Abstract
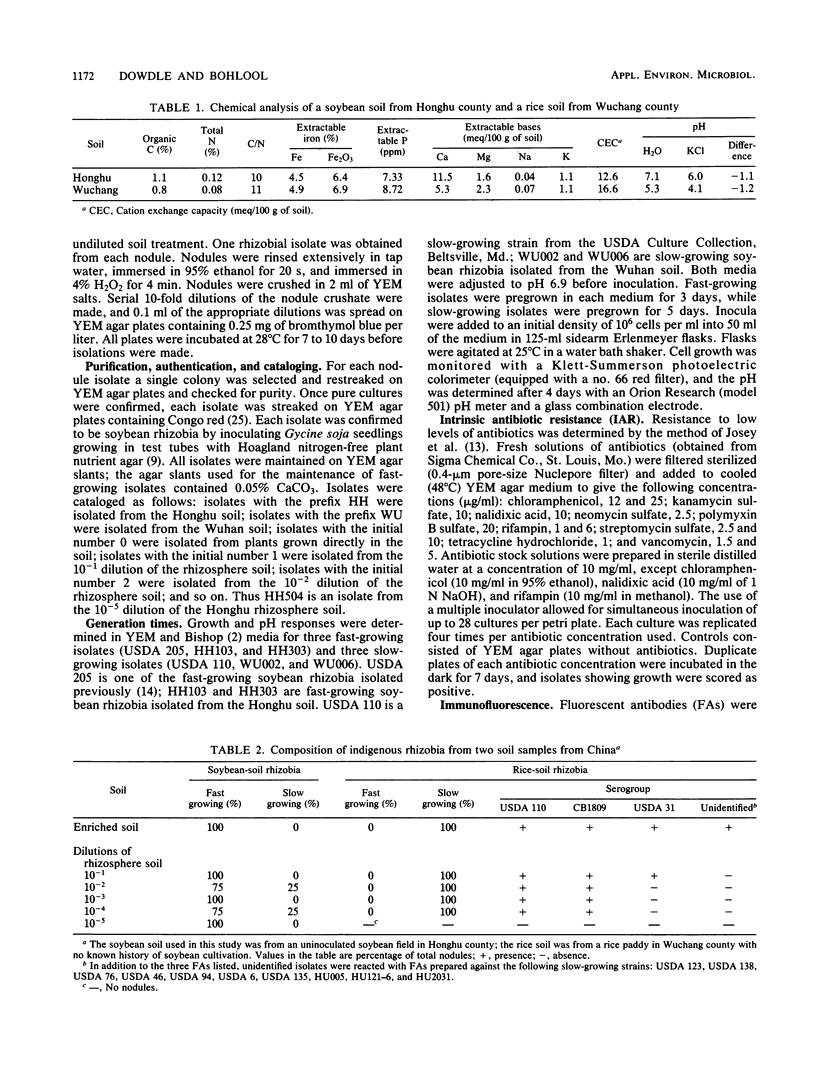
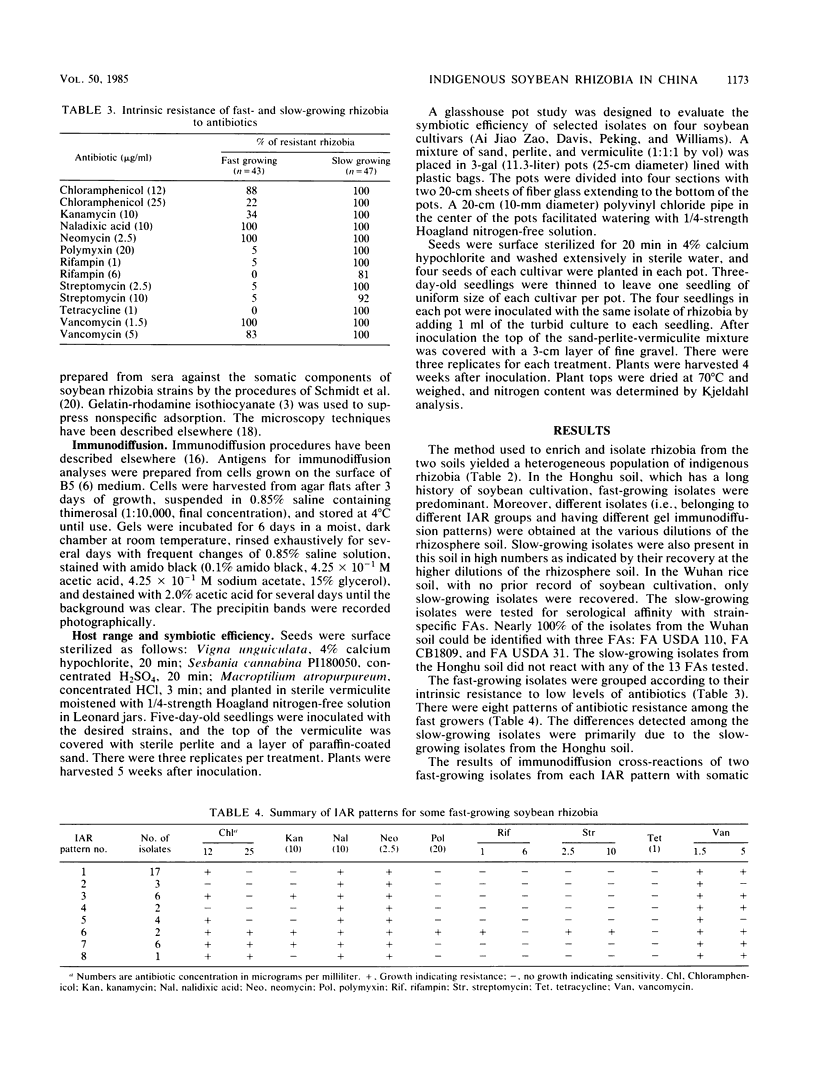
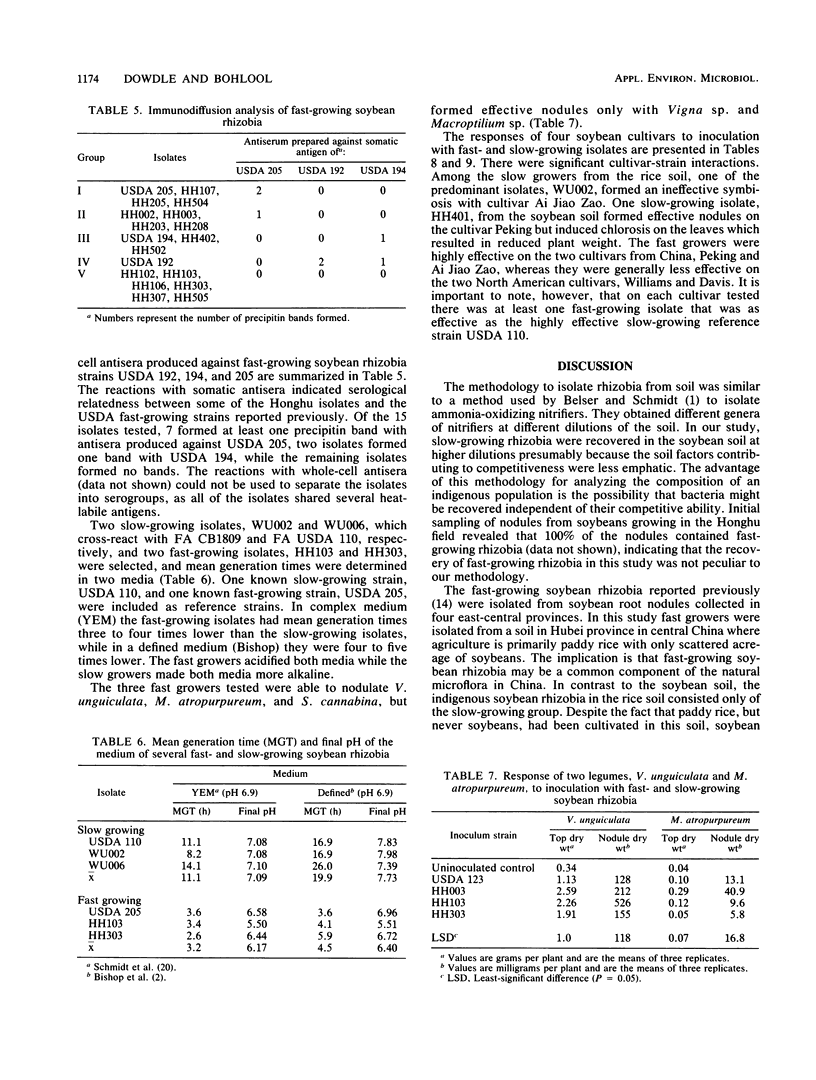
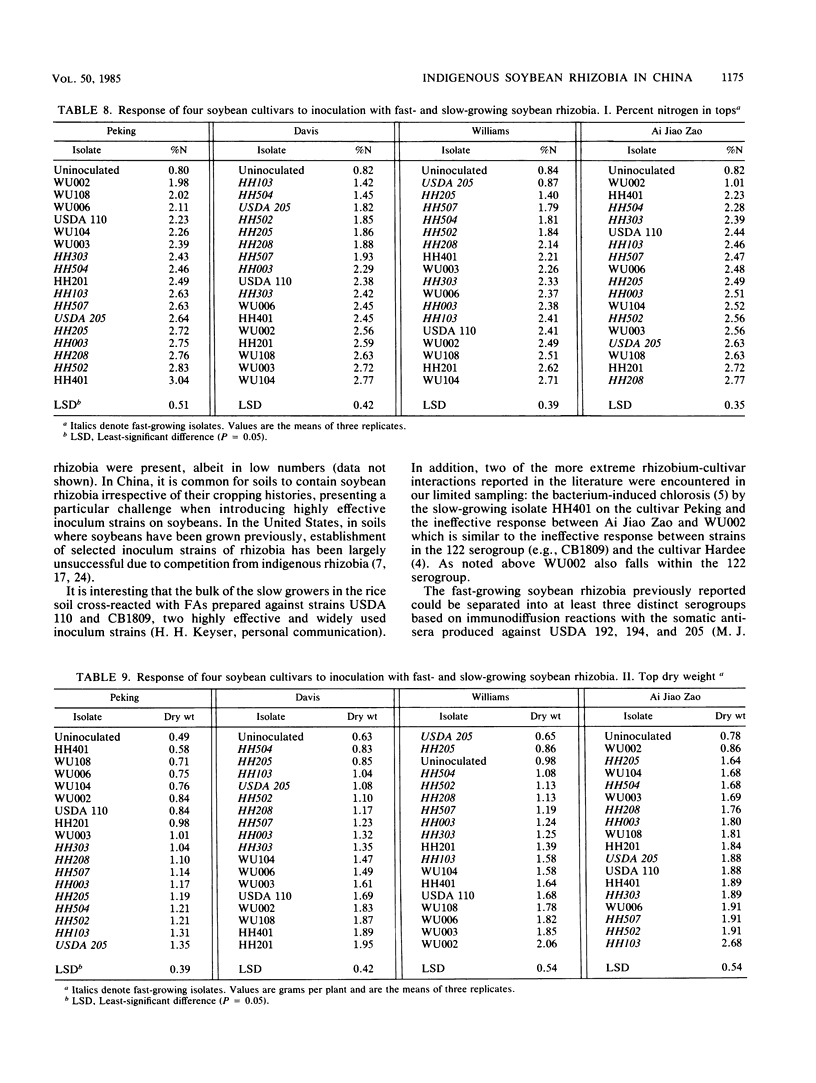
Soybean rhizobia were isolated from two soils with different cropping histories from Hubei province in central China. The first, from Honghu county, has been under soybean cultivation for decades. All of the isolates obtained from nodules on soybeans growing in this soil were fast-growing, acid-producing rhizobia. However, slow-growing, alkali-producing isolates were obtained at higher dilutions of the same soil. The second soil, from Wuchang county, has been under rice cultivation with no record of previous soybean cultivation. All of the soybean rhizobia recovered from this soil, and at higher dilutions of the soil, were typical slow-growing, alkali-producing isolates. The isolates from both soils were grouped by using intrinsic antibiotic resistance, gel immunodiffusion, and fluorescent-antibody procedures. Representative isolates were tested for symbiotic effectiveness with four soybean cultivars (Peking, Davis, Williams, and Ai Jiao Zao) in a pot