Abstract
Stromal-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) and its receptor, CXCR4, are essential for normal hematopoietic progenitor cell movement and adherence within the bone marrow microenvironment. In leukemia, the BCR-ABL1 oncoprotein inhibits SDF-1–dependent cell trafficking within the bone marrow through a mechanism that is not fully understood. Here, we report that BCR-ABL1 in malignant cells constitutively increases expression of activation-dependent epitopes of the β2 integrin LFA-1. This is associated with the complete loss of responsiveness of LFA-1 to SDF-1–induced “inside-out” signaling involving CXCR4 and Lyn, leading to aberrant adhesive responses. These data provide a novel, LFA-1–mediated mechanism whereby BCR-ABL1 inhibits SDF-1 action in malignant progenitors.
Introduction
Stromal-derived factor-1 (SDF-1)/CXCR4–regulated interaction of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells with stromal marrow cells is critical for normal hematopoiesis.1,2 The 2 mechanisms through which the BCR-ABL1 oncoprotein suppresses CXCR4-mediated interactions of progenitors with stromal cells in marrow have been described in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). One mechanism involves the inhibition of CXCR4 expression.3 A second proposed mechanism includes signaling defects without modification of CXCR4 expression.4,5 These opposing results suggest that the actual situation is more complex and that new signaling paradigms are needed
The movement and adhesion of hematopoietic progenitors is regulated at several levels, including regulation through “inside-out” integrin signal transduction.6 We recently identified a Lyn-mediated inside-out signaling pathway that relays signals from the chemokine receptor, CXCR4, to the β2 integrin LFA-1, which ultimately regulates the adhesive properties of normal progenitor cells in the bone marrow stromal microenvironment.7 Here, we report that the oncoprotein, BCR-ABL1, is able to prevent the action of this signaling mechanism. In this way, BCR-ABL1 inhibits SDF-1–regulated hematopietic cell adhesion. These results provide a molecular mechanism for abnormal interactions between malignant progenitors and the marrow stromal microenvironment in CML.
Methods
Antibodies, siRNA, and cells
Antibodies were purchased from sources described in Document S1 (available on the Blood website; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article). M-07e cells were transfected with Lyn siRNA and control siRNA (Dharmacon, Lafayette, CO) using the Nucleofector system kit V and transfection program Q29 (Amaxa, Cologne, Germany). Normal and CML blast-crisis CD34+ cells were obtained from Leukemia Core (University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA), using guidelines approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Pennsylvania.
Retroviral production and M-07e infection protocol, FACS analysis, and migration and adhesion assays
Standard methods were used as detailed in Document S1.
Results and discussion
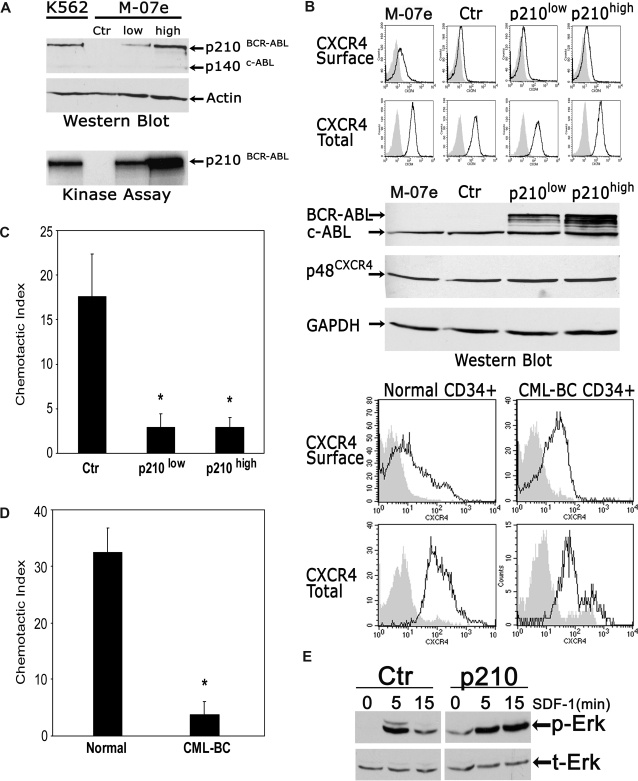
We began by analyzing the effects of BCR-ABL1 on CXCR4 expression in the pluripotent hematopoietic cell line M-07e. One control and 2 BCR-ABL1+ polyclonal cell populations, expressing different amounts of BCR-ABL1, were established (Figure 1A; Document S1). The presence of either low or high p210BCR-ABL1 had no effect on CXCR4 expression in M-07e cells, as measured by fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) and Western blotting (Figure 1B). In 4 populations of cells (M-07e, M-07e–control vector, M-07e–low BCR-ABL1, and M-07e–high BCR-ABL1), both surface and total (surface + intracellular) CXCR4 receptor levels were similar. As indicated by FACS analysis, the same was true for Western blot analysis of total protein, normalized to the housekeeping gene GAPDH, which also showed no differences in the total cellular expression of CXCR4 in BCR-ABL1+ M-07e and control