Abstract
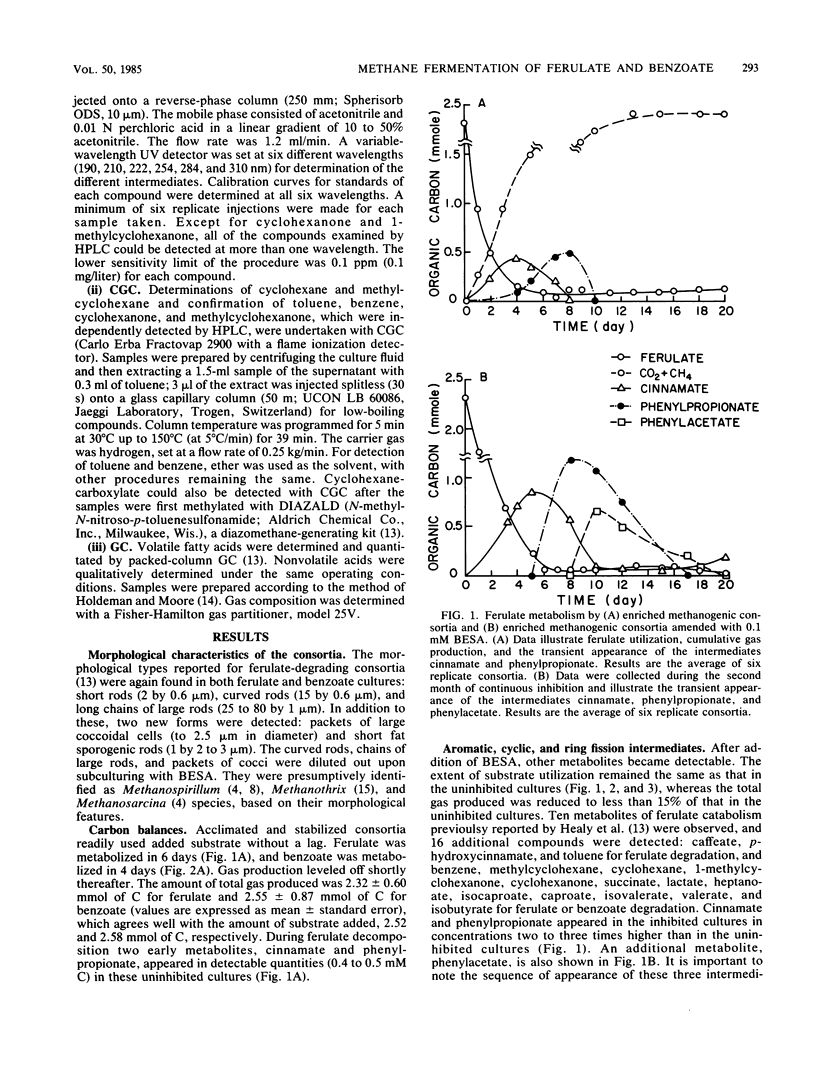
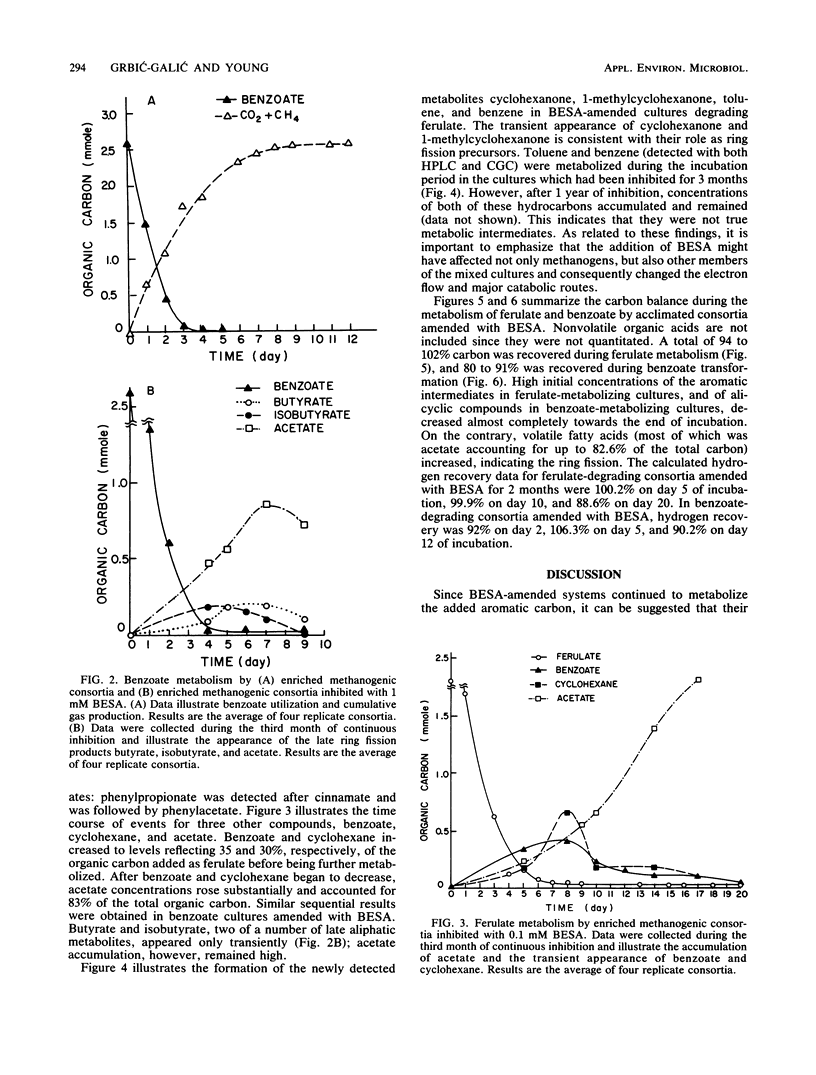
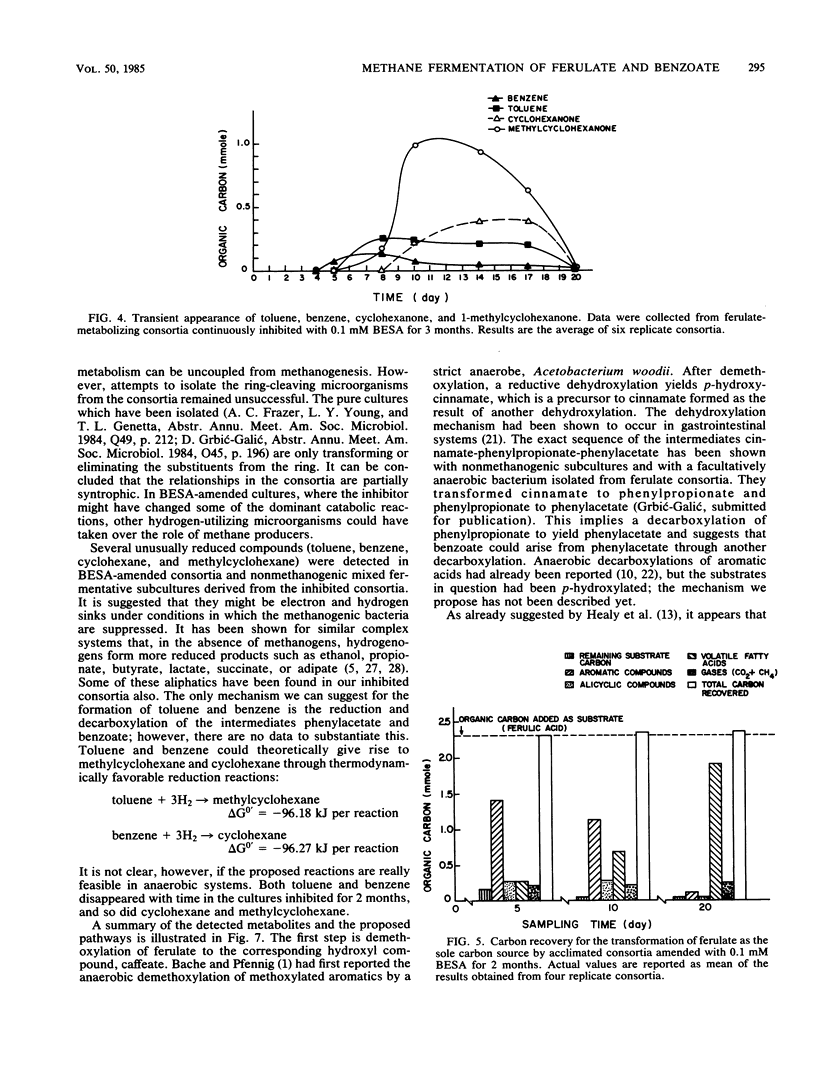
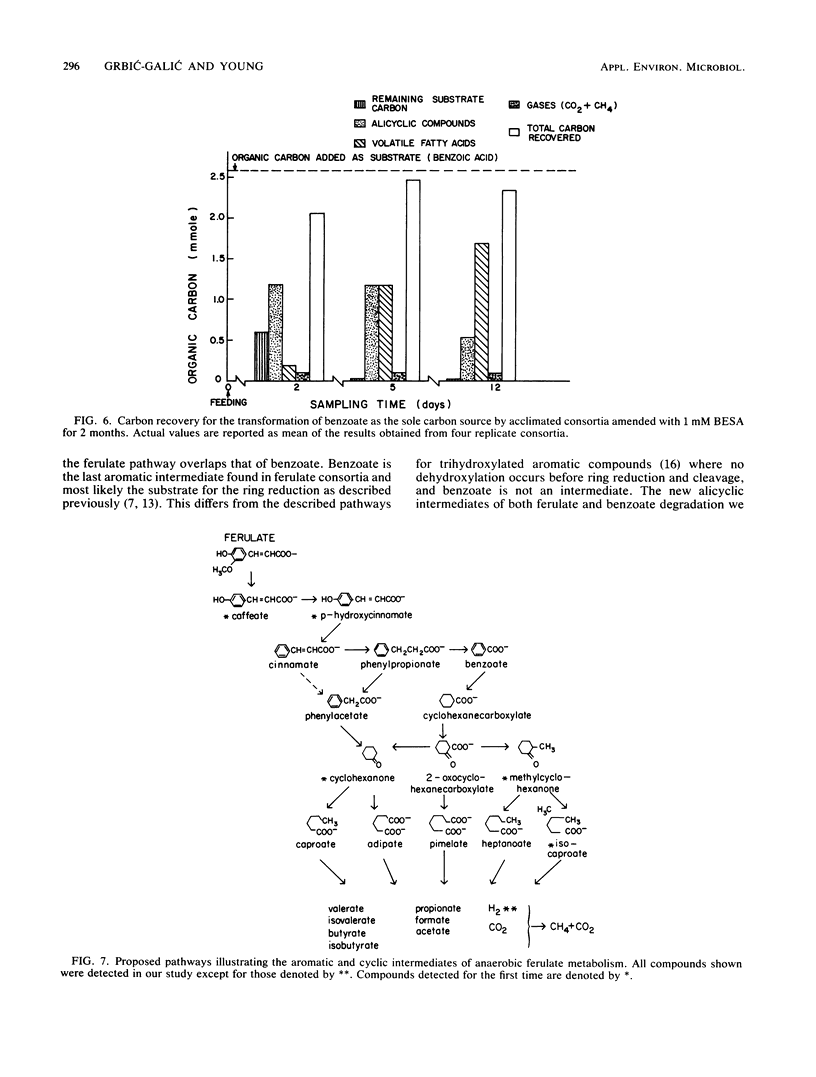
The anaerobic biodegradation of ferulate and benzoate in stabilized methanogenic consortia was examined in detail. Up to 99% of the ferulate and 98% of the benzoate were converted to carbon dioxide and methane. Methanogenesis was inhibited with 2-bromoethanesulfonic acid, which reduced the gas production and enhanced the buildup of intermediates. Use of high-performance liquid chromatography and two gas chromatographic procedures yielded identification of the following compounds: caffeate, p-hydroxycinnamate, cinnamate, phenylpropionate, phenylacetate, benzoate, and toluene during ferulate degradation; and benzene, cyclohexane, methylcyclohexane, cyclohexanecarboxylate, cyclohexanone, 1-methylcyclohexanone, pimelate, adipate, succinate, lactate, heptanoate, caproate, isocaproate, valerate, butyrate, isobutyrate, propionate, and acetate during the degradation of either benzoate or ferulate. Based on the identification of the above compounds, more complete reductive pathways for ferulate and benzoate are proposed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balba M. T., Evans W. C. The methanogenic fermentation of aromatic substrates. Biochem Soc Trans. 