Abstract
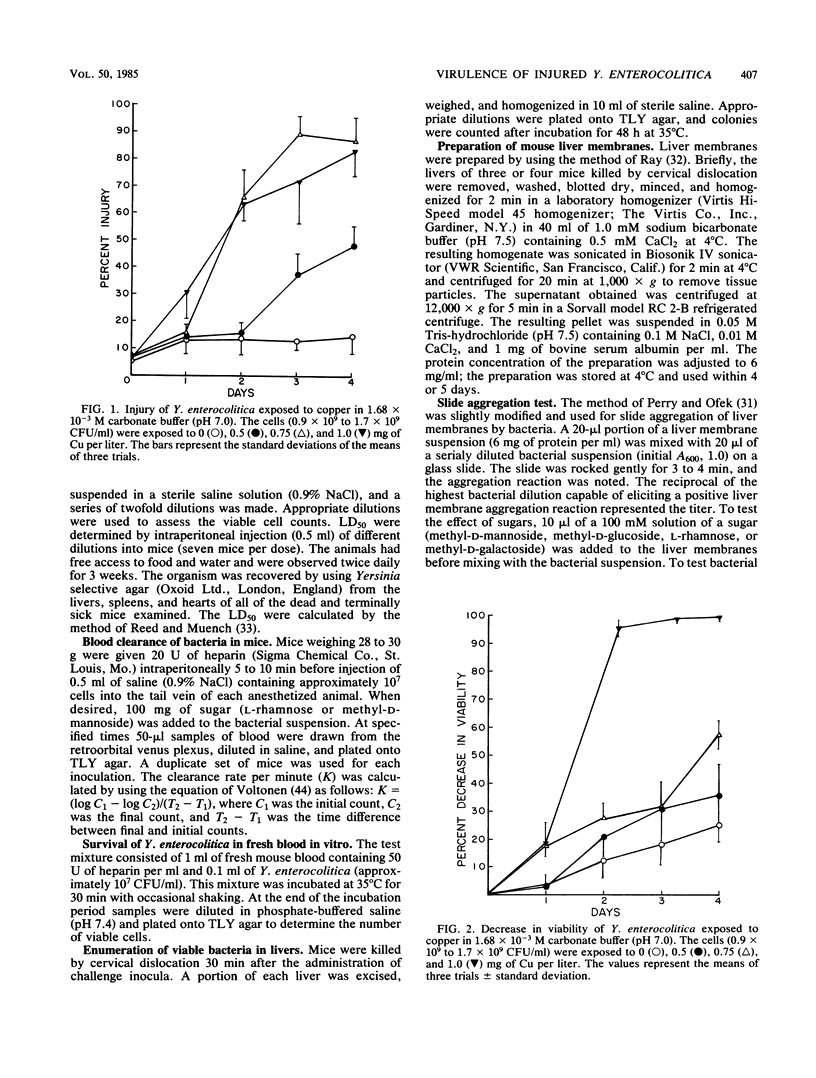
A sublethal concentration of copper (0.75 mg/liter) caused substantial injury (87 to 95%) of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:8 cells in 72 h at 4 degrees C without producing extensive cell death. Copper-injured cells had a higher 50% lethal dose in mice (2,700 CFU) than uninjured cells (150 CFU). This reduced virulence correlated with more rapid clearance of the injured cells from the blood of mice after intravenous inoculation. A possible role of the liver in this process was shown by significant cell accumulation in mouse livers when copper-injured Y. enterocolitica cells were administered, compared with uninjured bacteria. In vitro studies with isolated mouse liver membranes showed higher titers of aggregation with copper-injured cells than control cells. The in vitro aggregation reaction and blood clearance activity in vivo were abolished by sugars that are known to interact with a hepatic lectin. Our data suggest that copper-induced injury reduces the virulence of Y. enterocolitica and that the liver may be involved in nonimmune rapid clearance of the injured cells, probably by interaction with a hepatic lectin(s).