M-07e cells. Similarly, we could not detect substantial differences in CXCR4 receptor expression between the normal primary CD34+ marrow progenitors and BCR-ABL1+ CML blast crisis CD34+ cells (Figure 1B). The mean percentages of cells expressing surface or total CXCR4, as measured by FACS, were only slightly reduced in blast crisis cells, as compared with normal cells (Figure 1B legend). To be certain that BCR-ABL1 exerts an inhibitory effect in these cells that could account for the block of SDF-1–dependent signaling, we also measured cell migration. As shown in Figure 1C,D, BCR-ABL1 strongly inhibited SDF-1–dependent migration in M-07 cells and primary CML blast crisis cells as reflected by approximately 80% to 90% reduction in the chemotactic index. These results indicate that BCR-ABL1 profoundly inhibits SDF-1–mediated chemotactic response in leukemia cells while not decreasing in any substantial way the expression levels of CXCR4 in these cells. To further confirm that BCR-ABL1–expressing cells have the functional CXCR4 receptor, we measured the downstream signaling pathways in SDF-1–stimulated BCR-ABL1+ M-07e cells. Notably, the duration of peak Erk phosphorylation, after stimulation with SDF-1, increased in BCR-ABL1–expressing M-07e cells as compared with control M-07e cells (Figure 1E). Consistent with the data of Figure 1E, we previously demonstrated that the binding of BCR-ABL1 to Lyn resulted in the prolonged activation of Lyn.5 Overall, these results suggest that BCR-ABL1 alters the action of SDF-1 by disrupting intracellular signaling pathways downstream of CXCR4, while not decreasing the expression levels of the CXCR4 receptor.
Figure 1.
BCR-ABL1 profoundly inhibits chemotactic responses to SDF-1 and alters SDF-1–induced signal transduction while not decreasing the expression levels of the CXCR4 receptor. (A) A total of 3 polyclonal M-07e cell populations, one control (Ctr; transfected with empty vector) and 2 expressing different amounts of p210–BCR-ABL1, were generated through infection with retroviral vectors (Document S1). Western blotting and kinase assays showed an approximately 5-fold difference in BCR-ABL1 protein and function, respectively, between a high p210 BCR-ABL and low p210 BCR-ABL cell population. Total-cell lysate from M-07e-control vector cells was used as negative control; lysates from K562 cells were used as positive control. (B) CXCR4 surface and total cellular expression in control and BCR-ABL1+ M-07e cells were evaluated by FACS (top panel; Document S1). The expression levels of p210 BCR-ABL in these cells were determined by Western blot using c-ABL antibody. The blot was stripped and reprobed with an anti-CXCR4 antibody and then with an anti-GAPDH antibody. CXCR4 membrane and CXCR4 total cellular expression was determined by FACS in normal CD34+ cells obtained from healthy individuals and BCR-ABL+ CD34+ cells from patients with CML in blast crisis (bottom panel). The result shown is representative of 3 independent experiments with 3 different cell donors. The percentage of CXCR4 surface-positive cells was 30.2% plus or minus 7.6% and 27.1% plus or minus 18.9%, and the percentage of CXCR4 total-positive cells was 65.4% plus or minus 15.1% and 48.6% plus or minus 14.1% (mean ± SEM), in normal CD34+ cells and CML blast crisis CD34+ cells, respectively. (C) Chemotaxis assays in SDF-1–stimulated control M-07e and BCR-ABL1+ M-07e cells (Document S1). Values in chemotaxis assays are means plus or minus SEM (n = 4). (D) Chemotaxis assay in SDF-1–stimulated normal CD34+ cells and CML blast crisis CD34+ cells. Values in chemotaxis assays are means plus or minus SEM (n = 3); *P < .05. (E) Time course of Erk activation after SDF-1 stimulation (100 ng/mL for 5 and 10 minutes) in M-07e cells transfected with control (Ctr) or p210-BCR-ABL (p210) vector was measured by phosphor-Erk (p-Erk) Western blotting (top). The membrane was stripped and reprobed with anti–total Erk (t-Erk; bottom).
