Abstract
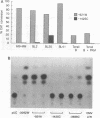
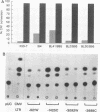
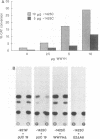
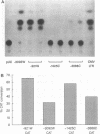
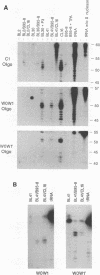
The six latent-cycle nuclear antigens (EBNAs) of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), whose genes share 5' leader exons and two promoters (Cp and Wp), are differentially expressed by cells of the B lineage. To examine the possibility that EBNA gene expression is regulated through selective use of Cp and Wp, we monitored the activity of promoter-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene constructs transfected into EBV-positive and EBV-negative B lymphocytes and Burkitt's lymphoma cells. Wp was a much stronger promoter than Cp in EBV genome-negative B-cell lines and was used exclusively in primary B cells. When B cells were infected with transforming EBV, Cp became the stronger promoter. This switch was not observed when B cells were infected with an immortalization-deficient virus, P3HR-1, which lacks the EBNA-2 open reading frame and expresses a mutant leader protein (EBNA-LP). Cp function was transactivated when EBV-negative or P3HR-1-infected B cells were cotransfected with Cp and a 12-kb fragment of DNA (BamHI-WWYH) that spanned the P3HR-1 deletion. This activity was mapped to the EBNA-2 gene within WWYH; constructs expressing EBNA-LP did not induce Cp function, and the deletion of 405 bp from the EBNA-2 open reading frame abolished transactivation. This research demonstrates host cell and EBNA-2 regulation of latent-cycle promoter activity in B lymphocytes, a mechanism with implications for persistence of EBV-infected lymphoid cells in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbot S. D., Rowe M., Cadwallader K., Ricksten A., Gordon J., Wang F., Rymo L., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 induces expression of the virus-encoded latent membrane protein. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2126–2134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2126-2134.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfieri C., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection of human B lymphocytes. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):595–608. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90893-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A promoter for the highly spliced EBNA family of RNAs of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3424–3430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3424-3430.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornkamm G. W., Hudewentz J., Freese U. K., Zimber U. Deletion of the nontransforming Epstein-Barr virus strain P3HR-1 causes fusion of the large internal repeat to the DSL region. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):952–968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.952-968.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows S. R., Sculley T. B., Misko I. S., Schmidt C., Moss D. J. An Epstein-Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T cell epitope in EBV nuclear antigen 3 (EBNA 3). J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):345–349. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschle M., Brenner M. K., Chen I. S., Drexler H. G., Gignac S. M., Rooney C. M. Transfection and gene expression in normal and malignant primary B lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Oct 4;133(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90321-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calender A., Billaud M., Aubry J. P., Banchereau J., Vuillaume M., Lenoir G. M. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) induces expression of B-cell activation markers on in vitro infection of EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8060–8064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fåhraeus R., Jansson A., Ricksten A., Sjöblom A., Rymo L. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen 2 activates the viral latent membrane protein promoter by modulating the activity of a negative regulatory element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7390–7394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Walker L., Guy G., Brown G., Rowe M., Rickinson A. Control of human B-lymphocyte replication. II. Transforming Epstein-Barr virus exploits three distinct viral signals to undermine three separate control points in B-cell growth. Immunology. 1986 Aug;58(4):591–595. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney S., Kamine J., Holley-Guthrie E., Lin J. C., Mar E. C., Pagano J. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BZLF1 immediate-early gene product differentially affects latent versus productive EBV promoters. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1729–1736. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1729-1736.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W., Dambaugh T., Heller M., Dowling J., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus DNA XII. A variable region of the Epstein-Barr virus genome is included in the P3HR-1 deletion. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):979–986. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.979-986.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Robinson J., Heston L., Lipman M. Differences between laboratory strains of Epstein-Barr virus based on immortalization, abortive infection, and interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4006–4010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. J., Sculley T. B., Pope J. H. Induction of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):988–990. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.988-990.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. J., Kurilla M. G., Griffin H. M., Brooks J. M., Mackett M., Arrand J. R., Rowe M., Burrows S. R., Moss D. J., Kieff E. Human cytotoxic T-cell responses against Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens demonstrated by using recombinant vaccinia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2906–2910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. J., Wang D., Young L. S., Wang F., Rowe M., Kieff E., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T-cell recognition of transfectants expressing the virus-coded latent membrane protein LMP. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3747–3755. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3747-3755.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson M., Gradoville L., Heston L., Miller G. Non-immortalizing P3J-HR-1 Epstein-Barr virus: a deletion mutant of its transforming parent, Jijoye. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):834–844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.834-844.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Sugden B. trans activation of an Epstein-Barr viral transcriptional enhancer by the Epstein-Barr viral nuclear antigen 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3838–3846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricksten A., Olsson A., Andersson T., Rymo L. The 5' flanking region of the gene for the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen 2 contains a cell type specific cis-acting regulatory element that activates transcription in transfected B-cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8391–8410. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricksten A., Svensson C., Welinder C., Rymo L. Identification of sequences in Epstein-Barr virus DNA required for the expression of the second Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen in COS-1 cells. J Gen Virol. 1987 Sep;68(Pt 9):2407–2418. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-9-2407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C. M., Rowe M., Wallace L. E., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus-positive Burkitt's lymphoma cells not recognized by virus-specific T-cell surveillance. Nature. 1985 Oct 17;317(6038):629–631. doi: 10.1038/317629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C., Howe J. G., Speck S. H., Miller G. Influence of Burkitt's lymphoma and primary B cells on latent gene expression by the nonimmortalizing P3J-HR-1 strain of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1531–1539. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1531-1539.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Rowe M., Evan G. I., Wallace L. E., Farrell P. J., Rickinson A. B. Restricted expression of EBV latent genes and T-lymphocyte-detected membrane antigen in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2599–2607. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Brooks L., Sample C., Young L., Rowe M., Gregory C., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Restricted Epstein-Barr virus protein expression in Burkitt lymphoma is due to a different Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6343–6347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Hummel M., Braun D., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequences of mRNAs encoding Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins: a probable transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Pfitzner A., Strominger J. L. An Epstein-Barr virus transcript from a latently infected, growth-transformed B-cell line encodes a highly repetitive polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9298–9302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Strominger J. L. Analysis of the transcript encoding the latent Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen I: a potentially polycistronic message generated by long-range splicing of several exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8305–8309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung N. S., Kenney S., Gutsch D., Pagano J. S. EBNA-2 transactivates a lymphoid-specific enhancer in the BamHI C promoter of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2164–2169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2164-2169.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walls D., Perricaudet M. Novel downstream elements upregulate transcription initiated from an Epstein-Barr virus latent promoter. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):143–151. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07930.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C., Sample C., Rowe M., Liebowitz D., Murray R., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein (LMP1) and nuclear proteins 2 and 3C are effectors of phenotypic changes in B lymphocytes: EBNA-2 and LMP1 cooperatively induce CD23. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2309–2318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2309-2318.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Tsang S. F., Kurilla M. G., Cohen J. I., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 transactivates latent membrane protein LMP1. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3407–3416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3407-3416.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisetschlaeger M., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Mutually exclusive use of viral promoters in Epstein-Barr virus latently infected lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6498–6502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisetschlaeger M., Yandava C. N., Furmanski L. A., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Promoter switching in Epstein-Barr virus during the initial stages of infection of B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1725–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L., Alfieri C., Hennessy K., Evans H., O'Hara C., Anderson K. C., Ritz J., Shapiro R. S., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus transformation-associated genes in tissues of patients with EBV lymphoproliferative disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 19;321(16):1080–1085. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910193211604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimber-Strobl U., Suentzenich K. O., Laux G., Eick D., Cordier M., Calender A., Billaud M., Lenoir G. M., Bornkamm G. W. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 activates transcription of the terminal protein gene. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):415–423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.415-423.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]