Abstract
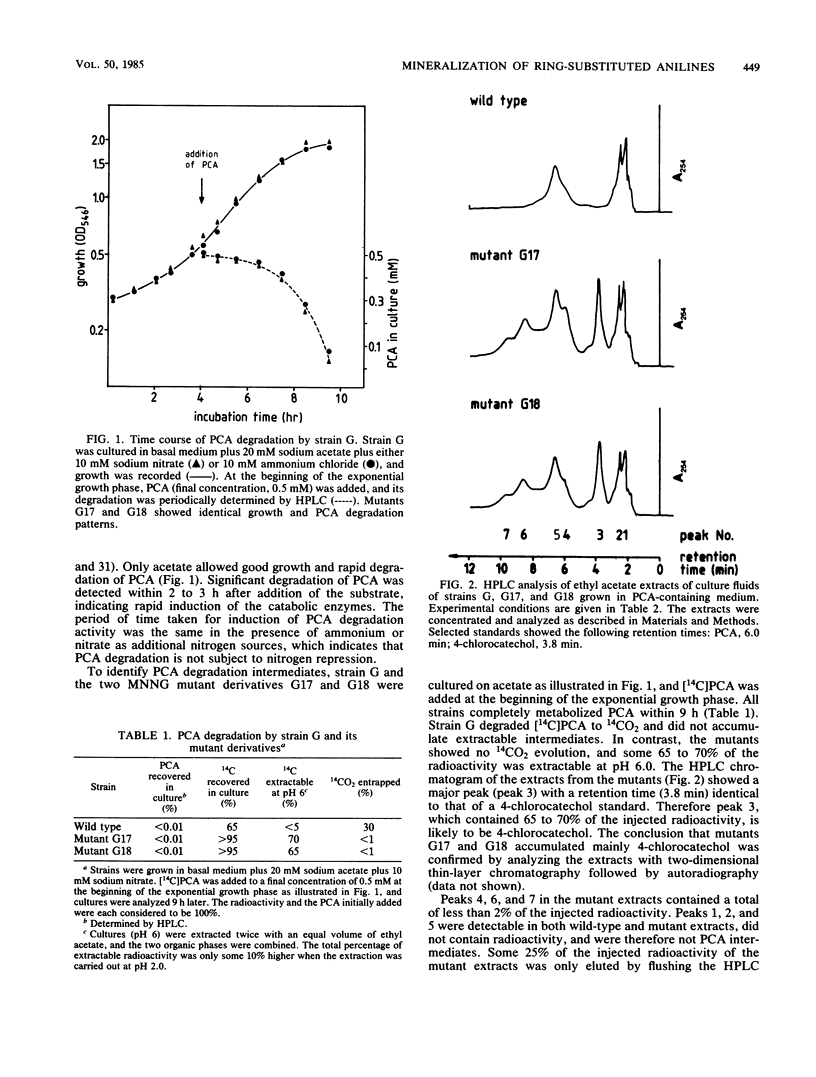
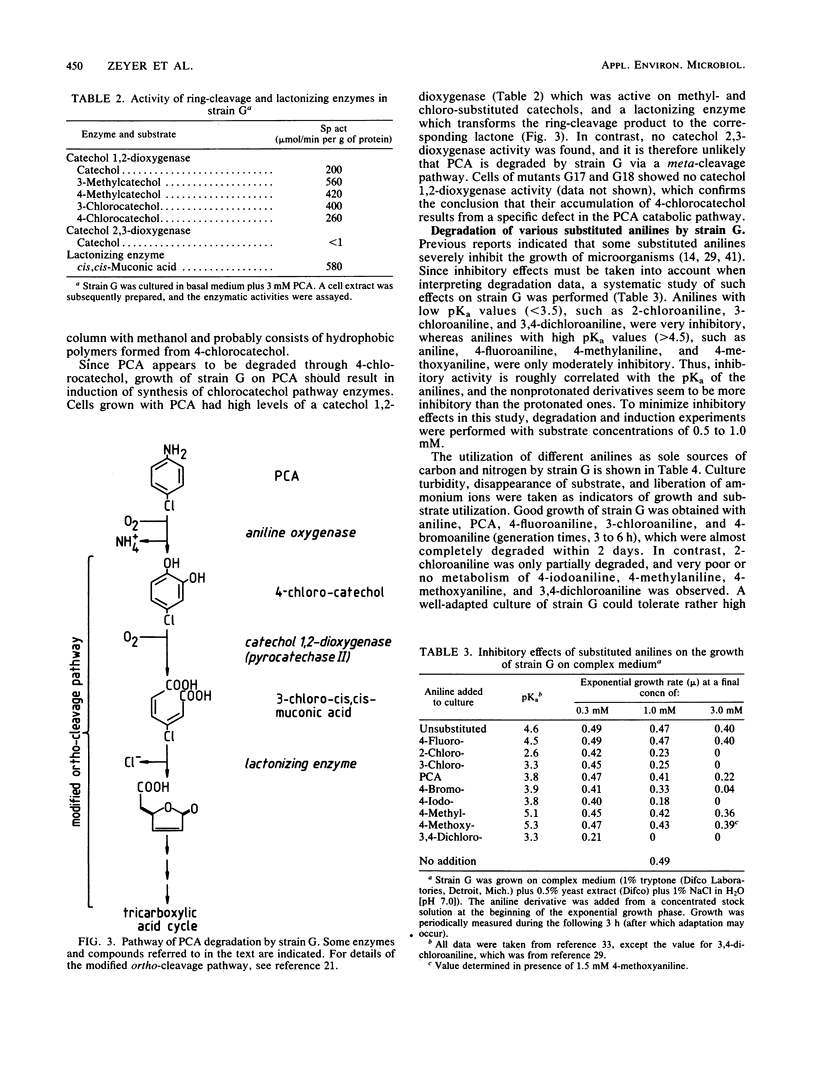
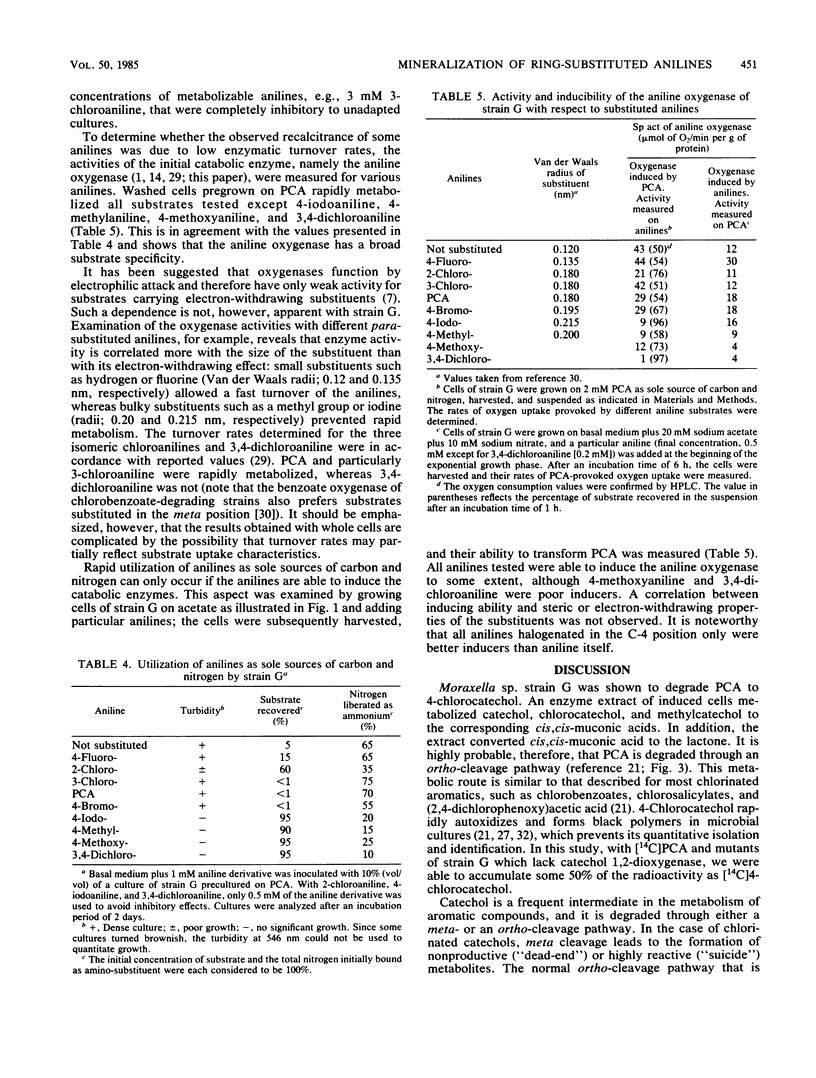
Moraxella sp. strain G is able to utilize as sole source of carbon and nitrogen aniline, 4-fluoroaniline, 2-chloroaniline, 3-chloroaniline, 4-chloroaniline (PCA), and 4-bromoaniline but not 4-iodoaniline, 4-methylaniline, 4-methoxyaniline, or 3,4-dichloroaniline. The generation time on PCA was 6 h. The pathway for the degradation of PCA was investigated by analysis of catabolic intermediates and enzyme activities. Mutants of strain G were isolated to enhance the accumulation of specific pathway intermediates. PCA was converted by an aniline oxygenase to 4-chlorocatechol, which in turn was degraded via a modified ortho-cleavage pathway. Synthesis of the aniline oxygenase was inducible by various anilines. This enzyme exhibited a broad substrate specificity. Its specific activity towards substituted anilines seemed to be correlated more with the size than with the electron-withdrawing effect of the substituent and was very low towards anilines having substituents larger than iodine or a methyl group. The initial enzyme of the modified ortho-cleavage pathway, catechol 1,2-dioxygenase, had similar characteristics to those of corresponding enzymes of pathways for the degradation of chlorobenzoic acid and chlorophenol, that is, a broad substrate specificity and high activity towards chlorinated and methylated catechols.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachofer R., Lingens F., Schäfer W. Conversion of aniline into pyrocatechol by a Nocardia sp.; incorporation of oxygen-18. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 1;50(2):288–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Doudoroff M., Stanier R. Y. Study of the Moraxella group. I. Genus Moraxella and the Neisseria catarrhalis group. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):58–73. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.58-73.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee D. K., Chakrabarty A. M. Genetic homology between independently isolated chlorobenzoate-degradative plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):532–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.532-534.