Abstract
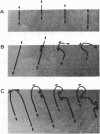
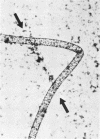
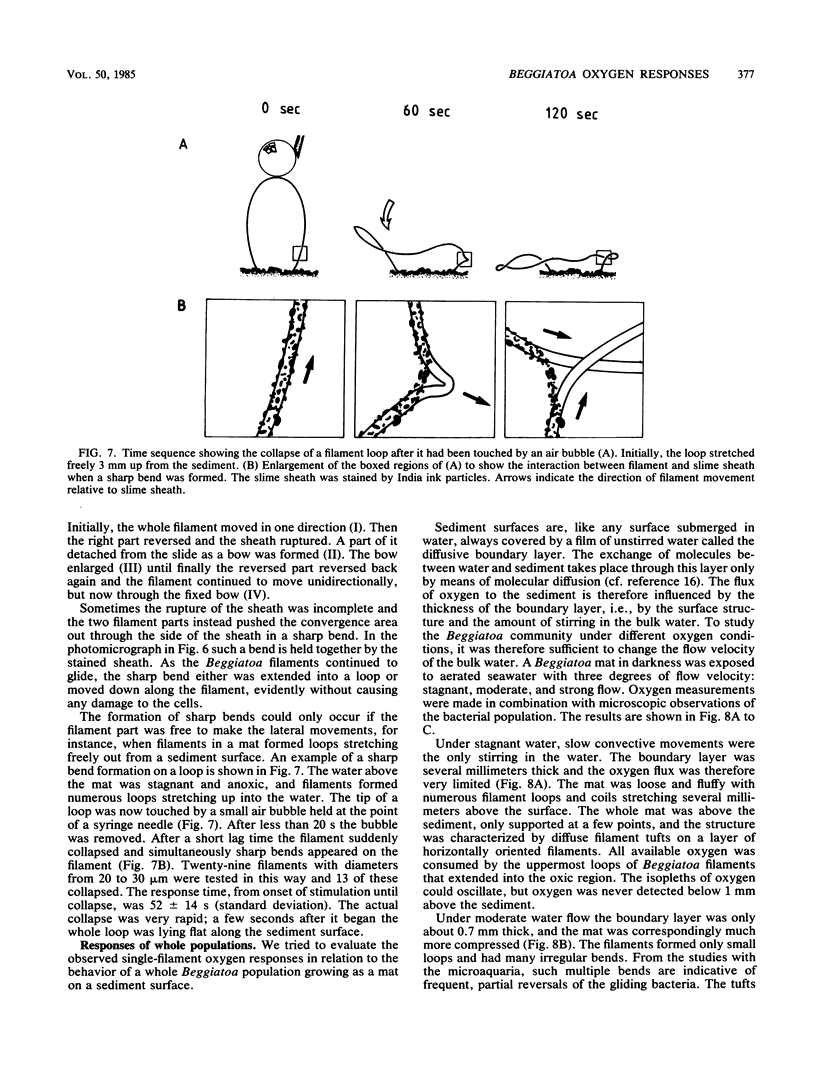
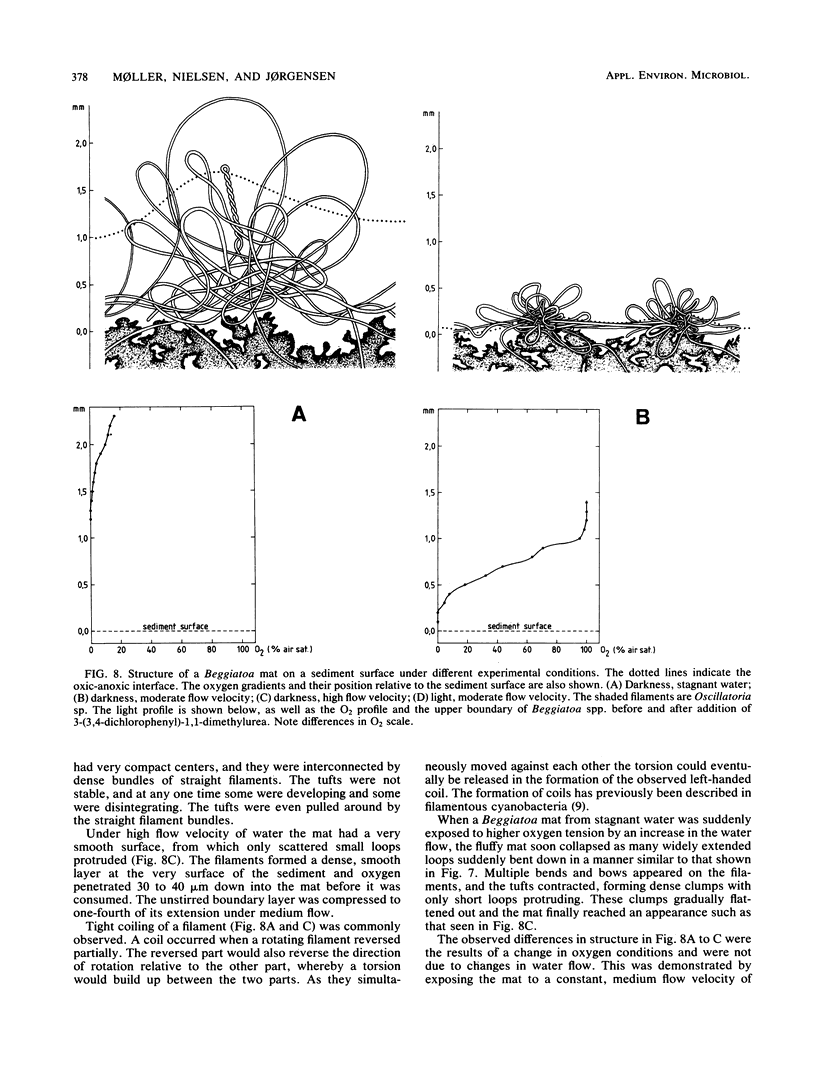
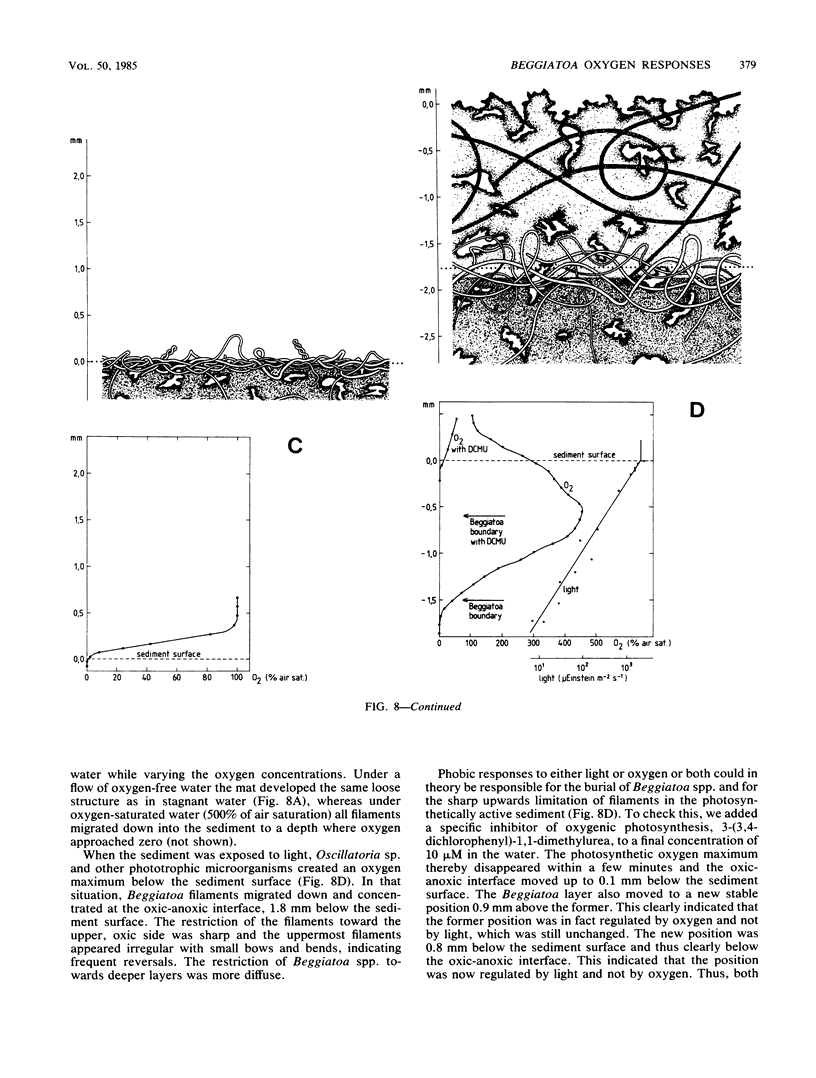
The behavioral response of single Beggiatoa sp. filaments moving on a gas-permeable membrane was studied by the combined use of microscopy and oxygen microelectrodes during controlled oscillations of oxygen tension. The bacteria reacted to increasing oxygen by reversing the direction of movement. The same step-up phobic response to oxygen was observed when a filament tip or loop glided into a stable microgradient of increasing oxygen. The response was sensitive to a change in oxygen tension of <5% of air saturation min−1. The response time was 20 to 50 s. Frequently, only part of the filament responded, which led to the formation of sharp bends, loops, and coils. This partial response facilitated the positioning of the long filaments within the narrow O2-H2S interface. The structure of whole Beggiatoa mats on sediment surfaces varied from loose to dense in relation to shallow or steep oxygen gradients in the 0.3- to 2-mm-thick, unstirred boundary layer. In an illuminated sediment Beggiatoa spp. lived together with photosynthetic organisms and migrated vertically in accordance with light/dark variations. The combined effect of phobic responses to light and oxygen can explain this migration.