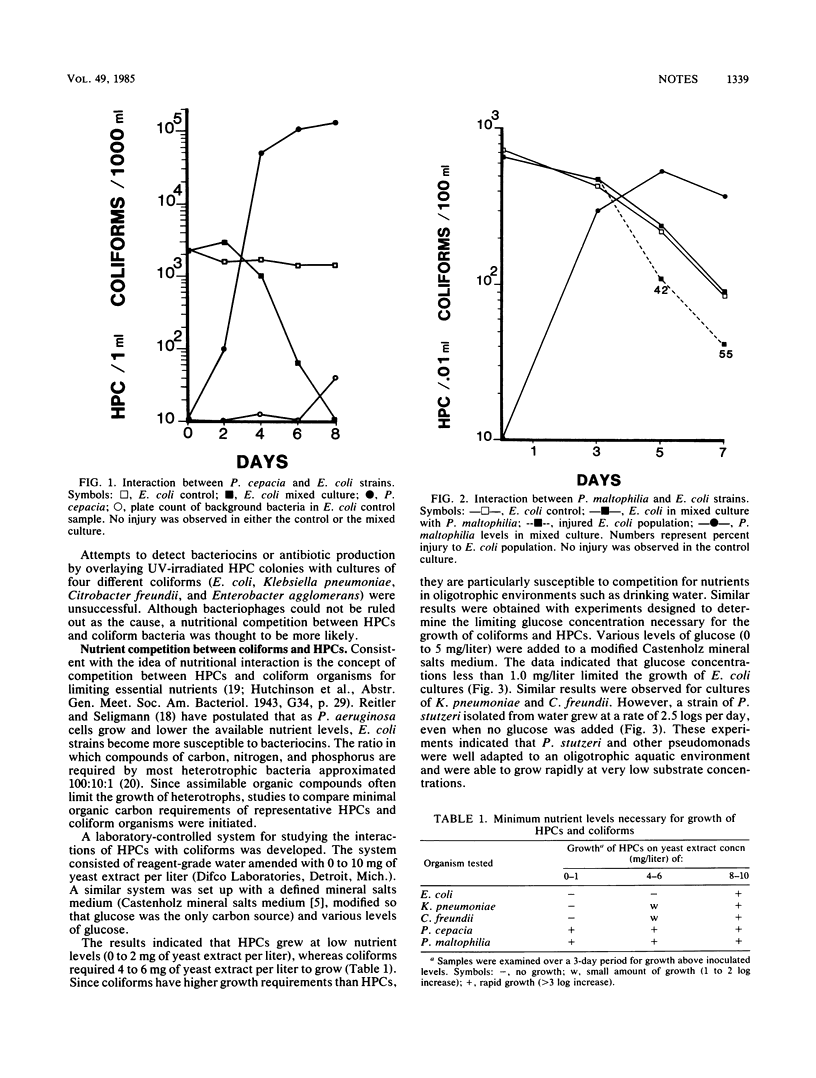
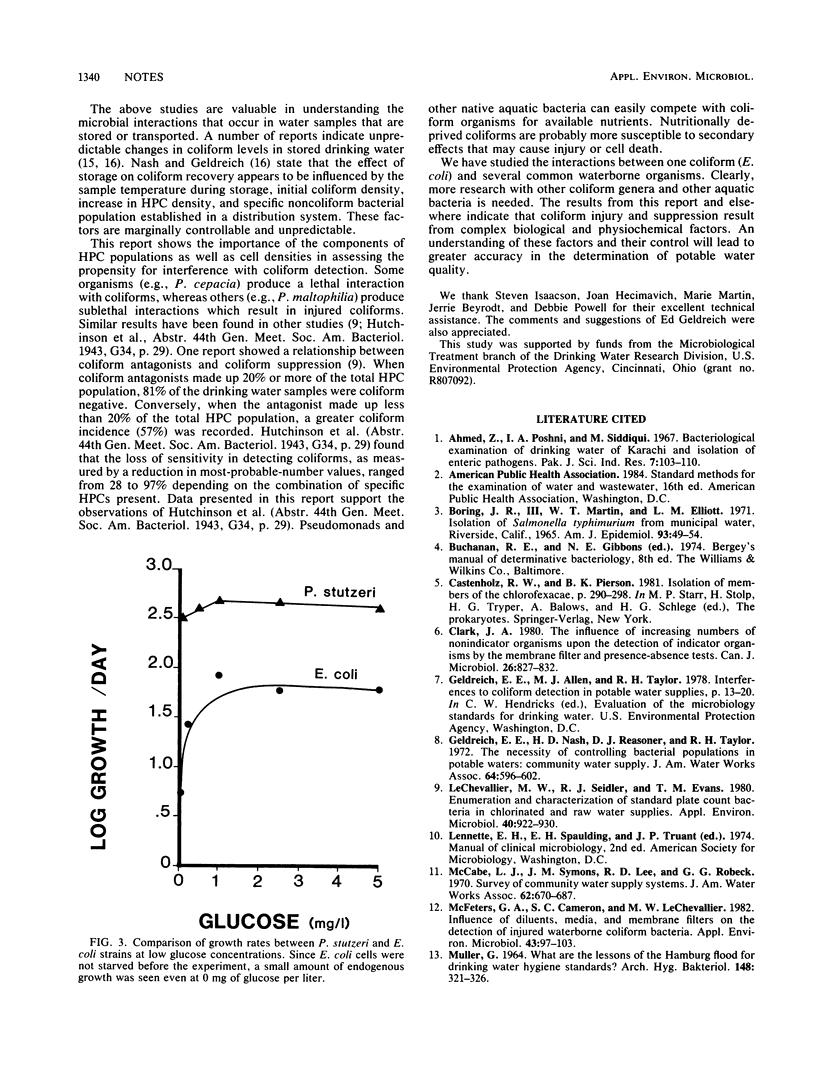
Abstract
Studies were initiated to investigate the interactions between heterotrophic plate count bacteria and coliform organisms. We used spiked samples to show that heterotrophic plate count bacteria could reduce coliform densities by more than 3 logs within 8 days. Some heterotrophic plate count bacteria were able to cause injury to the coliform population. A significant correlation (r = 0.66; P less than 0.05) was observed between the initial level of heterotrophic plate count bacteria and the rate of coliform decline. Competition for limiting organic carbon was hypothesized to be responsible for the observed effects.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boring J. R., 3rd, Martin W. T., Elliott L. M. Isolation of Salmonella typhi-murium from municipal water, Riverside, California, 1965. Am J Epidemiol. 1971 Jan;93(1):49–54. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeChevallier M. W., Seidler R. J., Evans T. M. Enumeration and characterization of standard plate count bacteria in chlorinated and raw water supplies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Nov;40(5):922–930. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.5.922-930.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFeters G. A., Cameron S. C., LeChevallier M. W. Influence of diluents, media, and membrane filters on detection fo injured waterborne coliform bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):97–103. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.97-103.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