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett M. D., Corbett B. R. Metabolism of 4-Chloronitrobenzene by the Yeast Rhodosporidium sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):942–949. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.942-949.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Pemberton J. M. Properties of six pesticide degradation plasmids isolated from Alcaligenes paradoxus and Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):681–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.681-686.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn E., Knackmuss H. J. Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds. Substituent effects on 1,2-dioxygenation of catechol. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):85–94. doi: 10.1042/bj1740085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallas L. E., Alexander M. Microbial transformation of nitroaromatic compounds in sewage effluent. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1234–1241. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1234-1241.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman G. D. Synthesis of the enzymes of the mandelate pathway by Pseudomonas putida. 3. Isolation and properties of constitutive mutants. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1161–1167. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1161-1167.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman G. D. Synthesis of the enzymes of the mandelate pathway by Pseudomonas putida. I. Synthesis of enzymes by the wild type. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1140–1154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1140-1154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegeman G. D. Synthesis of the enzymes of the mandelate pathway by Pseudomonas putida. II. Isolation and properties of blocked mutants. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1155–1160. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1155-1160.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. D., Plimmer J. R., Klingebiel U. I. Microbial oxidation of 4-chloroaniline. J Agric Food Chem. 1973 Jan-Feb;21(1):127–132. doi: 10.1021/jf60185a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinouchi T., Ohnishi Y. Purification and characterization of 1-nitropyrene nitroreductases from Bacteroides fragilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):596–604. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.596-604.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knackmuss H. J. Xenobiotic degradation in industrial sewage: haloaromatics as target substrates. Biochem Soc Symp. 1983;48:173–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick N. G., Feeherry F. E., Levinson H. S. Microbial transformation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene and other nitroaromatic compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):949–958. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.949-958.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minard R. D., Russel S., Bollag J. M. Chemical transformation of 4-chloroaniline to a triazene in a bacterial culture medium. J Agric Food Chem. 1977 Jul-Aug;25(4):841–844. doi: 10.1021/jf60212a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parris G. E. Environmental and metabolic transformations of primary aromatic amines and related compounds. Residue Rev. 1980;76:1–30. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-6107-0_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenate aromatic compounds. Substituent effects on 1,2-dioxygenation of benzoic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 6;542(3):412–423. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90372-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surovtseva E. G., Vasil'eva G. K., Vol'nova A. I., Baskunov B. P. Razrushenie monokhloranilinov po meta-puti Alcaligenes faecalis. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1980 Sep-Oct;254(1):226–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweedy B. G., Loeppky C., Ross J. A. Metabolism of 3-(p-bromophenyl)-1-methoxy-1-methylurea (metobromuron) by selected soil microorganisms. J Agric Food Chem. 1970 Sep-Oct;18(5):851–853. doi: 10.1021/jf60171a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- You I. S., Bartha R. Stimulation of 3,4-dichloroaniline mineralization by aniline. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):678–681. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.678-681.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



