Abstract
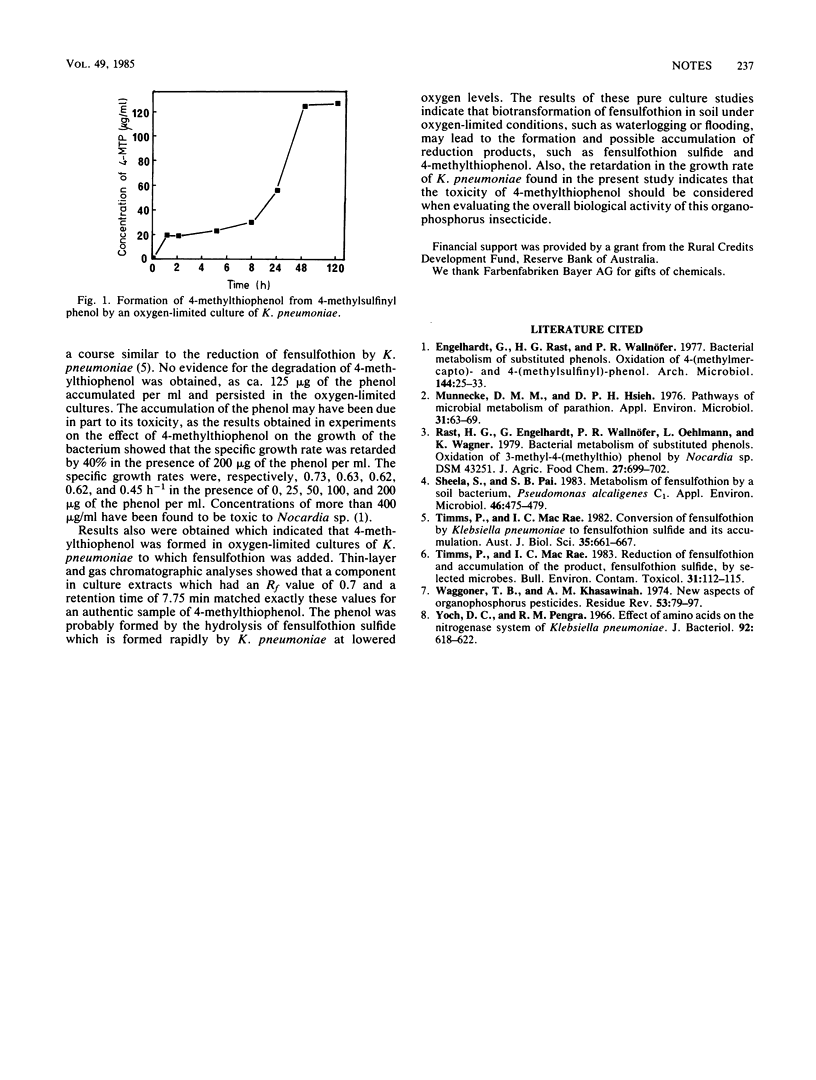
Oxygen-limited cultures of Klebsiella pneumoniae reduced 4-methylsulfinyl phenol to 4-methylthiophenol. A study of the effect of 4-methylthiophenol on the growth of K. pneumoniae revealed that the specific growth rate was retarded by 40% in the presence of 200 micrograms of the phenol per ml. A soil bacterium, Hafnia sp., was isolated that could reduce the organophosphorus insecticide fensulfothion to fensulfothion sulfide.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Engelhardt G., Rast H. G., Wallnöfer P. R. Bacterial metabolism of substituted phenols. Oxidation of 4-(methylmercapto)-and 4-(methylsulfinyl)-phenol by Nocardia spec. DSM 43251. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Jul 26;114(1):25–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00429626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnecke D. M., Hsieh D. P. Pathways of microbial metabolism of parathion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jan;31(1):63–69. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.1.63-69.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheela S., Pai S. B. Metabolism of fensulfothion by a soil bacterium, Pseudomonas alcaligenes C1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):475–479. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.475-479.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timms P., MacRae I. C. Conversion of fensulfothion by Klebsiella pneumoniae to fensulfothion sulfide and its accumulation. Aust J Biol Sci. 1982;35(6):661–667. doi: 10.1071/bi9820661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timms P., MacRae I. C. Reduction of fensulfothion and accumulation of the product, fensulfothion sulfide, by selected microbes. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1983 Jul;31(1):112–115. doi: 10.1007/BF01608775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Pengra R. M. Effect of amino acids on the nitrogenase system of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):618–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.618-622.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



