Abstract
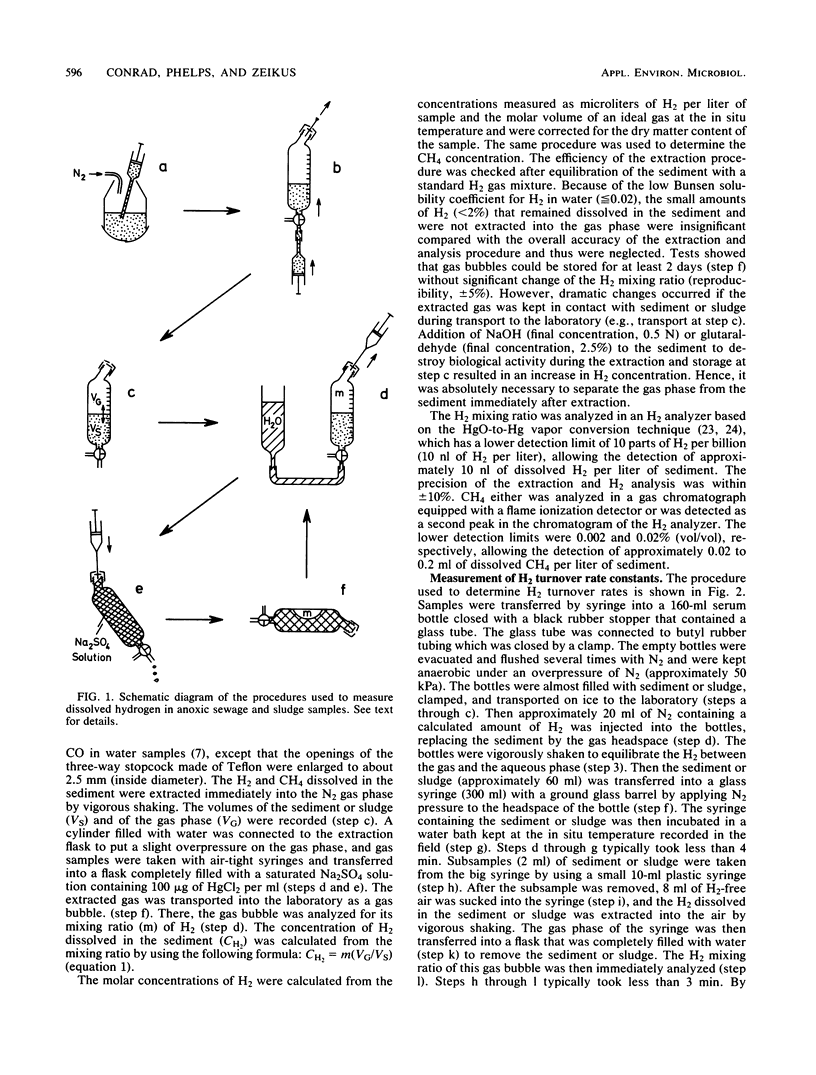
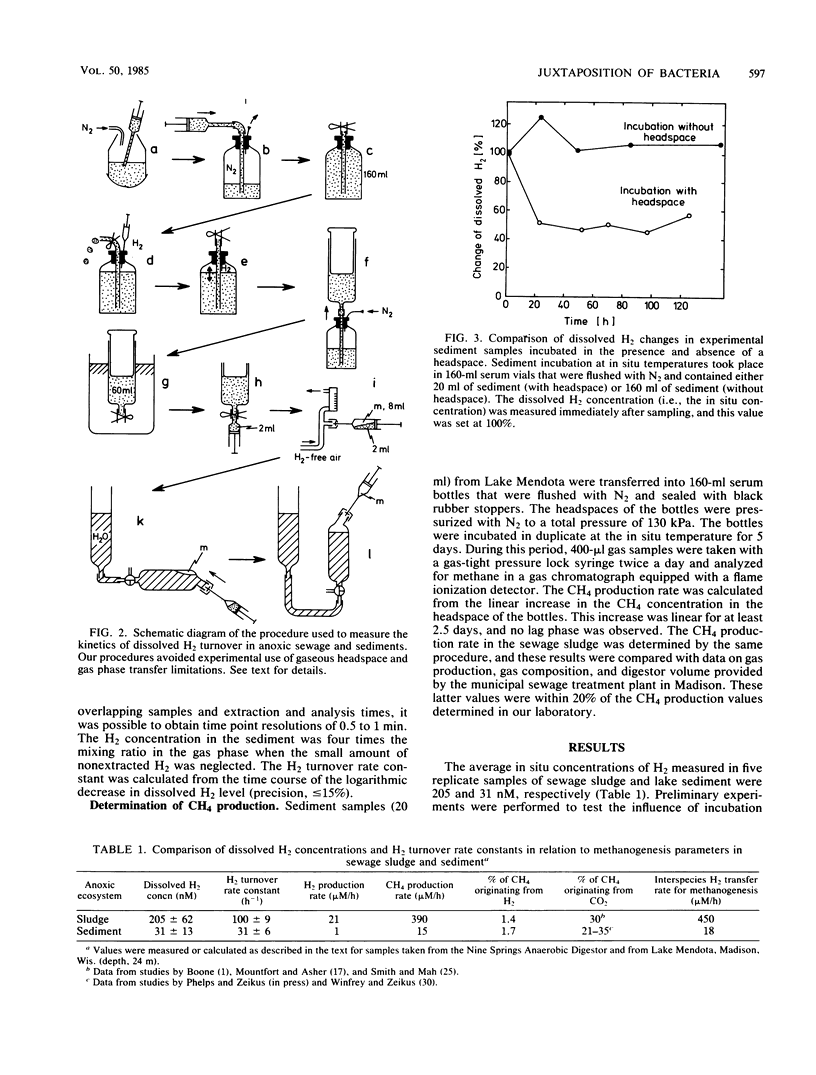
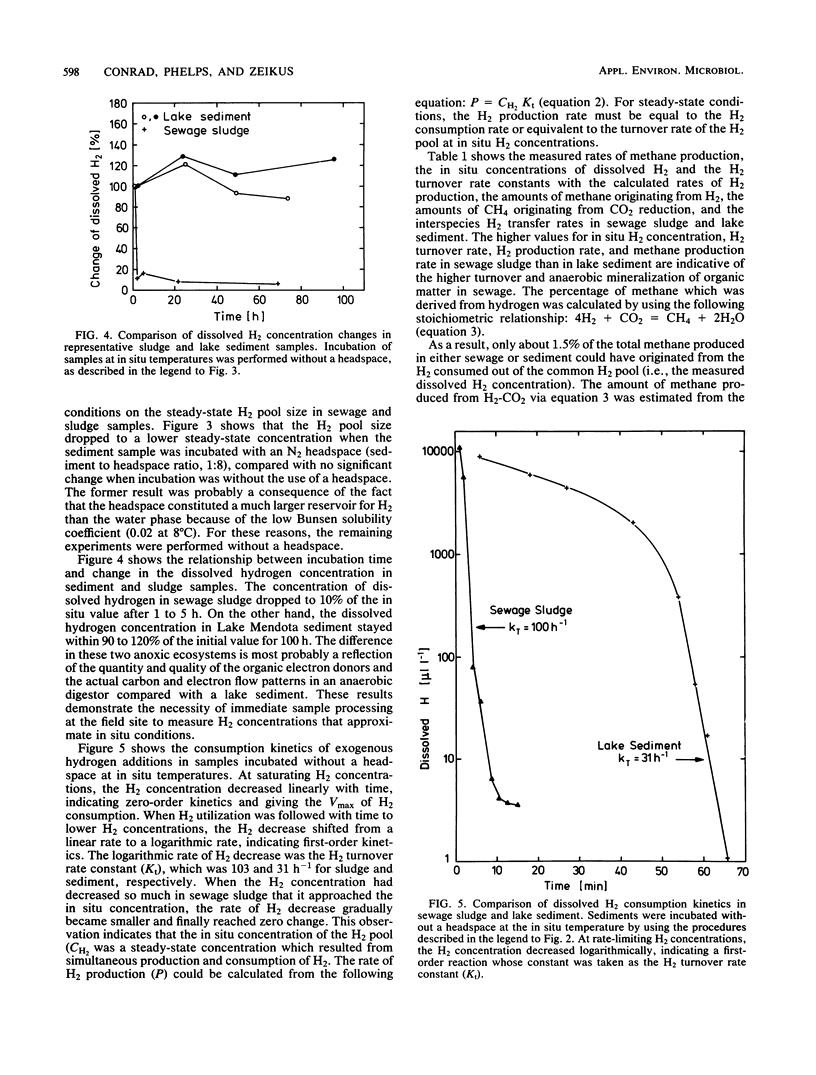
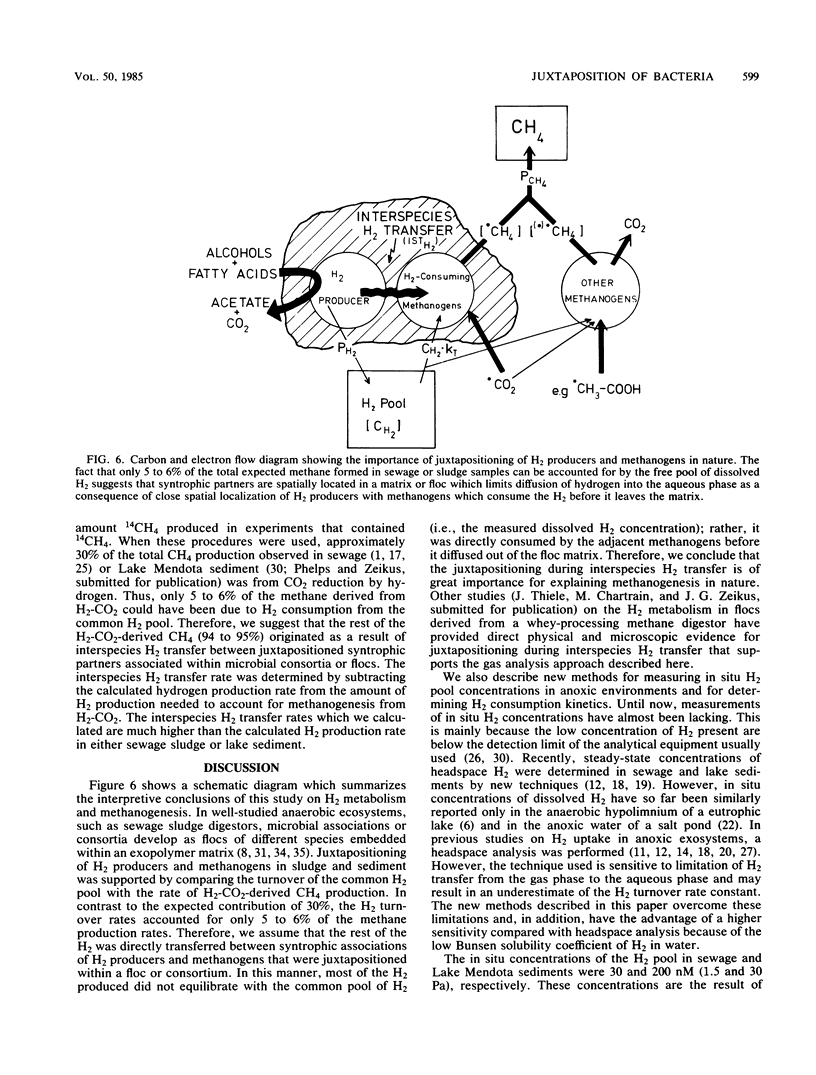
We developed new techniques to measure dissolved H2 and H2 consumption kinetics in anoxic ecosystems that were not dependent on headspace measurements or gas transfer-limited experimentation. These H2 metabolism parameters were then compared with measured methane production rates, and estimates of H2 production and interspecies H2 transfer were made. The H2 pool sizes were 205 and 31 nM in sewage sludge from an anaerobic digestor and in sediments (24 m) from Lake Mendota, respectively. The H2 turnover rate constants, as determined by using in situ pool sizes and temperatures, were 103 and 31 h−1 for sludge and sediment, respectively. The observed H2 turnover rate accounted for only 5 to 6% of the expected H2-CO2-dependent methanogenesis in these ecosystems. Our results are in general agreement with the results reported previously and are used to support the conclusion that most of the H2-dependent methanogenesis in these ecosystems occurs as a consequence of direct interspecies H2 transfer between juxtapositioned microbial associations within flocs or consortia.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boone D. R., Bryant M. P. Propionate-Degrading Bacterium, Syntrophobacter wolinii sp. nov. gen. nov., from Methanogenic Ecosystems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):626–632. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.626-632.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone D. R. Terminal reactions in the anaerobic digestion of animal waste. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):57–64. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.57-64.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P., Campbell L. L., Reddy C. A., Crabill M. R. Growth of desulfovibrio in lactate or ethanol media low in sulfate in association with H2-utilizing methanogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1162–1169. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1162-1169.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P., Wolin E. A., Wolin M. J., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacillus omelianskii, a symbiotic association of two species of bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):20–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00406313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappenberg T. E., Prins R. A. Interrelations between sulfate-reducing and methane-producing bacteria in bottom deposits of a fresh-water lake. 3. Experiments with 14C-labeled substrates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1974;40(3):457–469. doi: 10.1007/BF00399358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad R., Aragno M., Seiler W. Production and consumption of hydrogen in a eutrophic lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):502–510. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.502-510.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingvorsen K., Zeikus J. G., Brock T. D. Dynamics of bacterial sulfate reduction in a eutrophic lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Dec;42(6):1029–1036. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.6.1029-1036.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar H. F., Wuhrmann K. Kinetic parameters and relative turnovers of some important catabolic reactions in digesting sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.1-7.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Dwyer D. F., Klug M. J. Kinetic analysis of competition between sulfate reducers and methanogens for hydrogen in sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1373–1379. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1373-1379.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Klug M. J. Intermediary metabolism of organic matter in the sediments of a eutrophic lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):552–560. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.552-560.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Klug M. J. Sulfate reducers can outcompete methanogens at freshwater sulfate concentrations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):187–192. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.187-192.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInerney M. J., Bryant M. P., Hespell R. B., Costerton J. W. Syntrophomonas wolfei gen. nov. sp. nov., an Anaerobic, Syntrophic, Fatty Acid-Oxidizing Bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):1029–1039. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.1029-1039.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. A., Strayer R. F., Tiedje J. M. Method for measuring dissolved hydrogen in anaerobic ecosystems: application to the rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):545–548. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.545-548.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. A., Tiedje J. M. Kinetics of hydrogen consumption by rumen fluid, anaerobic digestor sludge, and sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1374–1384. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1374-1384.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. H., Mah R. A. Kinetics of acetate metabolism during sludge digestion. Appl Microbiol. 1966 May;14(3):368–371. doi: 10.1128/am.14.3.368-371.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strayer R. F., Tiedje J. M. Kinetic parameters of the conversion of methane precursors to methane in a hypereutrophic lake sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):330–340. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.330-340.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen J., Christensen D., Jørgensen B. B. Volatile Fatty acids and hydrogen as substrates for sulfate-reducing bacteria in anaerobic marine sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):5–11. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.5-11.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Jungermann K., Decker K. Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):100–180. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.100-180.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfrey M. R., Zeikus J. G. Anaerobic metabolism of immediate methane precursors in Lake Mendota. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Feb;37(2):244–253. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.2.244-253.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