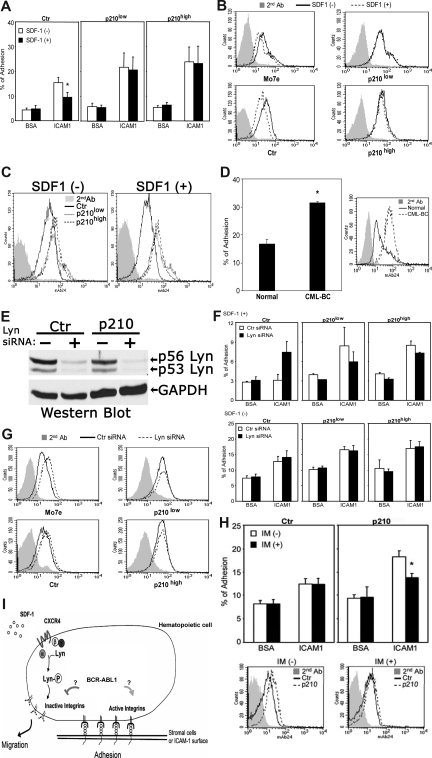
To address this further, we examined the effects of BCR-ABL1 on SDF-1–induced inside-out integrin signaling and its direct effect on cell adherence. We focused primarily on the β2 integrin LFA-1, since this particular integrin is an important target for SDF-1–induced inside-out signaling involving CXCR4 and Lyn in normal hematopoietic precursors.7 Stimulation of control BCR-ABL1− M-07e cells with SDF-1 showed reduced cell adherence to surfaces coated with ICAM-1, a ligand for LFA-1 (Figure 2A left panel), which correlated with the concomitant down-regulated expression of activation-dependent epitopes of LFA-1 (Figure 2B left panels). The introduction of BCR-ABL1 in these cells resulted in increased expression of activation-dependent epitopes of LFA-1 (Figure 2C) and prevented SDF-1–dependent inhibitory effects on both LFA-1 affinity and ICAM-1 adherence (Figure 2A-C). Notably, attachment of unstimulated BCR-ABL1+ M-07e cells to surfaces coated with ICAM-1 was increased compared with BCR-ABL− control M-07e cells (Figure 2A). As a further indication of the involvement of BCR-ABL1 in the activation of LFA-1, we also observed that the expression levels of activation-dependent epitopes of LFA-1 were considerably increased in primary CML blast-crisis CD34+ cells compared with normal primary cells (Figure 2D). Consistent with this, attachment of primary BCR-ABL+ CD34+ cells to stromal cells was increased compared with normal CD34+ cells (Figure 2D). Combined, these results indicate that BCR-ABL1 constitutively up-regulates the expression of high-affinity LFA-1 epitopes, which promotes ICAM-1–mediated cell adhesion, thus suppressing CXCR4-mediated down-regulation of LFA-1 affinity.
Figure 2.
