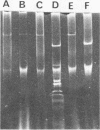
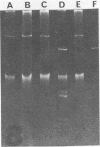
Abstract
Plasmids conferring tellurite resistance were transferred at low temperature (27 degrees C) from Escherichia coli strains isolated from chicken carcasses at the time of slaughter and after storage. They belonged to group IncH, as evidenced by their large molecular weight and incompatibility with plasmid pIP233. E. coli strains contaminating chickens meat can thus represent a source of IncH plasmids in the food chain of humans.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensink J. C., Botham F. P. Antibiotic resistant coliform bacilli, isolated from freshly slaughtered poultry and from chilled poultry at retail outlets. Aust Vet J. 1983 Mar;60(3):80–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1983.tb05876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caudry S. D., Stanisich V. A. Incidence of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli associated with frozen chicken carcasses and characterization of conjugative R plasmids derived from such strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Dec;16(6):701–709. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.6.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabbert Y. A., Scavizzi M. R., Witchitz J. L., Gerbaud G. R., Bouanchaud D. H. Incompatibility groups and the classification of fi - resistance factors. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):666–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.666-675.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaslus-Dancla E., Guillot J. F., Lafont J. P. Evolution de l'antibiorésistance bactérienne dans des élevages avicoles. Ann Rech Vet. 1979;10(1):77–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaslus-Dancla E., Lafont J. P., Guillot J. F. Inc groups among plasmids harbored by Escherichia coli of avian origin. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1980 Sep-Oct;131B(2):203–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Minor L., Coynault C., Chabbert Y., Gerbaud G., Le Minor S. Groupes de compatibilité de plasmides métaboliques. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1976 Jul;127(1):31–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. H., Howe K., Bennett P. M., Richmond M. H., Whiteside E. J. The colonization of the human gut by antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli from chickens. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;43(3):465–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. The development and spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria as a consequence of feeding antibiotics to livestock. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;368:23–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb15430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl P., Thomas J. Détection et identification rapides de certains plasmides du groupe d'incompatibilité H infectant des souches de Salmonella typhi-murium épidémiques. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1980 May-Jun;131(3):315–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangnekar V. M., Banker D. D., Jhala H. I. Some phenotypic characteristics of group H plasmids from human isolates of Salmonella & Escherichia coli. Indian J Med Res. 1983 Oct;78:450–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato A., Tagawa K., Ike Y., Mitsuhashi S. Drug resistance of Escherichia coli strains isolated from chicken. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1980 Jun;33(3):185–188. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.33.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers A. O., Jacoby G. A. Plasmid-determined resistance to tellurium compounds. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):276–281. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.276-281.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Levine J. G. Studies of temperature-sensitive transfer and maintenance of H incompatibility group plasmids. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Feb;116(2):475–484. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-2-475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terakado N., Sato G. Demonstration of the so-called Mexican type R plasmids in Escherichia coli isolated from domestic animals and pigeons. Microbiol Immunol. 1978;22(4):227–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1978.tb00366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timoney J. F., Linton A. H. Experimental ecological studies on H2 plasmids in the intestine and faeces of the calf. J Appl Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;52(3):417–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1982.tb05072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley M., Taylor D. E. Identification of DNA homologies among H incompatibility group plasmids by restriction enzyme digestion and Southern transfer hybridization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):194–200. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]