Abstract
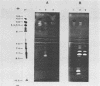
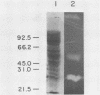
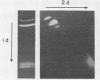
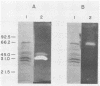
A system was developed for the rapid characterization of microbial pectic enzyme complexes and then tested on Erwinia chrysanthemi and Sclerotium rolfsii. Pectic enzymes in minute samples of crude culture filtrates were resolved by ultrathin-layer polyacrylamide gel isoelectric focusing and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and then assayed with an ultrathin pectate-agarose overlay stained with ruthenium red. The simple procedure can be completed within 30 min after isoelectric focusing, can detect extremely low levels of pectate lyase (6.4 × 10−6 μmol of product per min), and is sufficiently sensitive to determine the pectate lyase isozyme profile of a single bacterial colony with a diameter of 4 mm. Pectate lyases and polygalacturonases can be distinguished by altering buffer conditions in the overlays. The assay system revealed additional isozymes not resolved by classical techniques and generally corroborated the previously published isoelectric points and molecular weights of the pectate lyase isozymes and exo-poly-α-d-galacturonosidase produced by E. chrysanthemi and the endopolygalacturonase and exopolygalacturonase produced by S. rolfsii.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer W. D., Talmadge K. W., Keegstra K., Albersheim P. The Structure of Plant Cell Walls: II. The Hemicellulose of the Walls of Suspension-cultured Sycamore Cells. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):174–187. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertheau Y., Madgidi-Hervan E., Kotoujansky A., Nguyen-The C., Andro T., Coleno A. Detection of depolymerase isoenzymes after electrophoresis or electrofocusing, or in titration curves. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jun;139(2):383–389. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank A., Sugiyama R. H., Dekker C. A. Activity staining of nucleolytic enzymes after sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis: use of aqueous isopropanol to remove detergent from gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;120(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collmer A., Bateman D. F. Impaired induction and self-catabolite repression of extracellular pectate lyase in Erwinia chrysanthemi mutants deficient in oligogalacturonide lyase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3920–3924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collmer A., Schoedel C., Roeder D. L., Ried J. L., Rissler J. F. Molecular cloning in Escherichia coli of Erwinia chrysanthemi genes encoding multiple forms of pectate lyase. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):913–920. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.913-920.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collmer A., Whalen C. H., Beer S. V., Bateman D. F. An exo-poly-alpha-D-galacturonosidase implicated in the regulation of extracellular pectate lyase production in Erwinia chrysanthemi. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):626–634. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.626-634.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruickshank R. H., Wade G. C. Detection of pectic enzymes in pectin-acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90508-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis K. R., Lyon G. D., Darvill A. G., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions : XXV. Endopolygalacturonic Acid Lyase from Erwinia carotovora Elicits Phytoalexin Accumulation by Releasing Plant Cell Wall Fragments. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jan;74(1):52–60. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English P. D., Maglothin A., Keegstra K., Albersheim P. A Cell Wall-degrading Endopolygalacturonase Secreted by Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Plant Physiol. 1972 Mar;49(3):293–298. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppel L. A. Selective release of enzymes from bacteria. Science. 1967 Jun 16;156(3781):1451–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3781.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höfelmann M., Kittsteiner-Eberle R., Schreier P. Ultrathin-layer agar gels: a novel print technique for ultrathin-layer isoelectric focusing of enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jan;128(1):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90367-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen N. T., Dahlbeck D., Staskawicz B., Belser W. Molecular cloning of pectate lyase genes from Erwinia chrysanthemi and their expression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):825–831. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.825-831.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. A., Springhorn S. S. Renaturation of enzymes after polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7467–7473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. A., Springhorn S. S., Rosenthal A. L. Effect of the composition of sodium dodecyl sulfate preparations on the renaturation of enzymes after polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1979 Dec;100(2):357–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90241-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., West C. A. Polygalacturonase from Rhizopus stolonifer, an Elicitor of Casbene Synthetase Activity in Castor Bean (Ricinus communis L.) Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1981 Apr;67(4):633–639. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.4.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisker N., Retig N. Detection of polygalacturonase and pectin lyase isoenzymes in polyacrylamide gels. J Chromatogr. 1974 Sep 11;96(2):245–249. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)98570-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil M., Darvill A. G., Fry S. C., Albersheim P. Structure and function of the primary cell walls of plants. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:625–663. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARR M. P., MORAN F. Eliminative split of pectic substances by phytopathogenic soft-rot bacteria. Science. 1962 Mar 16;135(3507):920–921. doi: 10.1126/science.135.3507.920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegeman H. Enzym-Elektrophorese in Einschluss-Polymerisaten des Acrylamids. B. Polygalakturonasen (Pektinasen) Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Jul;348(7):951–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge K. W., Keegstra K., Bauer W. D., Albersheim P. The Structure of Plant Cell Walls: I. The Macromolecular Components of the Walls of Suspension-cultured Sycamore Cells with a Detailed Analysis of the Pectic Polysaccharides. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jan;51(1):158–173. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]