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON S. D., MORITA R. Y. EFFECT OF CATALASE AND CULTURAL CONDITIONS ON GROWTH OF BEGGIATOA. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1755–1761. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1755-1761.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAYTON R. K. Studies in the phototaxis of Rhodospirillum rubrum. III. Quantitative relations between stimulus and response. Arch Mikrobiol. 1953;19(2):141–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00446397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAUST L., WOLFE R. S. Enrichment and cultivation of Beggiatoa alba. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jan;81:99–106. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.1.99-106.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen B. B., Revsbech N. P., Blackburn T. H., Cohen Y. Diurnal cycle of oxygen and sulfide microgradients and microbial photosynthesis in a cyanobacterial mat sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):46–58. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.46-58.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen B. B., Revsbech N. P. Colorless Sulfur Bacteria, Beggiatoa spp. and Thiovulum spp., in O(2) and H(2)S Microgradients. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1261–1270. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1261-1270.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkin J. M., Strohl W. R. Beggiatoa, Thiothrix, and Thioploca. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:341–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S., Diehn B. Cytochrome c oxidase as the receptor molecule for chemoaccumulation (chemotaxis) of Euglena toward oxygen. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):548–549. doi: 10.1126/science.205948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. C., Castenholz R. W. Use of reduced sulfur compounds by Beggiatoa sp. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jul;147(1):140–154. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.1.140-154.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohl W. R., Larkin J. M. Enumeration, isolation, and characterization of beggiatoa from freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Nov;36(5):755–770. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.5.755-770.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. L., Miller J. B., Warrick H. M., Koshland D. E., Jr Electron acceptor taxis and blue light effect on bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):567–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.567-573.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]