Abstract
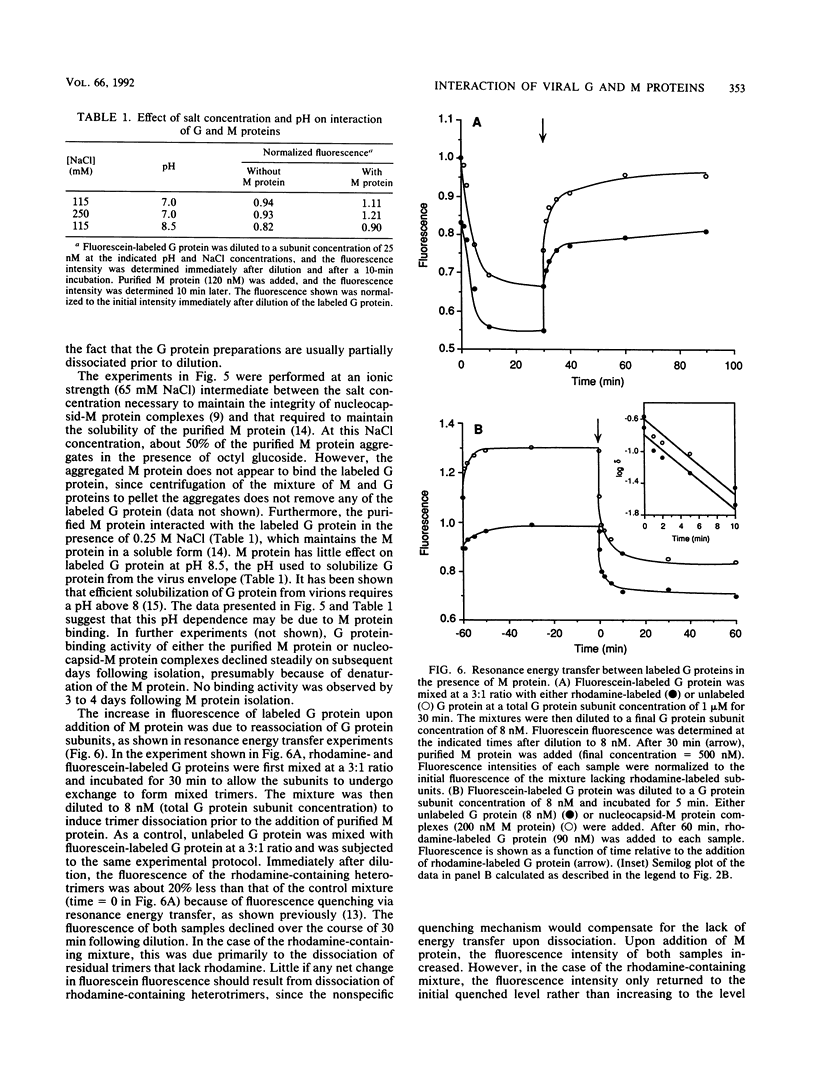
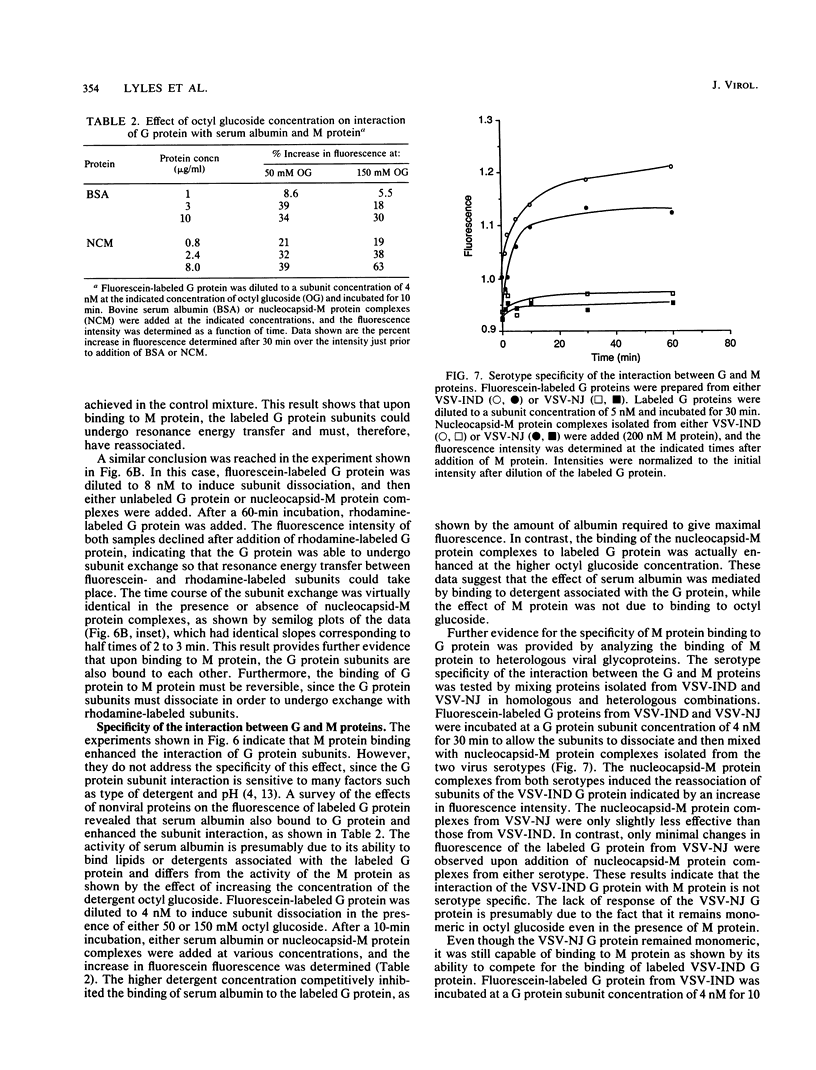
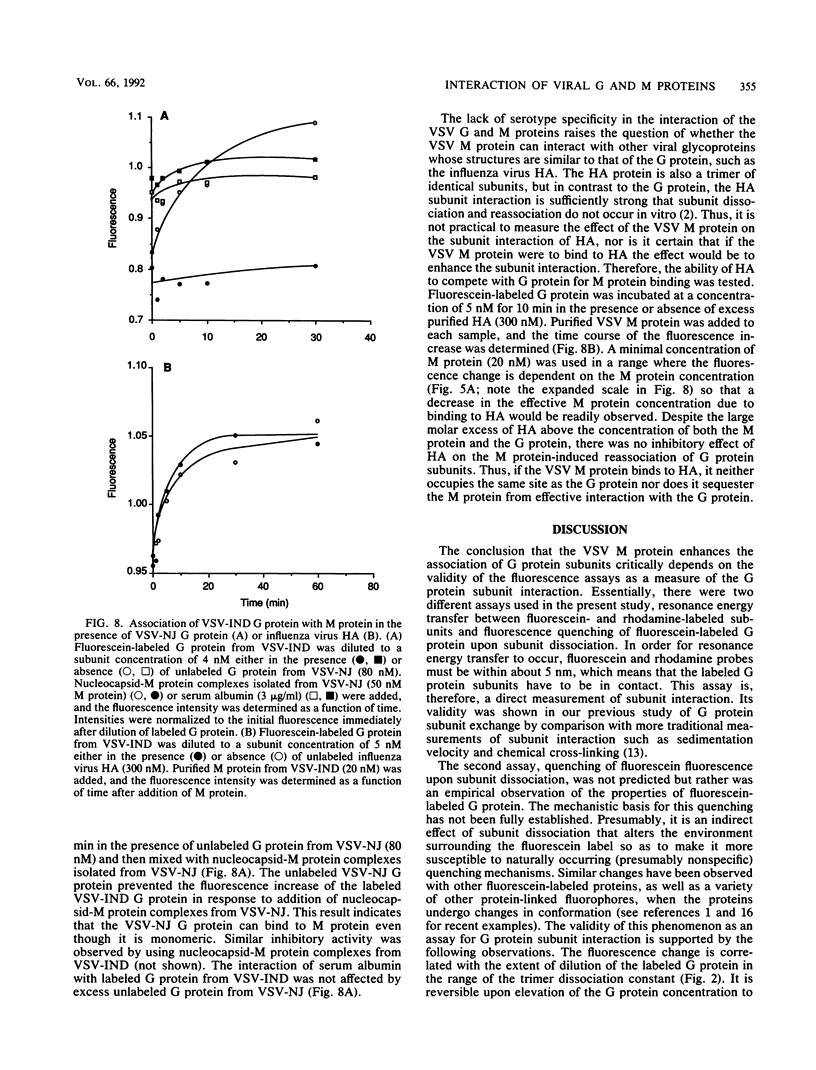
The mechanism by which viral glycoproteins are incorporated into virus envelopes during budding from host membranes is a major question of virus assembly. Evidence is presented here that the envelope glycoprotein (G protein) of vesicular stomatitis virus binds to the viral matrix protein (M protein) in vitro with the specificity, reversibility, and affinity necessary to account for virus assembly in vivo. The assay for the interaction is based on the ability of M protein to stabilize the interaction of G protein subunits, which exist as trimers of identical subunits in the virus envelope. The interaction with M protein was shown by using G proteins labeled with fluorescent probes capable of detecting subunit dissociation and reassociation in vitro. The results show that the M protein isolated from virions either as purified soluble protein or as nucleocapsid-M protein complexes interacts with the G protein in vitro and that the reaction is reversible. The interaction between the G and M proteins was not serotype specific, but no interaction between the vesicular stomatitis virus M protein and the influenza virus hemagglutinin could be detected. These results support the conclusion that the interactions described here are the ones that govern assembly of G protein into virus envelopes in vivo.
Full text
PDF
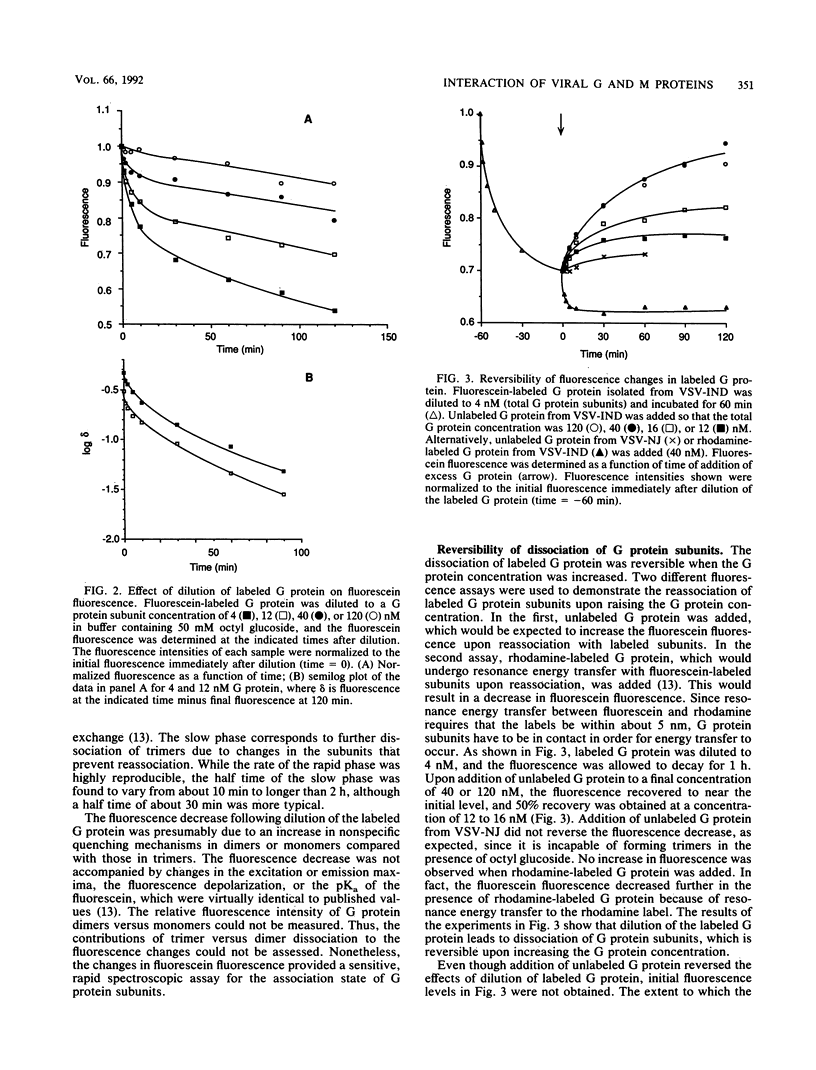
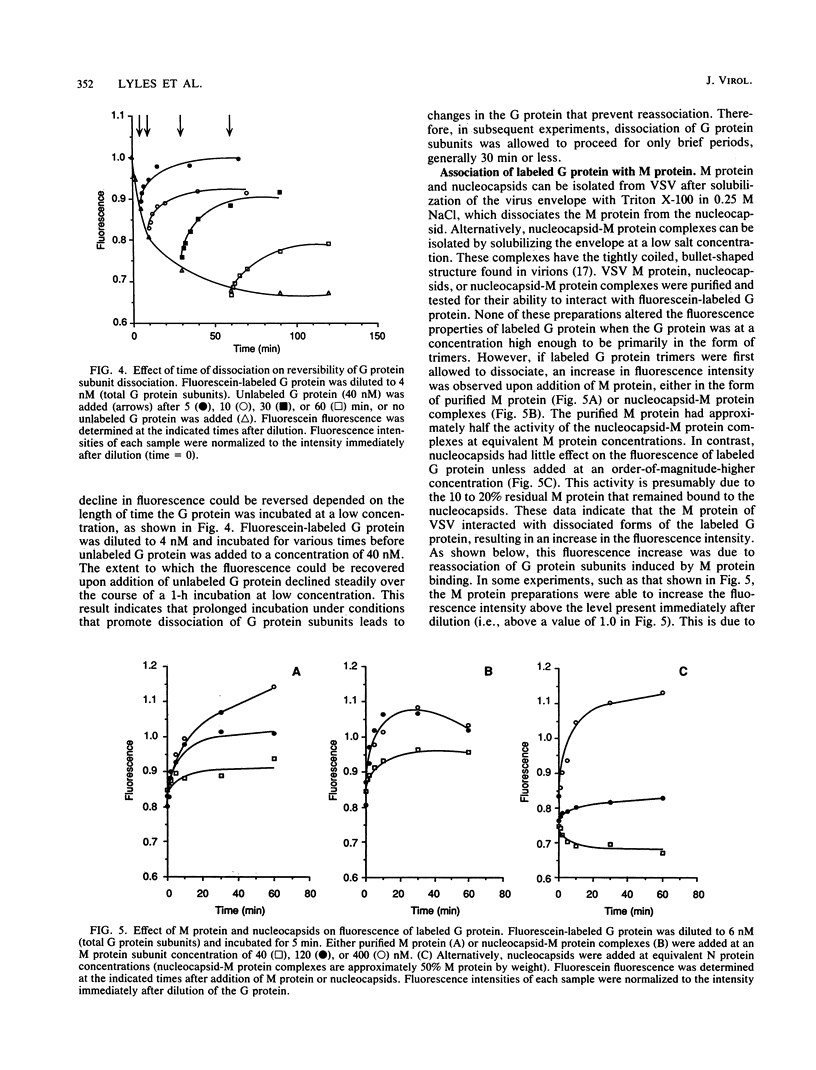



