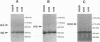Abstract
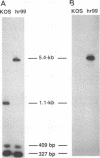
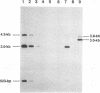
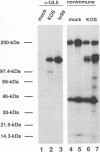
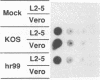
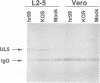
The UL5 gene product is required continuously during viral DNA synthesis (L. Zhu and S. K. Weller, Virology 166:366-378, 1988) and has been shown to be a component of a three protein helicase-primase complex encoded by herpes simplex virus type 1 (J. J. Crute, T. Tsurumi, L. Zhu, S. K. Weller, P.D. Olivo, M. D. Challberg, E. S. Mocarski, and I. R. Lehman, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:2186-2189, 1989). The other members of the complex are viral proteins encoded by genes UL8 and UL52. In this study, we isolated a permissive cell line (L2-5) which contains the wild-type UL5 gene under the control of the strong and inducible promoter for the large subunit of herpes simplex virus type 1 ribonucleotide reductase (ICP6). An insertion mutant containing a mutation in the UL5 gene (hr99) was isolated by using the insertional mutagen ICP6::lacZ, in which the Escherichia coli lacZ gene is expressed under control of the viral ICP6 promoter. When grown on Vero cells, hr99 does not form plaques or synthesize viral DNA, although both defects are complemented efficiently on the L2-5 cells. These results confirm that the UL5 gene product is essential for viral growth and DNA replication. Furthermore, since no detectable UL5 protein is synthesized in hr99-infected cells, these cells provide a valuable control not only for the detection of the UL5 protein itself but also for the detection of protein-protein interactions with UL8 and UL52 by coimmunoprecipitation. In addition, the lacZ insertion in hr99 provides a convenient screening system for the introduction of site-specific mutations into the viral genome (L. Zhu and S. K. Weller, J. Virol. 66:469-479, 1992). Thus, hr99 is a valuable tool in the structure-function analysis of the UL5 gene.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calder J. M., Stow N. D. Herpes simplex virus helicase-primase: the UL8 protein is not required for DNA-dependent ATPase and DNA helicase activities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3573–3578. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael E. P., Kosovsky M. J., Weller S. K. Isolation and characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 host range mutants defective in viral DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.91-99.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael E. P., Weller S. K. Herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA synthesis requires the product of the UL8 gene: isolation and characterization of an ICP6::lacZ insertion mutation. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):591–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.591-599.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand P., Crumpacker C. S., Schaffer P. A., Wilkie N. M. Physical and genetic analysis of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase locus. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90190-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Aschman D. P., Gelep P. T., Retondo M. J., Weller S. K., Schaffer P. A. Fine mapping and molecular cloning of mutations in the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase locus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):236–247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.236-247.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Weinheimer S. P., McKnight S. L. A genetic approach to promoter recognition during trans induction of viral gene expression. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):53–59. doi: 10.1126/science.3018926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley A. J., Knipe D. M., Jones P. C., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VII. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant produced by in vitro mutagenesis and defective in DNA synthesis and accumulation of gamma polypeptides. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):191–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.191-206.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. A DNA helicase induced by herpes simplex virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14A):6585–6596. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., Tsurumi T., Zhu L. A., Weller S. K., Olivo P. D., Challberg M. D., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. Herpes simplex virus 1 helicase-primase: a complex of three herpes-encoded gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2186–2189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Courtney M. A., Schaffer P. A. Temperature-sensitive mutants in herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP4 permissive for early gene expression. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):767–776. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.767-776.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., McCarthy A. M., Schaffer P. A. Isolation and characterization of deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 in the gene encoding immediate-early regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):558–570. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.558-570.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M. S., Crute J. J., Bruckner R. C., Lehman I. R. Overexpression and assembly of the herpes simplex virus type 1 helicase-primase in insect cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20835–20838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M. S., Lehman I. R. Association of DNA helicase and primase activities with a subassembly of the herpes simplex virus 1 helicase-primase composed of the UL5 and UL52 gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1105–1109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney D. F., McLauchlan J., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. A modular system for the assay of transcription regulatory signals: the sequence TAATGARAT is required for herpes simplex virus immediate early gene activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7847–7863. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo M. L., Dorsky D. I., Crumpacker C. S., Parris D. S. The essential 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein of herpes simplex virus stimulates the virus-encoded DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5023–5029. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5023-5029.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Weller S. K. An ICP6::lacZ insertional mutagen is used to demonstrate that the UL52 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1 is required for virus growth and DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2970–2977. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2970-2977.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Weller S. K. Factor(s) present in herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells can compensate for the loss of the large subunit of the viral ribonucleotide reductase: characterization of an ICP6 deletion mutant. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Weller S. K. Herpes simplex virus type 1-induced ribonucleotide reductase activity is dispensable for virus growth and DNA synthesis: isolation and characterization of an ICP6 lacZ insertion mutant. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):196–205. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.196-205.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland L. E., Anderson K. P., Stringer J. R., Wagner E. K. Isolation and localization of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA abundant before viral DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):447–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.447-462.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Separation of sequences defining basal expression from those conferring alpha gene recognition within the regulatory domains of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4065–4069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langelier Y., Buttin G. Characterization of ribonucleotide reductase induction in BHK-21/C13 Syrian hamster cell line upon infection by herpes simplex virus (HSV). J Gen Virol. 