BCR-ABL1 alters adhesive responses to SDF-1 through a LFA-1 integrin-mediated mechanism. (A) Attachment of SDF-1–stimulated or –unstimulated M-07e cells to surfaces coated with ICAM-1 or BSA (control) after transfection with p210BCR-ABL1 or control vector (Document S1). See Figure 1A for the BCR-ABL1 Western blot. Values are means plus or minus SEM (n = 4); *P < .05. (B) FACS analysis of β2 integrin-activation epitope expression in control and BCR-ABL1–transfected M-07e cells stimulated with SDF-1. Cells were stained with anti-human integrin monoclonal antibody 24 (which recognizes a conformationally dependent high-affinity epitope on β2 integrins), followed by secondary antibodies and FACS analysis (Document S1). (C) FACS analysis showing increased expression of β2 integrin-activation epitope 24 in BCR-ABL+ M-07e cells compared with BCR-ABL− M-07e cells. (D) Adhesion of primary human CML blast crisis CD34+ cells or normal CD34+ cells to stromal marrow cells obtained from a healthy individual. FACS analysis shows the expression level of the β2 integrin-activation epitope. Cells were stained with anti–human integrin monoclonal antibody 24, followed by secondary antibodies and FACS analysis. Values in adhesion assays are means plus or minus SEM (n = 3); *P < .05. (E) The expression levels of Lyn in control and BCR-ABL+ M-07e cells were determined by Western blotting 48 hours after nucleoporation with Lyn siRNA or control siRNA (Document S1). The blot was stripped and reprobed with an anti-GAPDH antibody. (F) Attachment of SDF-1–stimulated or –unstimulated BCR-ABL+ or control M-07e cells to surfaces coated with ICAM-1 or BSA (control) at 48 hours after transfection with Lyn siRNA or control siRNA. Values in adhesion assays are means plus or minus SEM (n = 3). (G) FACS analysis of β2 integrin-activation epitope 24 expression in SDF-1–stimulated BCR-ABL+ or control M-07e cells at 48 hours after nucleoporation with Lyn siRNA or control siRNA. We were unable to use primary blasts in these experiments because of apoptosis. As we previously showed, Lyn siRNA–treated BCR-ABL1+ primary blasts underwent apoptosis, whereas the same treatment inhibited the growth of several BCR-ABL1+ cell lines; however, they remained viable.8 (H) Effect of imatinib (IM) on the BCR-ABL1 kinase-dependent LFA-1 activity was measured by both adhesion assay and FACS analysis. M-07e cells transfected with control (Ctr) or p210-BCR-ABL (p210) were treated with or without IM (1 μM) for 16 to 18 hours; we then measured either attachment to surfaces coated with ICAM-1 and BSA (control) or β2 integrin-activation epitope 24 expression by FACS analysis. Values in adhesion assays are means plus or minus SEM (n = 3); *P < .05. (I) We propose that BCR-ABL1 alters SDF-1–mediated cell adhesion and movement via constitutively activating LFA-1 and inhibiting SDF-1–induced inside-out signaling involving CXCR4 and Lyn.
To investigate the possibility that Lyn-mediated down-regulation of LFA-17 also could be affected by BCR-ABL1, we tested the adherence of cells lacking Lyn to surfaces coated with the LFA-1 integrin ligand ICAM-1. Figure 2E shows that Lyn siRNA efficiently inhibited Lyn gene expression in BCR-ABL1− and BCR-ABL+ M-07e cell lines as reflected by an approximately 90% reduction in Lyn protein in cells. Inhibition of Lyn expression with siRNA in control BCR-ABL1− cells increased SDF-1–mediated affinity of LFA-1 and cell adherence, indicating that CXCR4 inhibits LFA-1 through Lyn (Figure 2F,G left panels). The expression of BCR-ABL1 in these cells prevented Lyn-mediated inhibition of cell adhesion to ICAM-1 (Figure 2F) as well as Lyn-mediated down-regulation of LFA-1 conformational activation (Figure 2G right panels). Surprisingly, we did not observe a dose-dependent effect of BCR-ABL1 expression on LFA-1 conformational activation (Figure 2B,G). One possibility is that the low expression level of BCR-ABL1 has already exerted the greatest possible effect on LFA-1. Consistent with this, we observed that activity of BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase was rather high in M-07e cells expressing the low amount of BCR-ABL1 protein, suggesting that function can compensate for low amounts (Figure 1A). This conclusion is further supported by our migration and attachment experiments (Figures 1C,2A).
We also determined whether the enhanced attachment of p210 M-07e cells to ICAM-1 could be inhibited by the BCR-ABL kinase inhibitor imatinib. As shown in Figure 2H, imatinib effectively blocked the increase in attachment of BCR-ABL1–transfected M-07e cells to ICAM-1. Consistent with this, the expression levels of activation-dependent epitopes of LFA-1 were decreased in BCR-ABL1+ cells treated with imatinib (Figure 2H). Thus, the enhanced attachment to ICAM-1, and increased expression of the activation epitopes of LFA-1, are due to BCR-ABL1 kinase activity. Taken together, these results indicate that the BCR-ABL1 kinase constitutively increases the conformational activation of LFA-1 and prevents the responsiveness of LFA-1 to SDF-1-induced inside-out signaling involving CXCR4 and Lyn. Importantly, the expression of the activation-dependent epitopes for the β2 integrin Mac-1 as well as protein expression of the β2 integrin subunit CD18 were unchanged in BCR-ABL1+ cells compared with BCR-ABL− cells (data not shown). Thus, BCR-ABL1 does not affect LFA-1 integrin expression levels but only alters the conformational activation of LFA-1 that is already present on the cell surface.