experiment. There were significant cultivar-rhizobial interactions. Moreover, on each cultivar, there was at least one fast-growing isolate among these new rhizobia that was as effective as the highly effective slow-growing reference strain USDA 110.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belser L. W., Schmidt E. L. Diversity in the ammonia-oxidizing nitrifier population of a soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Oct;36(4):584–588. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.4.584-588.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Guevara J. G., Engelke J. A., Evans H. J. Relation between Glutamine Synthetase and Nitrogenase Activities in the Symbiotic Association between Rhizobium japonicum and Glycine max. Plant Physiol. 1976 Apr;57(4):542–546. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.4.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Nonspecific staining: its control in immunofluorescence examination of soil. Science. 1968 Nov 29;162(3857):1012–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3857.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori J., Johnson D. A. Fast-Growing Rhizobium japonicum That Effectively Nodulates Several Commercial Glycine max L. Merrill Cultivars. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):234–235. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.234-235.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyser H. H., Bohlool B. B., Hu T. S., Weber D. F. Fast-growing rhizobia isolated from root nodules of soybean. Science. 1982 Mar 26;215(4540):1631–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4540.1631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May S. N., Bohlool B. B. Competition Among Rhizobium leguminosarum Strains for Nodulation of Lentils (Lens esculenta). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):960–965. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.960-965.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. L., Bakole R. O., Bohlool B. B. Fluorescent-antibody approach to study of rhizobia in soil. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):1987–1992. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.1987-1992.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


