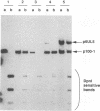
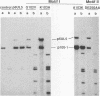
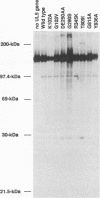
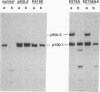
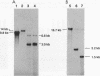
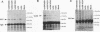Abstract
The UL5 protein of herpes simplex virus type 1, one component of the viral helicase-primase complex, contains six sequence motifs found in all members of a superfamily of DNA and RNA helicases. Although this superfamily contains more than 20 members ranging from bacteria to mammalian cells and their viruses, the importance of these motifs has not been addressed experimentally for any one of them. In this study, we have examined the functional significance of these six motifs for the UL5 protein through the introduction of site-specific mutations resulting in single amino acid substitutions of the most highly conserved residues within each motif. A transient replication complementation assay was used to test the effect of each mutation on the function of the UL5 protein in viral DNA replication. In this assay, a mutant UL5 protein expressed from an expression clone is used to complement a replication-deficient null mutant with a mutation in the UL5 gene for the amplification of herpes simplex virus origin-containing plasmids. Eight mutations in conserved regions and three similar mutations in nonconserved regions of the UL5 gene were analyzed, and the results indicate that all six conserved motifs are essential to the function of UL5 protein in viral DNA replication; on the other hand, mutations in nonconserved regions are tolerated. These data provide the first direct evidence for the importance of these conserved regions in any member of the superfamily of DNA and RNA helicases. In addition, three motif mutations were introduced into the viral genome, and the phenotypic analyses of these mutants are consistent with results from the transient replication complementation assay. The ability of these three mutant UL5 proteins to form specific interactions with other members of the helicase-primase complex, UL8 and UL52, indicates that the functional domains required for replication activity of UL5 are separable from domains responsible for protein-protein interactions. It is anticipated that this type of structure-function analysis will lead to the identification of protein domains that contribute not only to the enzymatic activities of helicase or primase but also to protein-protein interactions within members of the complex.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azzaria M., Schurr E., Gros P. Discrete mutations introduced in the predicted nucleotide-binding sites of the mdr1 gene abolish its ability to confer multidrug resistance. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5289–5297. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder J. M., Stow N. D. Herpes simplex virus helicase-primase: the UL8 protein is not required for DNA-dependent ATPase and DNA helicase activities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3573–3578. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D. A method for identifying the viral genes required for herpesvirus DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9094–9098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. A., Gaudreau P., Brazeau P., Langelier Y. Specific inhibition of herpesvirus ribonucleotide reductase by a nonapeptide derived from the carboxy terminus of subunit 2. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):441–443. doi: 10.1038/321441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., Lehman I. R. Herpes simplex virus-1 helicase-primase. Physical and catalytic properties. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4484–4488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. A DNA helicase induced by herpes simplex virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14A):6585–6596. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crute J. J., Tsurumi T., Zhu L. A., Weller S. K., Olivo P. D., Challberg M. D., Mocarski E. S., Lehman I. R. Herpes simplex virus 1 helicase-primase: a complex of three herpes-encoded gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2186–2189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F. B., Bullock P., Murakami Y., Wobbe C. R., Weissbach L., Hurwitz J. Simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA replication: SV40 large T antigen unwinds DNA containing the SV40 origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):16–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M. S., Crute J. J., Bruckner R. C., Lehman I. R. Overexpression and assembly of the herpes simplex virus type 1 helicase-primase in insect cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20835–20838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M. S., Lehman I. R. Association of DNA helicase and primase activities with a subassembly of the herpes simplex virus 1 helicase-primase composed of the UL5 and UL52 gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1105–1109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutia B. M., Frame M. C., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Clark W. N., Marsden H. S. Specific inhibition of herpesvirus ribonucleotide reductase by synthetic peptides. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):439–441. doi: 10.1038/321439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. C., Kuby S. A., Mildvan A. S. ATP-binding site of adenylate kinase: mechanistic implications of its homology with ras-encoded p21, F1-ATPase, and other nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):907–911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Weller S. K. An ICP6::lacZ insertional mutagen is used to demonstrate that the UL52 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1 is required for virus growth and DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2970–2977. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2970-2977.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Weller S. K. Factor(s) present in herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells can compensate for the loss of the large subunit of the viral ribonucleotide reductase: characterization of an ICP6 deletion mutant. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. A conserved NTP-motif in putative helicases. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):22–22. doi: 10.1038/333022a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. A novel superfamily of nucleoside triphosphate-binding motif containing proteins which are probably involved in duplex unwinding in DNA and RNA replication and recombination. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 1;235(1-2):16–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81226-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. Two related superfamilies of putative helicases involved in replication, recombination, repair and expression of DNA and RNA genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4713–4730. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V. One more conserved sequence motif in helicases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7734–7734. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilbronn R., zur Hausen H. A subset of herpes simplex virus replication genes induces DNA amplification within the host cell genome. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3683–3692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3683-3692.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgman T. C. A new superfamily of replicative proteins. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):22–23. doi: 10.1038/333022b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. Enlarged family of putative helicases. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):478–478. doi: 10.1038/334478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Lasko P. F., Ashburner M., Leroy P., Nielsen P. J., Nishi K., Schnier J., Slonimski P. P. Birth of the D-E-A-D box. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):121–122. doi: 10.1038/337121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Q. Y., Summers W. C. Site-directed mutagenesis of a nucleotide-binding domain in HSV-1 thymidine kinase: effects on catalytic activity. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):638–642. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90308-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W., Kaiser-Rogers K. A. DNA helicases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:289–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Dolan A., McNab D., Perry L. J., Taylor P., Challberg M. D. Structures of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for replication of virus DNA. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):444–453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.444-453.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski L., Chu G., Berg P., Friedberg E. C. RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: nucleotide sequence of wild-type and mutant alleles, transcript mapping, and aspects of gene regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):17–26. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski L., Friedberg E. C. Analysis of the essential and excision repair functions of the RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1218–1227. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski L., Friedberg E. C. The RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: isolation and characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant in the essential function and of extragenic suppressors of this mutant. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):458–466. doi: 10.1007/BF00331150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus DNA replication: the UL9 gene encodes an origin-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5414–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakula A. A., Sauer R. T. Genetic analysis of protein stability and function. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:289–310. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel M., Kidd S., Kelley M. R. An improved filamentous helper phage for generating single-stranded plasmid DNA. Gene. 1986;45(3):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Dröge P., Knippers R. DNA helicase activity of SV40 large tumor antigen. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1939–1944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Localization of an origin of DNA replication within the TRS/IRS repeated region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):863–867. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., McMonagle E. C. Characterization of the TRS/IRS origin of DNA replication of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):427–438. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Higgins D., Prakash L., Prakash S. Mutation of lysine-48 to arginine in the yeast RAD3 protein abolishes its ATPase and DNA helicase activities but not the ability to bind ATP. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3263–3269. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03193.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeda G., van Ham R. C., Vermeulen W., Bootsma D., van der Eb A. J., Hoeijmakers J. H. A presumed DNA helicase encoded by ERCC-3 is involved in the human repair disorders xeroderma pigmentosum and Cockayne's syndrome. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):777–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90122-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Aschman D. P., Sacks W. R., Coen D. M., Schaffer P. A. Genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants of HSV-1: the combined use of complementation and physical mapping for cistron assignment. Virology. 1983 Oct 30;130(2):290–305. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Spadaro A., Schaffer J. E., Murray A. W., Maxam A. M., Schaffer P. A. Cloning, sequencing, and functional analysis of oriL, a herpes simplex virus type 1 origin of DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):930–942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. A., Nelson N. J., McGeoch D. J., Challberg M. D. Identification of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for origin-dependent DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.435-443.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L. A., Weller S. K. The UL5 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1: isolation of a lacZ insertion mutant and association of the UL5 gene product with other members of the helicase-primase complex. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):458–468. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.458-468.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., Weller S. K. UL5, a protein required for HSV DNA synthesis: genetic analysis, overexpression in Escherichia coli, and generation of polyclonal antibodies. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):366–378. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90507-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- la Cour T. F., Nyborg J., Thirup S., Clark B. F. Structural details of the binding of guanosine diphosphate to elongation factor Tu from E. coli as studied by X-ray crystallography. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2385–2388. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03943.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]