Abstract
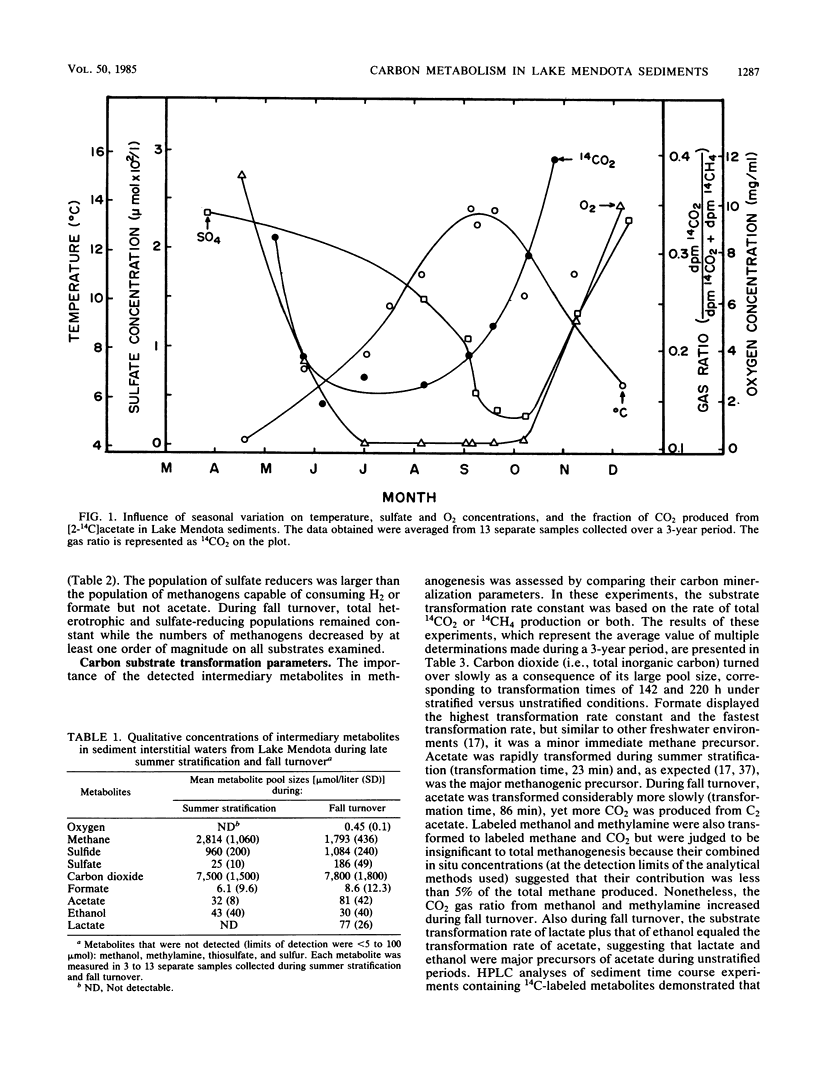
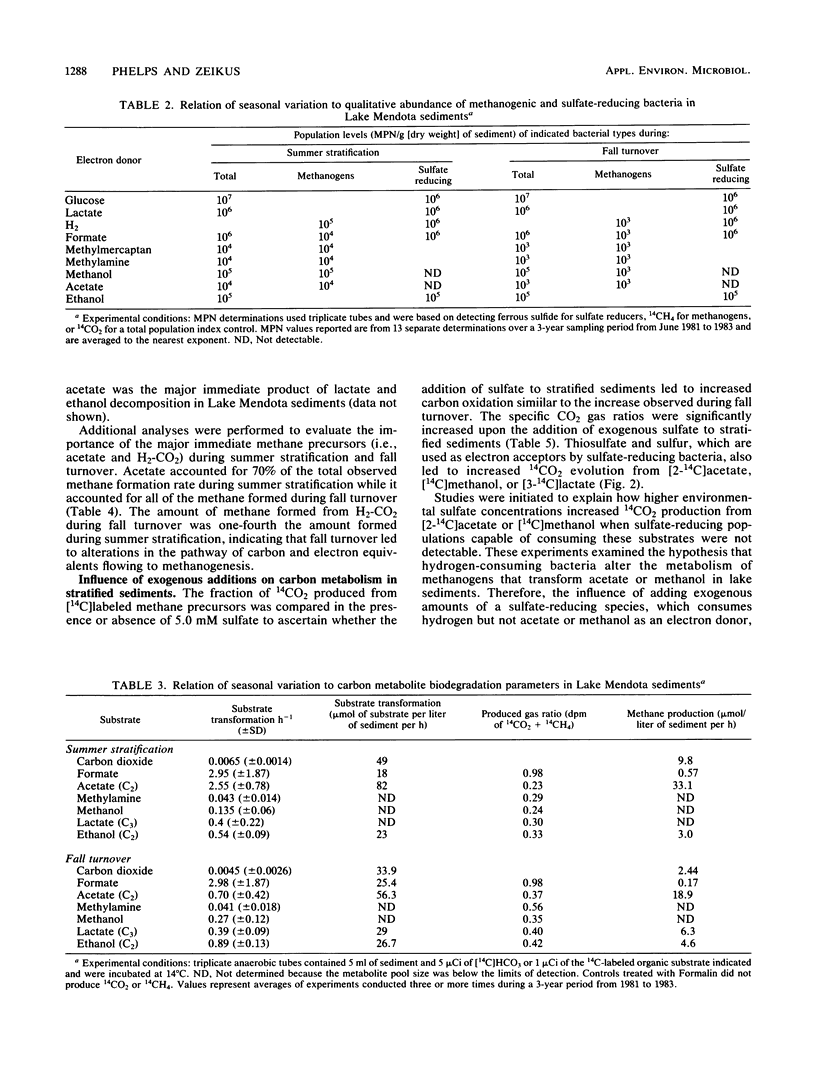
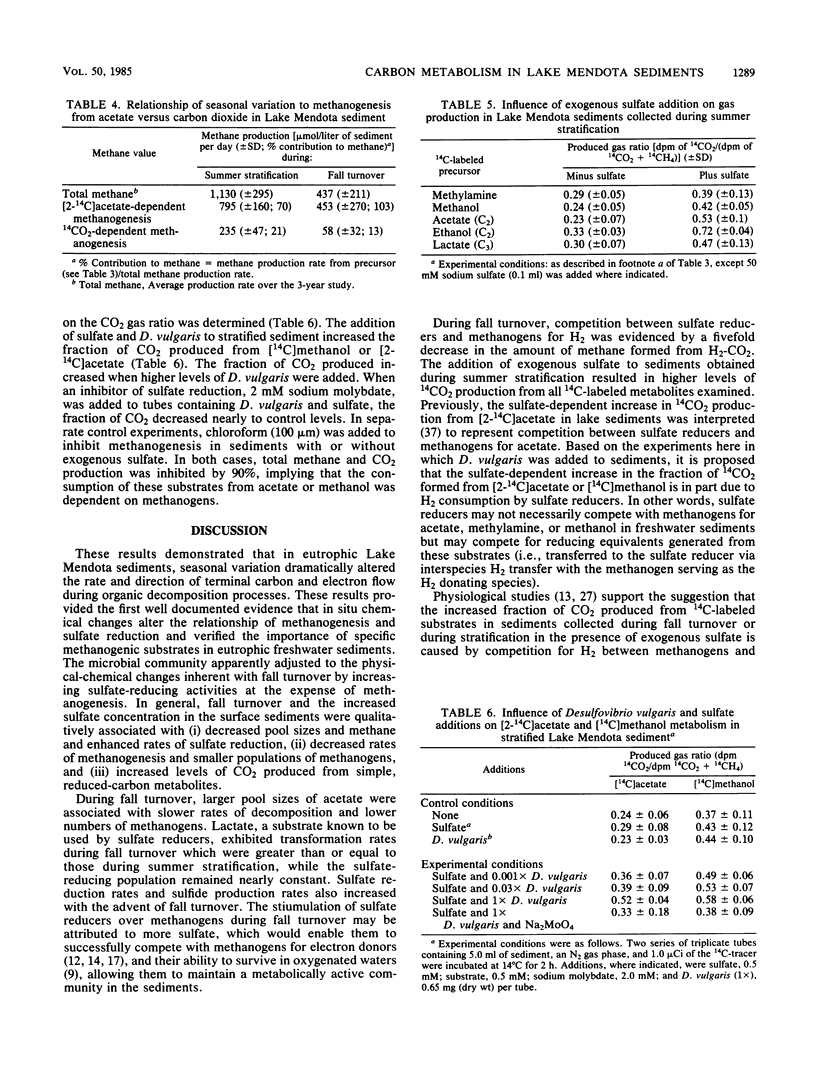
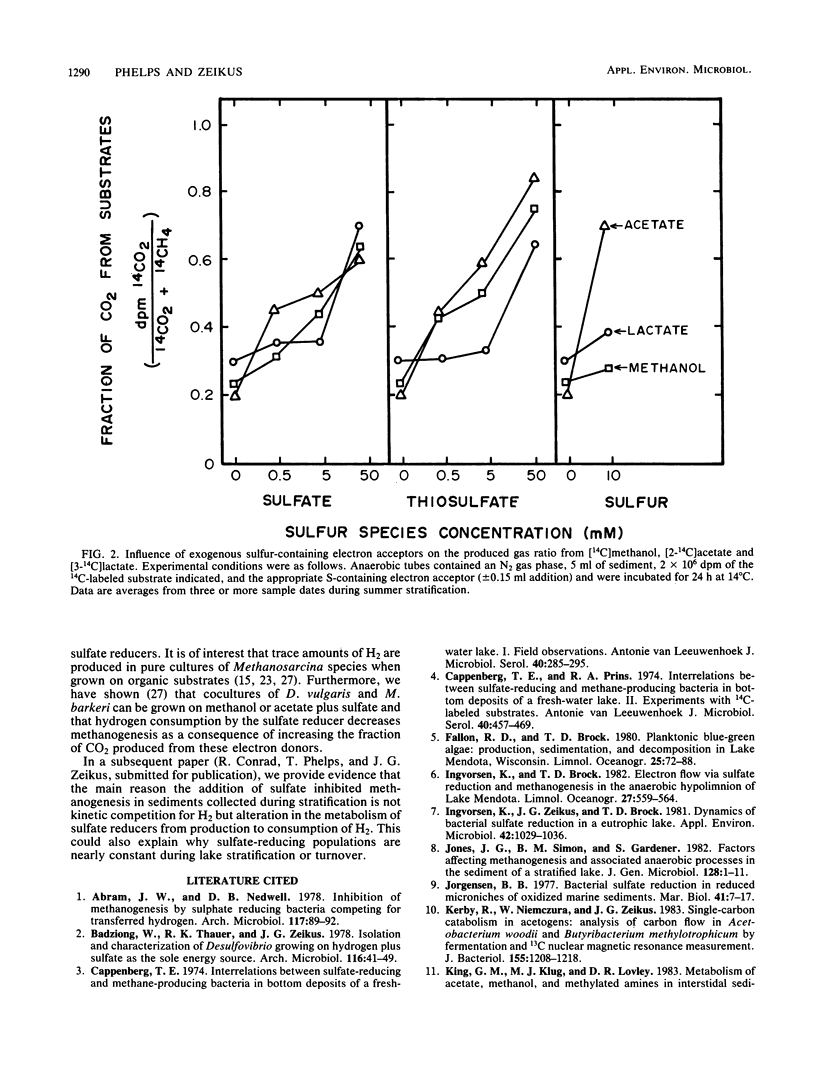
The carbon and electron flow pathways and the bacterial populations responsible for the transformation of H2-CO2, formate, methanol, methylamine, acetate, ethanol, and lactate were examined in eutrophic sediments collected during summer stratification and fall turnover. The rate of methane formation averaged 1,130 μmol of CH4 per liter of sediment per day during late-summer stratification versus 433 μmol of CH4 per liter of sediment per day during the early portion of fall turnover, whereas the rate of sulfate reduction was 280 μmol of sulfate per liter of sediment per day versus 1,840 μmol of sulfate per liter of sediment per day during the same time periods, respectively. The sulfate-reducing population remained constant while the methanogenic population decreased by one to two orders of magnitude during turnover. The acetate concentration increased from 32 to 81 μmol per liter of sediment while the acetate transformation rate constant decreased from 3.22 to 0.70 per h, respectively, during stratification versus turnover. Acetate accounted for nearly 100% of total sedimentary methanogenesis during turnover versus 70% during stratification. The fraction of 14CO2 produced from all 14C-labeled substrates examined was 10 to 40% higher during fall turnover than during stratification. The addition of sulfate, thiosulfate, or sulfur to stratified sediments mimicked fall turnover in that more CO2 and CH4 were produced. The addition of Desulfovibrio vulgaris to sulfate-amended sediments greatly enhanced the amount of CO2 produced from either [14C]methanol or [2-14C]acetate, suggesting that H2 consumption by sulfate reducers can alter methanol or acetate transformation by sedimentary methanogens. These data imply that turnover dynamically altered carbon transformation in eutrophic sediments such that sulfate reduction dominated over methanogenesis principally as a consequence of altering hydrogen metabolism.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abram J. W., Nedwell D. B. Inhibition of methanogenesis by sulphate reducing bacteria competing for transferred hydrogen. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Apr 27;117(1):89–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00689356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badziong W., Thauer R. K., Zeikus J. G. Isolation and characterization of Desulfovibrio growing on hydrogen plus sulfate as the sole energy source. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Jan 23;116(1):41–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00408732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappenberg T. E. Interrelations between sulfate-reducing and methane-producing bacteria in bottom deposits of a fresh-water lake. I. Field observations. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1974;40(2):285–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00394387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappenberg T. E., Prins R. A. Interrelations between sulfate-reducing and methane-producing bacteria in bottom deposits of a fresh-water lake. 3. Experiments with 14C-labeled substrates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1974;40(3):457–469. doi: 10.1007/BF00399358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingvorsen K., Zeikus J. G., Brock T. D. Dynamics of bacterial sulfate reduction in a eutrophic lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Dec;42(6):1029–1036. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.6.1029-1036.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerby R., Niemczura W., Zeikus J. G. Single-carbon catabolism in acetogens: analysis of carbon flow in Acetobacterium woodii and Butyribacterium methylotrophicum by fermentation and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance measurement. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1208–1218. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1208-1218.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. M., Klug M. J., Lovley D. R. Metabolism of acetate, methanol, and methylated amines in intertidal sediments of lowes cove, maine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jun;45(6):1848–1853. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.6.1848-1853.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzycki J. A., Wolkin R. H., Zeikus J. G. Comparison of unitrophic and mixotrophic substrate metabolism by acetate-adapted strain of Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):247–254. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.247-254.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovitt R. W., Longin R., Zeikus J. G. Ethanol Production by Thermophilic Bacteria: Physiological Comparison of Solvent Effects on Parent and Alcohol-Tolerant Strains of Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):171–177. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.171-177.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Dwyer D. F., Klug M. J. Kinetic analysis of competition between sulfate reducers and methanogens for hydrogen in sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1373–1379. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1373-1379.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Ferry J. G. Production and Consumption of H(2) during Growth of Methanosarcina spp. on Acetate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):247–249. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.247-249.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Klug M. J. Intermediary metabolism of organic matter in the sediments of a eutrophic lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):552–560. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.552-560.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Klug M. J. Sulfate reducers can outcompete methanogens at freshwater sulfate concentrations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):187–192. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.187-192.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynd L., Kerby R., Zeikus J. G. Carbon monoxide metabolism of the methylotrophic acidogen Butyribacterium methylotrophicum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):255–263. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.255-263.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Zeikus J. G. Rapid method for the radioisotopic analysis of gaseous end products of anaerobic metabolism. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):258–261. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.258-261.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. M., Wolkin R. H., Moench T. T., Morgan J. B., Zeikus J. G. Association of hydrogen metabolism with unitrophic or mixotrophic growth of Methanosarcina barkeri on carbon monoxide. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):373–375. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.373-375.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oremland R. S., Polcin S. Methanogenesis and sulfate reduction: competitive and noncompetitive substrates in estuarine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1270–1276. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1270-1276.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps T. J., Conrad R., Zeikus J. G. Sulfate-Dependent Interspecies H(2) Transfer between Methanosarcina barkeri and Desulfovibrio vulgaris during Coculture Metabolism of Acetate or Methanol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Sep;50(3):589–594. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.3.589-594.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps T. J., Zeikus J. G. Influence of pH on Terminal Carbon Metabolism in Anoxic Sediments from a Mildly Acidic Lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1088–1095. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1088-1095.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansone F. J., Martens C. S. Methane production from acetate and associated methane fluxes from anoxic coastal sediments. Science. 1981 Feb 13;211(4483):707–709. doi: 10.1126/science.211.4483.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior E., Lindström E. B., Banat I. M., Nedwell D. B. Sulfate reduction and methanogenesis in the sediment of a saltmarsh on the East coast of the United kingdom. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):987–996. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.987-996.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Klug M. J. Electron donors utilized by sulfate-reducing bacteria in eutrophic lake sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):116–121. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.116-121.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strayer R. F., Tiedje J. M. Kinetic parameters of the conversion of methane precursors to methane in a hypereutrophic lake sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):330–340. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.330-340.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfrey M. R., Nelson D. R., Klevickis S. C., Zeikus J. G. Association of hydrogen metabolism with methanogenesis in Lake Mendota sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):312–318. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.312-318.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfrey M. R., Ward D. M. Substrates for sulfate reduction and methane production in intertidal sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):193–199. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.193-199.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfrey M. R., Zeikus J. G. Anaerobic metabolism of immediate methane precursors in Lake Mendota. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Feb;37(2):244–253. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.2.244-253.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfrey M. R., Zeikus J. G. Effect of sulfate on carbon and electron flow during microbial methanogenesis in freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):275–281. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.275-281.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G. Metabolism of one-carbon compounds by chemotrophic anaerobes. Adv Microb Physiol. 1983;24:215–299. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60387-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



