Abstract
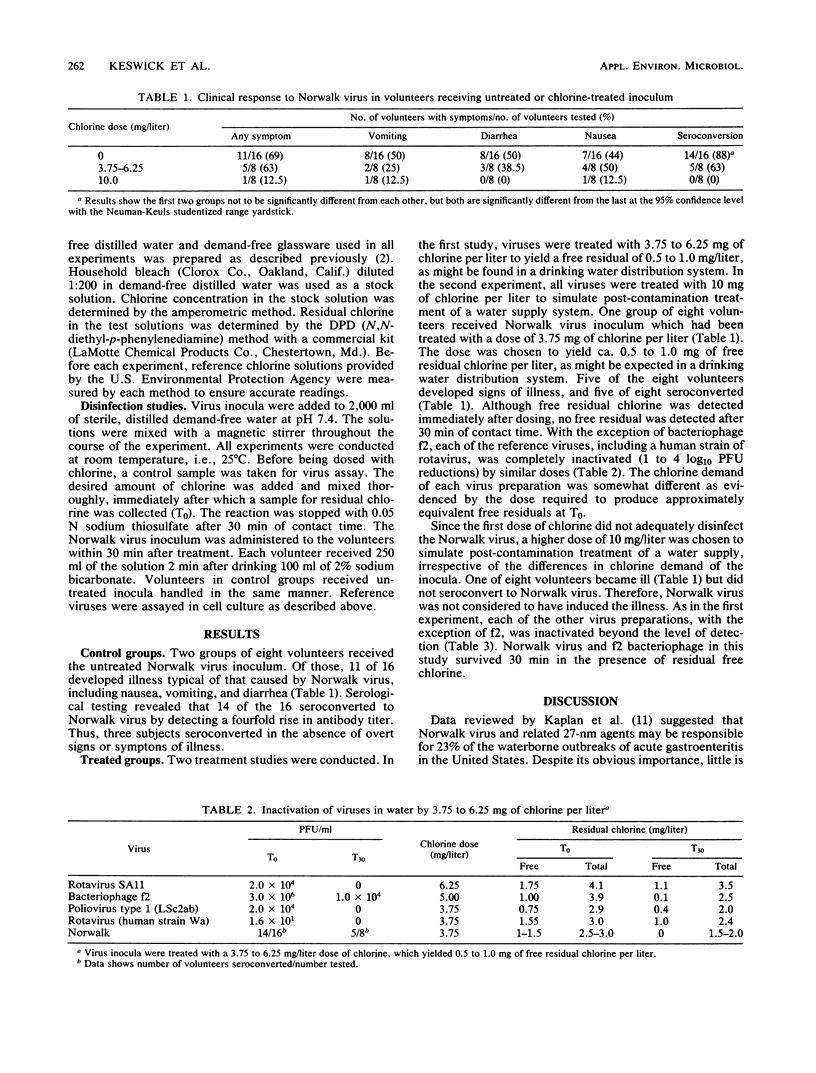
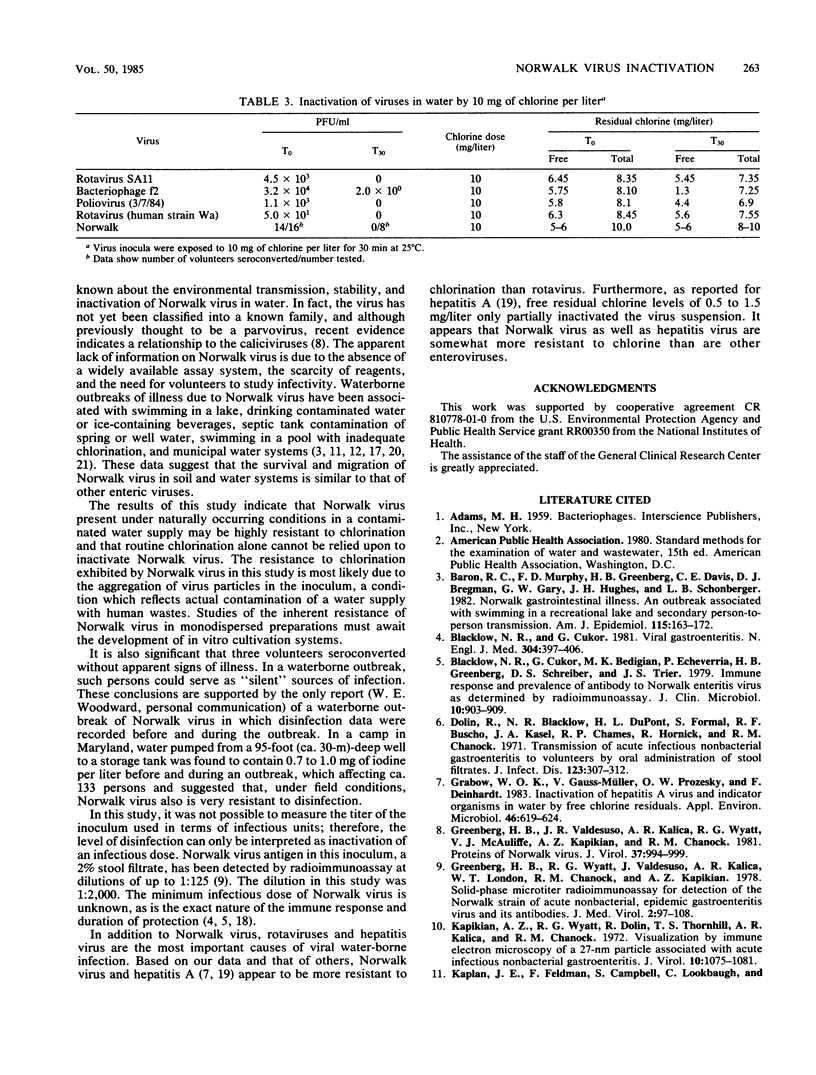
Norwalk virus in water was found to be more resistant to chlorine inactivation than poliovirus type 1 (LSc2Ab), human rotavirus (Wa), simian rotavirus (SA11), or f2 bacteriophage. A 3.75 mg/liter dose of chlorine was found to be effective against other viruses but failed to inactivate Norwalk virus. The Norwalk virus inoculum remained infectious for five of eight volunteers, despite the initial presence of free residual chlorine. Infectivity in volunteers was demonstrated by seroconversion to Norwalk virus. Fourteen of 16 subjects receiving untreated inoculum seroconverted to Norwalk virus. Illness was produced in four of the eight volunteers and in 11 of 16 control subjects. A similar Norwalk virus inoculum treated with a 10 mg/liter dose of chlorine produced illness in only one and failed to induce seroconversion in any of eight volunteers. Free chlorine (5 to 6 mg/liter) was measured in the reaction vessel after a 30-minute contact period. Norwalk virus appears to be very resistant to chlorine which may explain its importance in outbreaks of waterborne disease.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron R. C., Murphy F. D., Greenberg H. B., Davis C. E., Bregman D. J., Gary G. W., Hughes J. M., Schonberger L. B. Norwalk gastrointestinal illness: an outbreak associated with swimming in a recreational lake and secondary person-to-person transmission. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Feb;115(2):163–172. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacklow N. R., Cukor G., Bedigian M. K., Echeverria P., Greenberg H. B., Schreiber D. S., Trier J. S. Immune response and prevalence of antibody to Norwalk enteritis virus as determined by radioimmunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):903–909. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.903-909.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacklow N. R., Cukor G. Viral gastroenteritis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 12;304(7):397–406. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102123040705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolin R., Blacklow N. R., DuPont H., Formal S., Buscho R. F., Kasel J. A., Chames R. P., Hornick R., Chanock R. M. Transmission of acute infectious nonbacterial gastroenteritis to volunteers by oral administration of stool filtrates. J Infect Dis. 1971 Mar;123(3):307–312. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.3.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabow W. O., Gauss-Müller V., Prozesky O. W., Deinhardt F. Inactivation of hepatitis A virus and indicator organisms in water by free chlorine residuals. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):619–624. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.619-624.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Valdesuso J. R., Kalica A. R., Wyatt R. G., McAuliffe V. J., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Proteins of Norwalk virus. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):994–999. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.994-999.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Valdesuso J., Kalica A. R., London W. T., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Solid-phase microtiter radioimmunoassay for detection of the Norwalk strain of acute nonbacterial, epidemic gastroenteritis virus and its antibodies. J Med Virol. 1978;2(2):97–108. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890020204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Dolin R., Thornhill T. S., Kalica A. R., Chanock R. M. Visualization by immune electron microscopy of a 27-nm particle associated with acute infectious nonbacterial gastroenteritis. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1075–1081. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1075-1081.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. E., Feldman R., Campbell D. S., Lookabaugh C., Gary G. W. The frequency of a Norwalk-like pattern of illness in outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis. Am J Public Health. 1982 Dec;72(12):1329–1332. doi: 10.2105/ajph.72.12.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. E., Goodman R. A., Schonberger L. B., Lippy E. C., Gary G. W. Gastroenteritis due to Norwalk virus: an outbreak associated with a municipal water system. J Infect Dis. 1982 Aug;146(2):190–197. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.2.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappus K. D., Marks J. S., Holman R. C., Bryant J. K., Baker C., Gary G. W., Greenberg H. B. An outbreak of Norwalk gastroenteritis associated with swimming in a pool and secondary person-to-person transmission. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Nov;116(5):834–839. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keswick B. H. Survival of enteric viruses adsorbed on electropositive filters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):501–502. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.501-502.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman J. S., Eckert E. A., Greenberg H. B., Strohm B. C., Isaacson R. E., Monto A. S. Norwalk virus enteric illness acquired by swimming exposure. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Feb;115(2):173–177. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morens D. M., Zweighaft R. M., Vernon T. M., Gary G. W., Eslien J. J., Wood B. T., Holman R. C., Dolin R. A waterborne outbreak of gastroenteritis with secondary person-to-person spread. Association with a viral agent. Lancet. 1979 May 5;1(8123):964–966. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91734-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrino T. A., Schreiber D. S., Trier J. S., Kapikian A. Z., Blacklow N. R. Clinical immunity in acute gastroenteritis caused by Norwalk agent. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jul 14;297(2):86–89. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197707142970204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. A., Hurley T. R., Hoff J. C., Wolfe L. G. Effect of chlorine treatment on infectivity of hepatitis A virus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):223–227. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.223-227.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Gary G. W., Jr, Greenberg H. B. Norwalk-related viral gastroenteritis due to contaminated drinking water. Am J Epidemiol. 1981 Oct;114(4):584–592. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., Anderson L. J., Holman R. C., Gary G. W., Greenberg H. B. Waterborne gastroenteritis due to the Norwalk agent: clinical and epidemiologic investigation. Am J Public Health. 1982 Jan;72(1):72–74. doi: 10.2105/ajph.72.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt R. G., Dolin R., Blacklow N. R., DuPont H. L., Buscho R. F., Thornhill T. S., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M. Comparison of three agents of acute infectious nonbacterial gastroenteritis by cross-challenge in volunteers. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(6):709–714. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.6.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



