Abstract
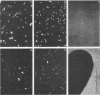
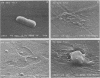
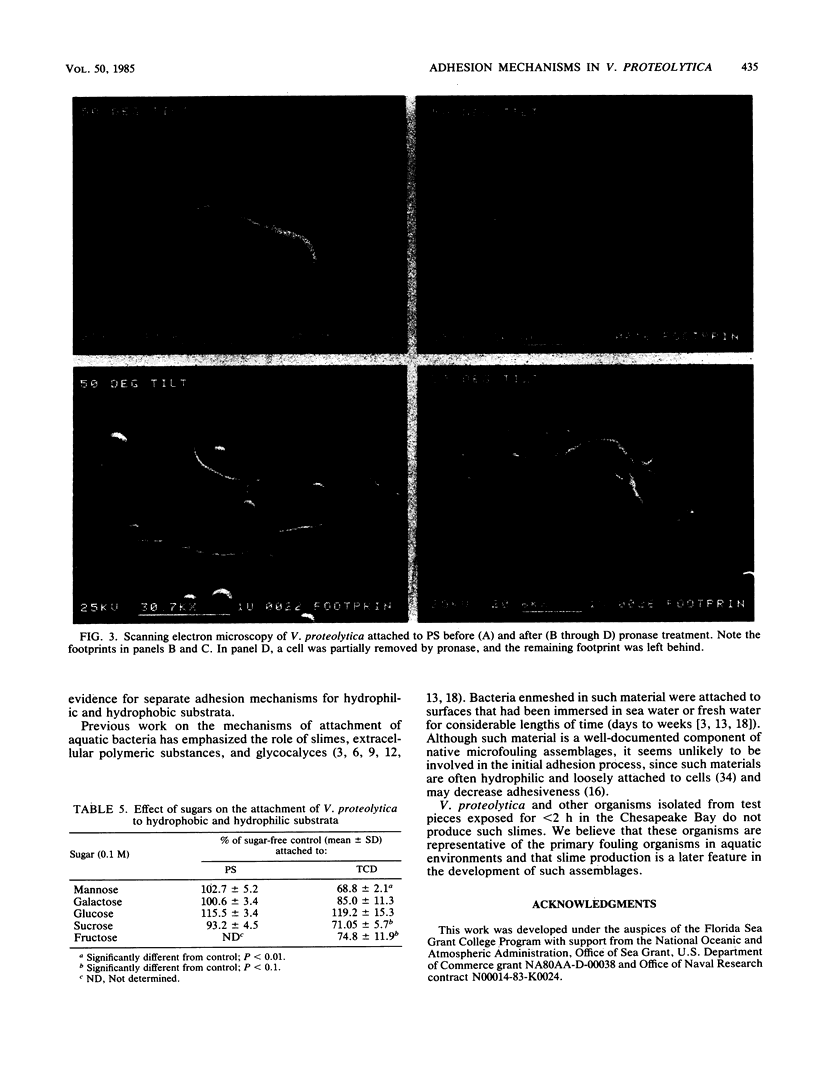
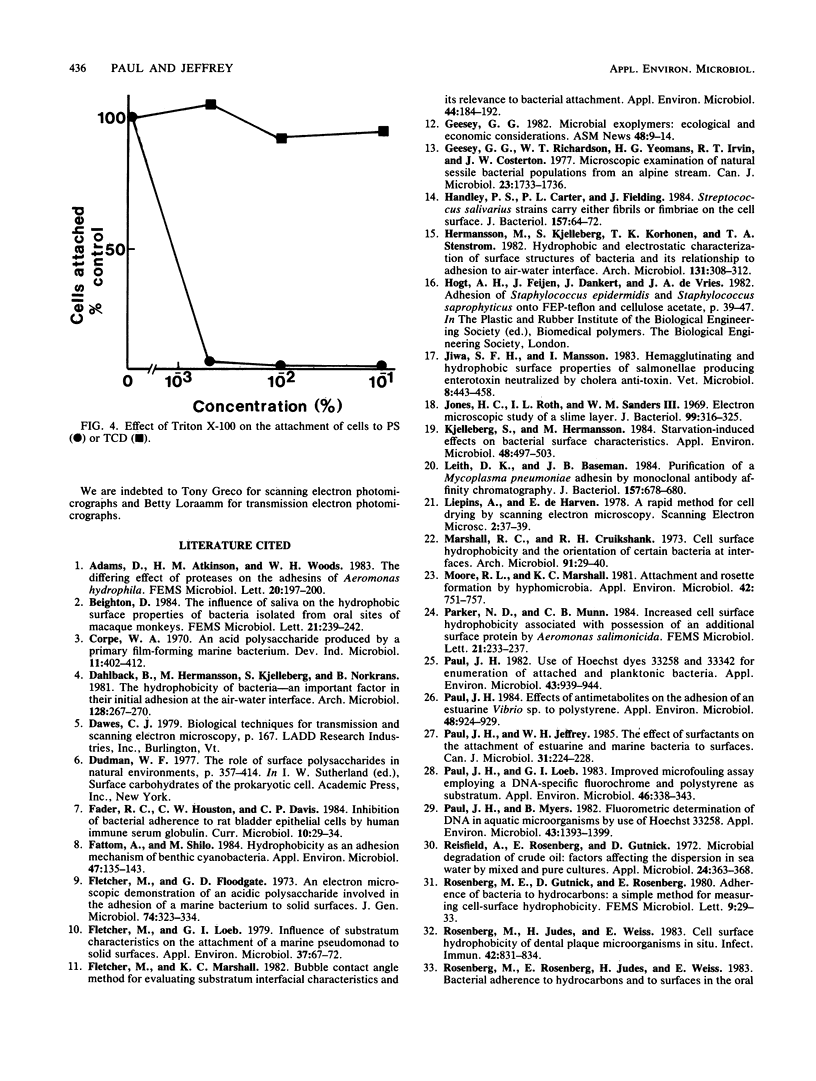
The proteolytic enzymes pronase, trypsin, and chymotrypsin and the surfactant Triton X-100 inhibited attachment of Vibrio proteolytica to the hydrophobic substratum polystyrene by >97%. These treatments had no effect on attachment to hydrophilic substrata such as glass or tissue culture dishes. Both pronase and Triton X-100 effected the removal of previously attached cells from polystyrene but not from hydrophilic surfaces. Removal of cells from polystyrene by pronase left material (which we have termed footprints) that stained with the protein-specific stain Hoechst 2495 but not with the DNA-specific stain Hoechst 33342. Pronase treatment also caused a significant decrease in cell surface hydrophobicity as determined by phase partitioning in hexane or petroleum ether. Collectively, these results imply the existence of separate mechanisms for the adhesion of V. proteolytica to hydrophilic and hydrophobic substrata and suggest a role for protein in the latter mechanism.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dahlbäck B., Hermansson M., Kjelleberg S., Norkrans B. The hydrophobicity of bacteria - an important factor in their initial adhesion at the air-water interface. Arch Microbiol. 1981 Jan;128(3):267–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00422527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattom A., Shilo M. Hydrophobicity as an adhesion mechanism of benthic cyanobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):135–143. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.135-143.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M., Loeb G. I. Influence of substratum characteristics on the attachment of a marine pseudomonad to solid surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):67–72. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.67-72.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M., Marshall K. C. Bubble contact angle method for evaluating substratum interfacial characteristics and its relevance to bacterial attachment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):184–192. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.184-192.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geesey G. G., Richardson W. T., Yeomans H. G., Irvin R. T., Costerton J. W. Microscopic examination of natural sessile bacterial populations from an alpine stream. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Dec;23(12):1733–1736. doi: 10.1139/m77-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley P. S., Carter P. L., Fielding J. Streptococcus salivarius strains carry either fibrils or fimbriae on the cell surface. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):64–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.64-72.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiwa S. F., Månsson I. Hemagglutinating and hydrophobic surface properties of salmonellae producing enterotoxin neutralized by cholera anti-toxin. Vet Microbiol. 1983 Oct;8(5):443–458. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(83)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones H. C., Roth I. L., Sanders W. M., 3rd Electron microscopic study of a slime layer. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):316–325. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.316-325.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelleberg S., Hermansson M. Starvation-induced effects on bacterial surface characteristics. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):497–503. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.497-503.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leith D. K., Baseman J. B. Purification of a Mycoplasma pneumoniae adhesin by monoclonal antibody affinity chromatography. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):678–680. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.678-680.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall K. C., Cruickshank R. H. Cell surface hydrophobicity and the orientation of certain bacteria at interfaces. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Apr 8;91(1):29–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00409536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. L., Marshall K. C. Attachment and rosette formation by hyphomicrobia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):751–757. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.751-757.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. H. Effects of antimetabolites on the adhesion of an estuarine Vibrio sp. to polystyrene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):924–929. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.924-929.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. H., Loeb G. I. Improved Microfouling Assay Employing a DNA-Specific Fluorochrome and Polystyrene as Substratum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):338–343. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.338-343.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. H., Myers B. Fluorometric determination of DNA in aquatic microorganisms by use of hoechst 33258. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1393–1399. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1393-1399.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. H. Use of hoechst dyes 33258 and 33342 for enumeration of attached and planktonic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Apr;43(4):939–944. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.4.939-944.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisfeld A., Rosenberg E., Gutnick D. Microbial degradation of crude oil: factors affecting the dispersion in sea water by mixed and pure cultures. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Sep;24(3):363–368. doi: 10.1128/am.24.3.363-368.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Judes H., Weiss E. Cell surface hydrophobicity of dental plaque microorganisms in situ. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):831–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.831-834.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]