This study suggests that inhibited CXCR4-mediated trafficking of malignant progenitors in CML is related to increased LFA-1 integrin-mediated adhesion rather than inhibition of the CXCR4 receptor expression.3 It seems likely that the migratory defect in BCR-ABL1–expressing leukemia cells is not merely due to the aberrant LFA-1 regulation, since this defect is observed during chemotaxis through both ICAM-1–coated filters and bare filters (data not shown). Thus, the defective chemotaxis of BCR-ABL1–expressing cells is likely to be intrinsic, but it also depends upon the altered activity of integrins on the cell surface due to the impaired inside-out integrin signaling in these cells. Our previous5 and present results clearly indicate that BCR-ABL1 alters signaling pathways downstream of CXCR4 (Figure 1E) and blocks the down-regulation of LFA-1 normally resulting from the activation of CXCR4-Lyn signaling (Figure 2A-H). The precise molecular mechanisms that link the BCR-ABL1 kinase activity to the conformational activation of LFA-1 remain to be elucidated. However, Lyn kinase can directly bind to the β2 integrin cytoplasmic tail in normal cells.9 Since Lyn is associated with and strongly activated by BCR-ABL1,5 it is possible that BCR-ABL1 is simply sequestering Lyn, preventing Lyn's access to LFA-1 and thus suppressing its ability to down-regulate LFA-1 in leukemia cells. An alternative explanation for our results would be the activation of an unknown protein in BCR-ABL1–expressing cells that could directly bind to the β2 integrin cytoplasmic tail and block Lyn's access. Experiments to test this possibility are in progress in our laboratory.
A previously published report10 and our results have shown that BCR-ABL1 stimulates the β1 subfamily of integrins and increases hematopoietic cell adhesion to their ligands, VCAM-1 and fibronectin (data not shown). This could be important because fibronectin11 is a key component of the bone marrow extracellular matrix.12 However, we recently demonstrated that the β2 integrin LFA-1 and its ligand ICAM-1, but not β1 integrin and its ligands, are directly involved in the SDF-1–induced inside-out signaling in human hematopoietic cells.7 Consistent with this, here we describe a previously unrecognized functional association between the BCR-ABL1 oncoprotein and the β2 integrin LFA1 in leukemia cells. We propose that BCR-ABL1 constitutively increases the affinity of the LFA-1 integrin to its ligand ICAM-1 (Figure 2I). This is associated with the loss of responsiveness of LFA-1 to SDF-1–induced inside-out signaling involving CXCR4 and Lyn kinase. This in turn increases attachment and hinders the movement of leukemia blasts toward the SDF-1 gradient, suppressing their ability to interact with the bone marrow microenvironment. Together, these findings indicate that BCR-ABL disrupts links between the CXCR4 chemokine receptor and β2 integrins in malignant progenitors, which results in the inhibition of chemotactic and adhesive cell responsiveness to SDF-1, eventually leading to an altered relationship between these cells and the stromal microenvironment.
In conclusion, our results describe a role for the BCR-ABL1 oncoprotein in the disruption of the SDF-1 chemokine–induced inside-out β2 integrin signaling in leukemia cells. It is tempting to speculate that other members of the Src family kinases, in addition to Lyn, might couple to this signaling pathway as well. Besides Lyn, Hck can also directly interact with the β2 integrin cytoplasmic tail.9 It was shown that Src family kinases Lyn, Hck, and Fgr were required for BCR-ABL1–induced B-lymphoblastic leukemia, but not myeloid leukemia.8,13 Thus, Lyn-deficient myeloid progenitors can be transformed by BCR-ABL1, at least to cause CML. On the other hand, it is well established that Lyn-regulated multikinase signaling complexes are critical regulators of chemokine signaling and chemotaxis of various normal and malignant primary cells5,7,14,15 (and R. Cheung, V. Ravyn, B.T., A.P., and R.G.C., manuscript submitted). Taken together, all available data suggest that Lyn, and likely other Src family kinases, may play an important role in determining the malignant adhesive and chemotactic phenotype rather than in the pathogenesis of BCR-ABL–expressing leukemia.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Monoclonal antibody (mAb) 24 for the active conformation of human β2 integrins was kindly provided by Dr Nancy Hogg (London Research Institute, London, United Kingdom). p210BCR-ABL-eGFP and eGFP retroviral vectors were generous gifts from Dr Catherine Verfaillie (Stem Cell Institute, Leuven, Belgium).
