Abstract
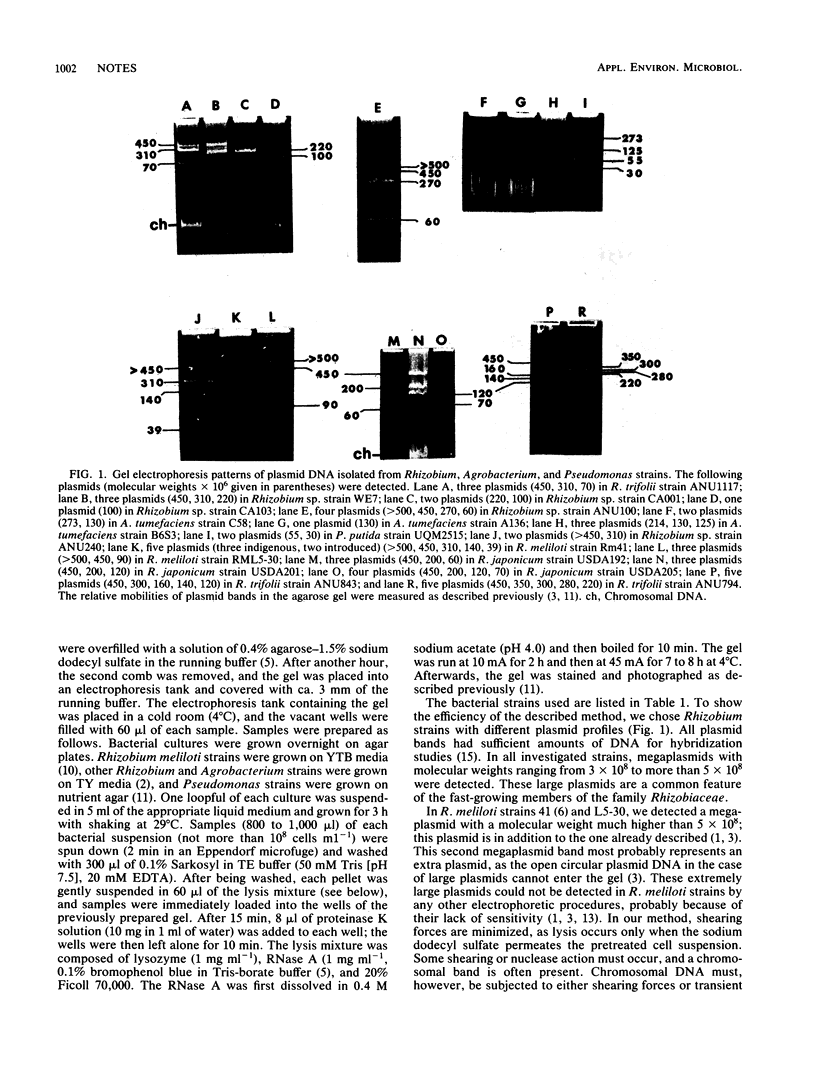
Using a horizontal gel electrophoresis method, we demonstrated reproducibly the presence of indigenous plasmids in different Rhizobium, Agrobacterium, and Pseudomonas strains. The method yields a large amount of plasmid DNA and is sensitive in detecting megaplasmids with molecular weights higher than 5 × 108. In two Rhizobium meliloti strains, a megaplasmid other than the low-mobility plasmid already known was detected.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bánfalvi Z., Sakanyan V., Koncz C., Kiss A., Dusha I., Kondorosi A. Location of nodulation and nitrogen fixation genes on a high molecular weight plasmid of R. meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):318–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00272925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djordjevic M. A., Zurkowski W., Rolfe B. G. Plasmids and stability of symbiotic properties of Rhizobium trifolii. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):560–568. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.560-568.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt T. A rapid method for the identification of plasmid desoxyribonucleic acid in bacteria. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):584–588. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M. Transducing phages of Rhizobium meliloti. Acta Microbiol Pol A. 1970;2(3):109–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison N. A., Hau C. Y., Trinick M. J., Shine J., Rolfe B. G. Heat curing of a sym plasmid in a fast-growing Rhizobium sp. that is able to nodulate legumes and the nonlegume Parasponia sp. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):527–531. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.527-531.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orosz L., Sváb Z., Kondorosi A., Sik T. Genetic studies on rhizobiophage 16-3. I. Genes and functions on the chromosome. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Sep 27;125(4):341–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plazinski J., Dart P. J., Rolfe B. G. Plasmid visualization and nif gene location in nitrogen-fixing Azospirillum strains. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1429–1433. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1429-1433.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash R. K., Schilperoort R. A., Nuti M. P. Large plasmids of fast-growing rhizobia: homology studies and location of structural nitrogen fixation (nif) genes. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1129–1136. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1129-1136.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg C., Casse-Delbart F., Dusha I., David M., Boucher C. Megaplasmids in the plant-associated bacteria Rhizobium meliloti and Pseudomonas solanacearum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):402–406. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.402-406.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]