1977;5(1):302–304. doi: 10.1042/bst0050302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balba M. T., Evans W. C. The methanogenic fermentation of omega-phenylalkane carboxylic acids [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1979 Apr;7(2):403–405. doi: 10.1042/bst0070403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Woese C. R., Wolfe R. S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):260–296. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.260-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton P. L., Evans W. C. The metabolism of aromatic compounds by Rhodopseudomonas palustris. A new, reductive, method of aromatic ring metabolism. Biochem J. 1969 Jul;113(3):525–536. doi: 10.1042/bj1130525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C. Biochemistry of the bacterial catabolism of aromatic compounds in anaerobic environments. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):17–22. doi: 10.1038/270017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKLE B. J., LEWIS J. C., CORSE J. W., LUNDIN R. E. Enzyme reactions with phenolic compounds: formation of hydroxystyrenes through the decarboxylation of 4-hydroxycinnamic acids by Aerobacter. J Biol Chem. 1962 Sep;237:2926–2931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferry J. G., Wolfe R. S. Anaerobic degradation of benzoate to methane by a microbial consortium. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Feb;107(1):33–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00427864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy J. B., Jr, Young L. Y. Catechol and phenol degradation by a methanogenic population of bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jan;35(1):216–218. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.1.216-218.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy J. B., Young L. Y. Anaerobic biodegradation of eleven aromatic compounds to methane. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):84–89. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.84-89.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy J. B., Young L. Y., Reinhard M. Methanogenic decomposition of ferulic Acid, a model lignin derivative. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):436–444. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.436-444.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith C. L., Bridges R. L., Fina L. R., Iverson K. L., Cloran J. A. The anaerobic decomposition of benzoic acid during methane fermentation. IV. Dearomatization of the ring and volatile fatty acids formed on ring rupture. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Aug 1;118(2):173–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00415726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. L., Wolin M. J. A serum bottle modification of the Hungate technique for cultivating obligate anaerobes. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):985–987. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.985-987.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nottingham P. M., Hungate R. E. Methanogenic fermentation of benzoate. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1170–1172. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1170-1172.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel T. R., Jure K. G., Jones G. A. Catabolism of phloroglucinol by the rumen anaerobe coprococcus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Dec;42(6):1010–1017. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.6.1010-1017.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Silva G., Rodriguez D., Perez-Silva J. Dehydroxylation of caffeic acid by a bacterium isolated from rat faeces. Nature. 1966 Oct 15;212(5059):303–304. doi: 10.1038/212303b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribbons D. W., Evans W. C. Oxidative metabolism of phthalic acid by soil pseudomonads. Biochem J. 1960 Aug;76(2):310–318. doi: 10.1042/bj0760310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. D., Wolfe R. S. Structure and methylation of coenzyme M(HSCH2CH2SO3). J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4879–4885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin M. J. Metabolic interactions among intestinal microorganisms. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Nov;27(11):1320–1328. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.11.1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