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott A. J., Amler E., Ball W. J., Jr Immunochemical and spectroscopic characterization of two fluorescein 5'-isothiocyanate labeling sites on Na+,K(+)-ATPase. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 12;30(6):1692–1701. doi: 10.1021/bi00220a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulay F., Doms R. W., Webster R. G., Helenius A. Posttranslational oligomerization and cooperative acid activation of mixed influenza hemagglutinin trimers. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):629–639. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crimmins D. L., Mehard W. B., Schlesinger S. Physical properties of a soluble form of the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus at neutral and acidic pH. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 6;22(25):5790–5796. doi: 10.1021/bi00294a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Keller D. S., Helenius A., Balch W. E. Role for adenosine triphosphate in regulating the assembly and transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein trimers. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):1957–1969. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Ruusala A., Machamer C., Helenius J., Helenius A., Rose J. K. Differential effects of mutations in three domains on folding, quaternary structure, and intracellular transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):89–99. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubovi E. J., Wagner R. R. Spatial relationships of the proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus: induction of reversible oligomers by cleavable protein cross-linkers and oxidation. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):500–509. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.500-509.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallione C. J., Rose J. K. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone encoding the entire glycoprotein from the New Jersey serotype of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):162–169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.162-169.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Kartenbeck J. The effects of octylglucoside on the Semliki forest virus membrane. Evidence for a spike-protein--nucleocapsid interaction. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(2):613–618. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04609.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaptur P. E., Rhodes R. B., Lyles D. S. Sequences of the vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein involved in binding to nucleocapsids. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1057–1065. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1057-1065.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenard J. Virus envelopes and plasma membranes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:139–165. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.001035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyles D. S., McKinnon K. P., Parce J. W. Labeling of the cytoplasmic domain of the influenza virus hemagglutinin with fluorescein reveals sites of interaction with membrane lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 31;24(27):8121–8128. doi: 10.1021/bi00348a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyles D. S., Varela V. A., Parce J. W. Dynamic nature of the quaternary structure of the vesicular stomatitis virus envelope glycoprotein. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 13;29(10):2442–2449. doi: 10.1021/bi00462a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCreedy B. J., Jr, McKinnon K. P., Lyles D. S. Solubility of vesicular stomatitis virus M protein in the cytosol of infected cells or isolated from virions. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):902–906. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.902-906.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. K., Feuer B. I., Vanderoef R., Lenard J. Reconstituted G protein-lipid vesicles from vesicular stomatitis virus and their inhibition of VSV infection. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):421–429. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller B., Restle T., Reinstein J., Goody R. S. Interaction of fluorescently labeled dideoxynucleotides with HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 16;30(15):3709–3715. doi: 10.1021/bi00229a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb W. W., Brown J. C. Role of the vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein in maintaining the viral nucleocapsid in the condensed form found in native virions. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):295–299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.295-299.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaut K. D., Birk D. E., Lenard J. Intracellular distribution of input vesicular stomatitis virus proteins after uncoating. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2622–2628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2622-2628.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens E. B., Compans R. W. Assembly of animal viruses at cellular membranes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:489–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. J., Helenius A., Mellman I. Spike--nucleocapsid interaction in Semliki Forest virus reconstructed using network antibodies. Nature. 1988 Nov 3;336(6194):36–42. doi: 10.1038/336036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitt M. A., Chong L., Rose J. K. Glycoprotein cytoplasmic domain sequences required for rescue of a vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein mutant. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3569–3578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3569-3578.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Nagai Y'Yoshii S., Maeno K., Matsumoto T. Membrane (M) protein of HVJ (Sendai virus): its role in virus assembly. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):143–161. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagouras P., Ruusala A., Rose J. K. Dissociation and reassociation of oligomeric viral glycoprotein subunits in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1976–1984. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1976-1984.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Závada J. The pseudotypic paradox. J Gen Virol. 1982 Nov;63(Pt 1):15–24. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-63-1-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