1981 Nov;57(Pt 1):21–31. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-57-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchetti M. E., Smith C. A., Schaffer P. A. A temperature-sensitive mutation in a herpes simplex virus type 1 gene required for viral DNA synthesis maps to coordinates 0.609 through 0.614 in UL. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):715–721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.715-721.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Crombie I. K., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Control of protein synthesis in herpesvirus-infected cells: analysis of the polypeptides induced by wild type and sixteen temperature-sensitive mutants of HSV strain 17. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jun;31(3):347–372. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-3-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W., Kaiser-Rogers K. A. DNA helicases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:289–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matz B., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Preston V. G. Physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutations of herpes simplex virus type 1 using cloned restriction endonuclease fragments. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2261–2270. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Dolan A., McNab D., Perry L. J., Taylor P., Challberg M. D. Structures of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for replication of virus DNA. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):444–453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.444-453.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Clements J. B. Organization of the herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription unit encoding two early proteins with molecular weights of 140000 and 40000. J Gen Virol. 1983 May;64(Pt 5):997–1006. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-5-997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Comparison of upstream sequence requirements for positive and negative regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate-early gene by three virus-encoded trans-acting factors. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.190-199.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus DNA replication: the UL9 gene encodes an origin-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5414–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus type 1 gene products required for DNA replication: identification and overexpression. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):196–204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.196-204.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parris D. S., Cross A., Haarr L., Orr A., Frame M. C., Murphy M., McGeoch D. J., Marsden H. S. Identification of the gene encoding the 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):818–825. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.818-825.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Cordingley M. G., Stow N. D. Analysis of DNA sequences which regulate the transcription of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):708–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.708-716.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purifoy D. J., Lewis R. B., Powell K. L. Identification of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):621–623. doi: 10.1038/269621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L. Temperature-sensitive mutants in two distinct complementation groups of herpes simplex virus type 1 specify thermolabile DNA polymerase. J Gen Virol. 1981 May;54(Pt 1):219–222. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-1-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson R. W., Nossal N. G. Characterization of the bacteriophage T4 gene 41 DNA helicase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4725–4731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Aron G. M., Biswal N., Benyesh-Melnick M. Temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1: isolation, complementation and partial characterization. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):57–71. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Carter V. C., Timbury M. C. Collaborative complementation study of temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):490–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.490-504.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Frenkel N. The herpes simplex virus amplicon: a new eucaryotic defective-virus cloning-amplifying vector. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Localization of an origin of DNA replication within the TRS/IRS repeated region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):863–867. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan P. J., Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L. DNA-binding protein associated with herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):501–508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.501-508.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Preston C. M., Clements J. B. Separation and characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early mRNA's. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):42–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.42-52.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Carmichael E. P., Aschman D. P., Goldstein D. J., Schaffer P. A. Genetic and phenotypic characterization of mutants in four essential genes that map to the left half of HSV-1 UL DNA. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):198–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Lee K. J., Sabourin D. J., Schaffer P. A. Genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants which define the gene for the major herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):354–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.354-366.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Seghatoleslami M. R., Shao L., Rowse D., Carmichael E. P. The herpes simplex virus type 1 alkaline nuclease is not essential for viral DNA synthesis: isolation and characterization of a lacZ insertion mutant. J Gen Virol. 1990 Dec;71(Pt 12):2941–2952. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-12-2941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Spadaro A., Schaffer J. E., Murray A. W., Maxam A. M., Schaffer P. A. Cloning, sequencing, and functional analysis of oriL, a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin of DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):930–942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. A., Nelson N. J., McGeoch D. J., Challberg M. D. Identification of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for origin-dependent DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.435-443.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wymer J. P., Chung T. D., Chang Y. N., Hayward G. S., Aurelian L. Identification of immediate-early-type cis-response elements in the promoter for the ribonucleotide reductase large subunit from herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2773–2784. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2773-2784.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L. A., Weller S. K. The six conserved helicase motifs of the UL5 gene product, a component of the herpes simplex virus type 1 helicase-primase, are essential for its function. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):469–479. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.469-479.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., Weller S. K. UL5, a protein required for HSV DNA synthesis: genetic analysis, overexpression in Escherichia coli, and generation of polyclonal antibodies. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):366–378. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]