Abstract
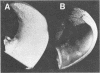
Isolates of an Arthrobacter species known to produce a positive host pathogenicity test were evaluated by the mushroom tissue block rapid pitting test. All 11 isolates of the Arthrobacter species yielded a positive test response. The time required for a positive test was the same for Pseudomonas tolaasi and the Arthrobacter species.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bessette A. E. Distribution of brown blotch bacteria in wild and cultivated species of basidiomycetes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):878–880. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.878-880.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelliott R. A., Billing E., Hayward A. C. A determinative scheme for the fluorescent plant pathogenic pseudomonads. J Appl Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;29(3):470–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1966.tb03499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]