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asakawa Y., Akahane S., Kagata N., Noguchi M., Sakazaki R. Two community outbreaks of human infection with Yersinia enterocolitica. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Dec;71(4):715–723. doi: 10.1017/s002217240002297x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asakawa Y., Akahane S., Shiozawa K., Honma T. Investigations of source and route of Yersinia enterocolitica infection. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1979;5:115–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashwell G., Harford J. Carbohydrate-specific receptors of the liver. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:531–554. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aulisio C. C., Mehlman I. J., Sanders A. C. Alkali method for rapid recovery of Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis from foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.135-140.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENACERRAF B., SEBESTYEN M. M., SCHLOSSMAN S. A quantitative study of the kinetics of blood clearance of P32-labelled Escherichia coli and Staphylococci by the reticuloendothelial system. J Exp Med. 1959 Jul 1;110(1):27–48. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babich H., Stotzky G. Environmental factors that influence the toxicity of heavy metal and gaseous pollutants to microorganisms. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1980;8(2):99–145. doi: 10.3109/10408418009081123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottone E. J. Yersinia enterocolitica: a panoramic view of a charismatic microorganism. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977;5(2):211–241. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botzler R. G., Wetzler F. T., Cowan A. B., Quan T. J. Yersiniae in pond water and snails. J Wildl Dis. 1976 Oct;12(4):492–496. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-12.4.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins-Thompson D. L., Hurst A., Kruse H. Synthesis of enterotoxin B by Staphylococcus aureus strain S6 after recovery from heat injury. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Dec;19(12):1463–1468. doi: 10.1139/m73-238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domek M. J., LeChevallier M. W., Cameron S. C., McFeters G. A. Evidence for the role of copper in the injury process of coliform bacteria in drinking water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.289-293.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EL-Zawahry Y. A., Grecz N. Inactivation and injury of Yersinia enterocolitica by radiation and freezing. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Sep;42(3):464–468. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.3.464-468.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eden K. V., Rosenberg M. L., Stoopler M., Wood B. T., Highsmith A. K., Skaliy P., Wells J. G., Feeley J. C. Waterborne gastrointestinal illness at a ski resort. --Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica from drinking water--. Public Health Rep. 1977 May-Jun;92(3):245–250. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Zawahry Y. A., Rowley D. B. Radiation resistance and injury of Yersinia enterocolitica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):50–54. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.50-54.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Moon R. J. Hepatic clearance of Salmonella typhimurium in silica-treated mice. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):1005–1012. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.1005-1012.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grecz N., El-Zawahry Y. A. Effect of radiation and freezing on [3H]DNA of Yersinia enterocolitica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):1101–1105. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.1101-1105.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S., Greenwood J. R., Pickett M. J., Mah R. A. Recovery of Yersinia enterocolitica from streams and lakes of California. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Sep;32(3):352–354. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.3.352-354.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keet E. E. Yersinia enterocolitica septicemia. Source of infection and incubation period identified. N Y State J Med. 1974 Nov;74(12):2226–2230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihlström E., Magnusson K. E. Haemagglutinating, adhesive and physico-chemical surface properties of different Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia enterocolitica-like bacteria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Apr;91(2):113–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Zink D. L., Ferris W. R. Association of fibril structure formation with cell surface properties of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):272–275. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.272-275.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassen J. Yersinia enterocolitica in drinking-water. Scand J Infect Dis. 1972;4(2):125–127. doi: 10.3109/inf.1972.4.issue-2.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leunk R. D., Moon R. J. Association of type 1 pili with the ability of livers to clear Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1168–1174. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1168-1174.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFeters G. A., Cameron S. C., LeChevallier M. W. Influence of diluents, media, and membrane filters on detection fo injured waterborne coliform bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):97–103. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.97-103.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsovský Z., Olsáková V., Chobot S., Sviridov V. Mass occurrence of Yersinia enterocolitica in two establishments of collective care of children. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1975;19(1):22–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry A., Ofek I. Inhibition of blood clearance and hepatic tissue binding of Escherichia coli by liver lectin-specific sugars and glycoproteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):257–262. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.257-262.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray T. K. A modified method for the isolation of the plasma membrane from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 6;196(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restaino L., Jeter W. S., Hill W. M. Thermal injury of Yersinia enterocolitica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Nov;40(5):939–949. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.5.939-949.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann D. A. Association of Yersinia enterocolitica with the manufacture of cheese and occurrence in pasteurized milk. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):274–277. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.274-277.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiemann D. A., Toma S. Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica from raw milk. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jan;35(1):54–58. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.1.54-58.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelye R. J., Yearbury B. J. Isolation of Yersinia enterocolitica-resembling organisms and Alteromonas putrefaciens from vacuum-packed chilled beef cuts. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;46(3):493–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb00848.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Parsell Z. The effect of virulence of converting the O antigen of Salmonella cholerae-suis from 627 to 617 by phage. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Mar;81(1):217–224. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-1-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrells K. M., Speck M. L., Warren J. A. Pathogenicity of Salmonella gallinarum after metabolic injury by freezing. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jan;19(1):39–43. doi: 10.1128/am.19.1.39-43.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan B., Harmon M. C., Mehlman I. J. Yersinia enterocolitica. J Appl Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;52(2):151–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1982.tb04838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtonen M. V. Role of phagocytosis in mouse virulence of Salmonella typhimurium recombinants with O antigen 6,7 or 4,12. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):574–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.574-582.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh S. M., Bissonnette G. K. Chlorine-induced damage to surface adhesions during sublethal injury of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1060–1065. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.1060-1065.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenyoji H., Maruyama T., Sakai S., Kimura S., Mizuno T. An outbreak of enteritis due to Yersinia enterocolitica occurring at a junior high school. Jpn J Microbiol. 1973 May;17(3):220–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1973.tb00730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch J. F., de Graaff J., MacLaren D. M. Virulence of Escherichia coli in experimental hematogenous pyelonephritis in mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):68–74. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.68-74.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



