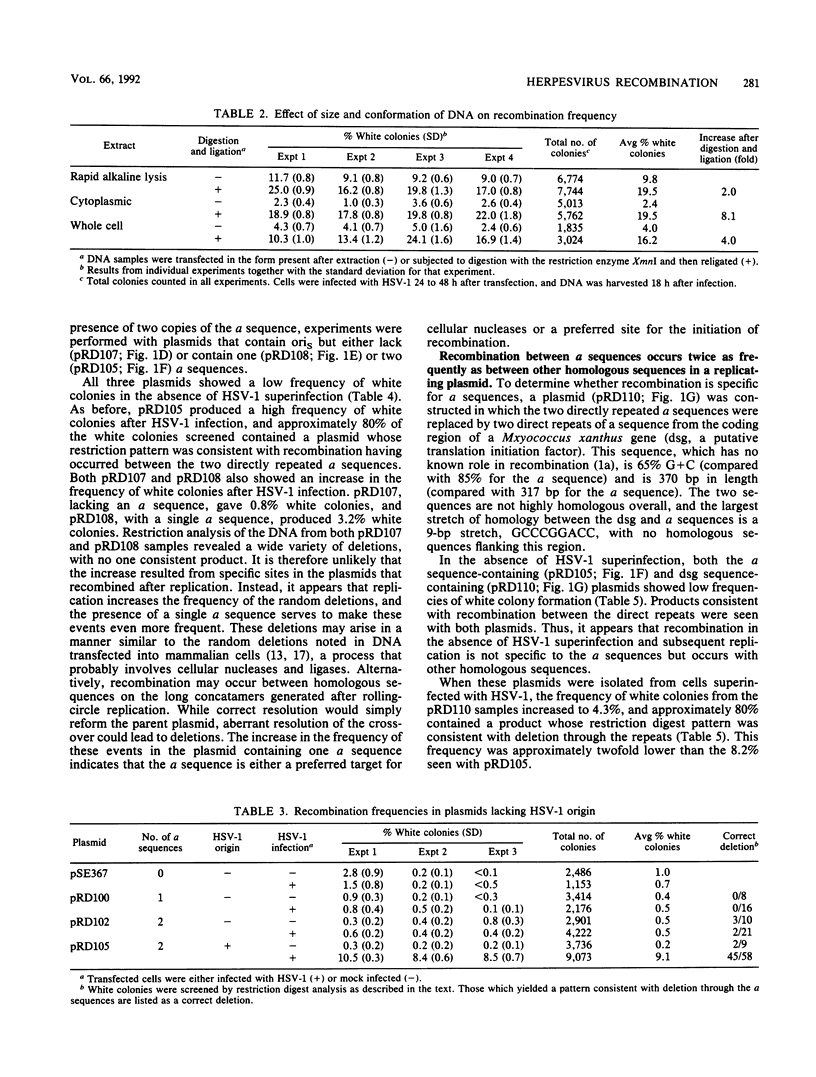
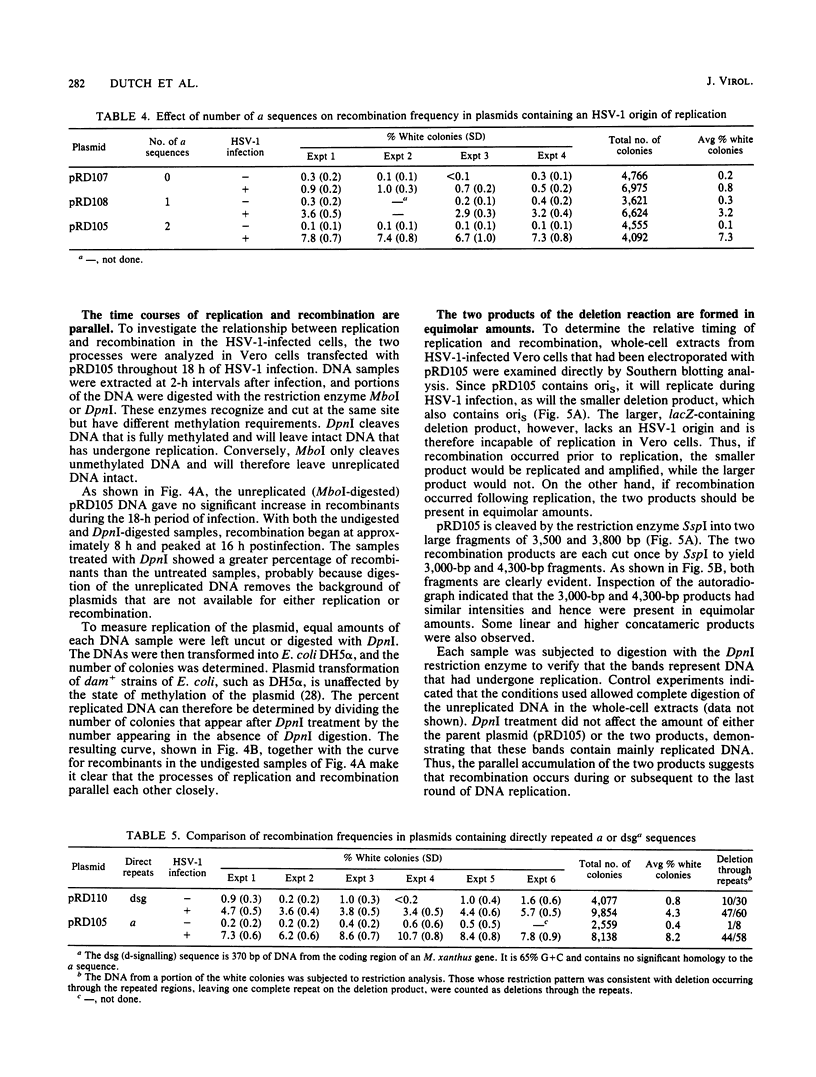


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Porat T., Tokazewski S. A. Replication of herpesvirus DNA. II. Sedimentation characteristics of newly synthesized DNA. Virology. 1977 Jun 15;79(2):292–301. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. Isomerization of herpes simplex virus 1 genome: identification of the cis-acting and recombination sites within the domain of the a sequence. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):803–811. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. The terminal a sequence of the herpes simplex virus genome contains the promoter of a gene located in the repeat sequences of the L component. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):629–637. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.629-637.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Wilkie N. M. Nucleotide sequences of the joint between the L and S segments of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Gen Virol. 1981 Aug;55(Pt 2):315–331. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius H., Clements J. B. A partial denaturation map of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA: evidence for inversions of the unique DNA regions. J Gen Virol. 1976 Oct;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-1-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S., Jacob R. J., Wadsworth S. C., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA: evidence for four populations of molecules that differ in the relative orientations of their long and short components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4243–4247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R. J., Morse L. S., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. XII. Accumulation of head-to-tail concatemers in nuclei of infected cells and their role in the generation of the four isomeric arrangements of viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):448–457. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.448-457.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins F. J., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus 1 recombinants with noninverting genomes frozen in different isomeric arrangements are capable of independent replication. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):494–499. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.494-499.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konrad E. B., Lehman I. R. A conditional lethal mutant of Escherichia coli K12 defective in the 5' leads to 3' exonuclease associated with DNA polymerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2048–2051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebkowski J. S., DuBridge R. B., Antell E. A., Greisen K. S., Calos M. P. Transfected DNA is mutated in monkey, mouse, and human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1951–1960. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Generation of an inverting herpes simplex virus 1 mutant lacking the L-S junction a sequences, an origin of DNA synthesis, and several genes including those specifying glycoprotein E and the alpha 47 gene. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):583–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.583-591.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. H., Lebkowski J. S., Greisen K. S., Calos M. P. Specificity of mutations induced in transfected DNA by mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3117–3121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02267.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Post L. E., Roizman B. Molecular engineering of the herpes simplex virus genome: insertion of a second L-S junction into the genome causes additional genome inversions. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):243–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90172-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Herpesvirus-dependent amplification and inversion of cell-associated viral thymidine kinase gene flanked by viral a sequences and linked to an origin of viral DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5626–5630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Site-specific inversion sequence of the herpes simplex virus genome: domain and structural features. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7047–7051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Structure and role of the herpes simplex virus DNA termini in inversion, circularization and generation of virion DNA. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90408-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W. Fungal recombination. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):33–58. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.33-58.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poffenberger K. L., Tabares E., Roizman B. Characterization of a viable, noninverting herpes simplex virus 1 genome derived by insertion and deletion of sequences at the junction of components L and S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2690–2694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogue-Geile K. L., Lee G. T., Spear P. G. Novel rearrangements of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences resulting from duplication of a sequence within the unique region of the L component. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):456–461. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.456-461.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogue-Geile K. L., Spear P. G. Enhanced rate of conversion or recombination of markers within a region of unique sequence in the herpes simplex virus genome. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):704–708. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.704-708.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Zinder N. D. Hemimethylation prevents DNA replication in E. coli. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1071–1079. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90173-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick P., Berthelot N. Inverted repetitions in the chromosome of herpes simplex virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):667–678. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. R., Duncan J., Howes M. Sequence requirements for DNA rearrangements induced by the terminal repeat of herpes simplex virus type 1 KOS DNA. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5036–5050. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5036-5050.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. R., Fong B. S., Leung W. C. Construction of a double-jointed herpes simplex viral DNA molecule: inverted repeats are required for segment inversion, and direct repeats promote deletions. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):345–362. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus amplicon: analyses of cis-acting replication functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):694–698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., McMonagle E. C. Characterization of the TRS/IRS origin of DNA replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmuza S. L., Smiley J. R. Signals for site-specific cleavage of HSV DNA: maturation involves two separate cleavage events at sites distal to the recognition sequences. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):793–802. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlazny D. A., Frenkel N. Replication of herpes simplex virus DNA: localization of replication recognition signals within defective virus genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Challberg M. D., Nelson N. J., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Inversion events in the HSV-1 genome are directly mediated by the viral DNA replication machinery and lack sequence specificity. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):369–381. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90200-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Recombinogenic properties of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA sequences resident in simian virus 40 minichromosomes. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):300–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.300-306.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlrab F., McLean M. J., Wells R. D. The segment inversion site of herpes simplex virus type 1 adopts a novel DNA structure. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6407–6416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wohlrab F., Wells R. D. Slight changes in conditions influence the family of non-B-DNA conformations of the herpes simplex virus type 1 DR2 repeats. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8207–8213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]