This work was supported by National Cancer Institute grant R01CA108552 (A.P.).
Footnotes
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Authorship
Contribution: Y.C., M.M., and B.E.T. performed research; R.G.C. analyzed data; and A.P. designed research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Andrzej Ptasznik, 522C Johnson Pavilion, 36th and Hamilton Walk, Philadelphia, PA 19104-6073; e-mail: andrzejp@mail.med.upenn.edu or andrzej.ptasznik@comcast.net.
References
- 1.Aiuti A, Turchetto L, Cota M, et al. Human CD34(+) cells express CXCR4 and its ligand stromal cell-derived factor-1. Implications for infection by T-cell tropic human immunodeficiency virus. Blood. 1999;94:62–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zou YR, Kottmann AH, Kuroda M, Taniuchi I, Littman DR. Function of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in haematopoiesis and in cerebellar development. Nature. 1998;393:595–599. doi: 10.1038/31269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Geay JF, Buet D, Zhang Y, et al. p210BCR-ABL inhibits SDF-1 chemotactic response via alteration of CXCR4 signaling and down-regulation of CXCR4 expression. Cancer Res. 2005;65:2676–2683. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Salgia R, Quackenbush E, Lin J, et al. The BCR/ABL oncoprotein alters the chemotactic response to stromal-derived factor-1. Blood. 1999;94:4233–4246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ptasznik A, Urbanowska E, Chinta S, et al. Crosstalk between BCR/ABL oncoprotein and CXCR4 signaling through a Src family kinase in human leukemia cells. J Exp Med. 2002;196:667–678. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ginsberg MH, Du X, Plow EF. Inside-out integrin signalling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992;4:766–771. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nakata Y, Tomkowicz B, Gewirtz AM, Ptasznik A. Integrin inhibition through Lyn-dependent cross talk from CXCR4 chemokine receptors in normal human CD34+ marrow cells. Blood. 2006;107:4234–4239. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-08-3343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ptasznik A, Nakata Y, Kalota A, Emerson SG, Gewirtz AM. Short interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting the Lyn kinase induces apoptosis in primary, and drug resistant, BCR-ABL(+) leukemia cells. Nat Med. 2004;10:1187–1189. doi: 10.1038/nm1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Arias-Salgado EG, Lizano S, Sarkar S, Brugge JS, Ginsberg MH, Shattil SJ. Src kinase activation by direct interaction with the integrin beta cytoplasmic domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:13298–13302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2336149100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bazzoni G, Carlesco N, Griffin JD, Hemler ME. Bcr/Abl expression stimulates integrin function in hematopopietic cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1996;98:521–528. doi: 10.1172/JCI118820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ruoslahti E. Fibronectin and its receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:375–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Greeberger JS. The hematopoietic microenvironment. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1991;11:65–84. doi: 10.1016/1040-8428(91)90018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hu Y, Liu Y, Pelletier S, et al. Requirement of Src kinases Lyn, Hck and Fgr for BCR-ABL1-induced B-lymphoblastic leukemia but not chronic myeloid leukemia. Nat Genet. 2004;36:440–444. doi: 10.1038/ng1343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ptasznik A, Traynor-Kaplan A, Bokoch GM. G protein-coupled chemoattractant receptors regulate Lyn tyrosine kinase-Shc adapter protein signaling complexes. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:19969–19973. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.34.19969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.O'Laughlin-Brunner B, Radosevic N, Taylor M, et al. Lyn is required for normal stem cell factor-induced proliferation and chemotaxis of primary hematopoietic cells. Blood. 2001;98:343–350. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.2.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.