Abstract
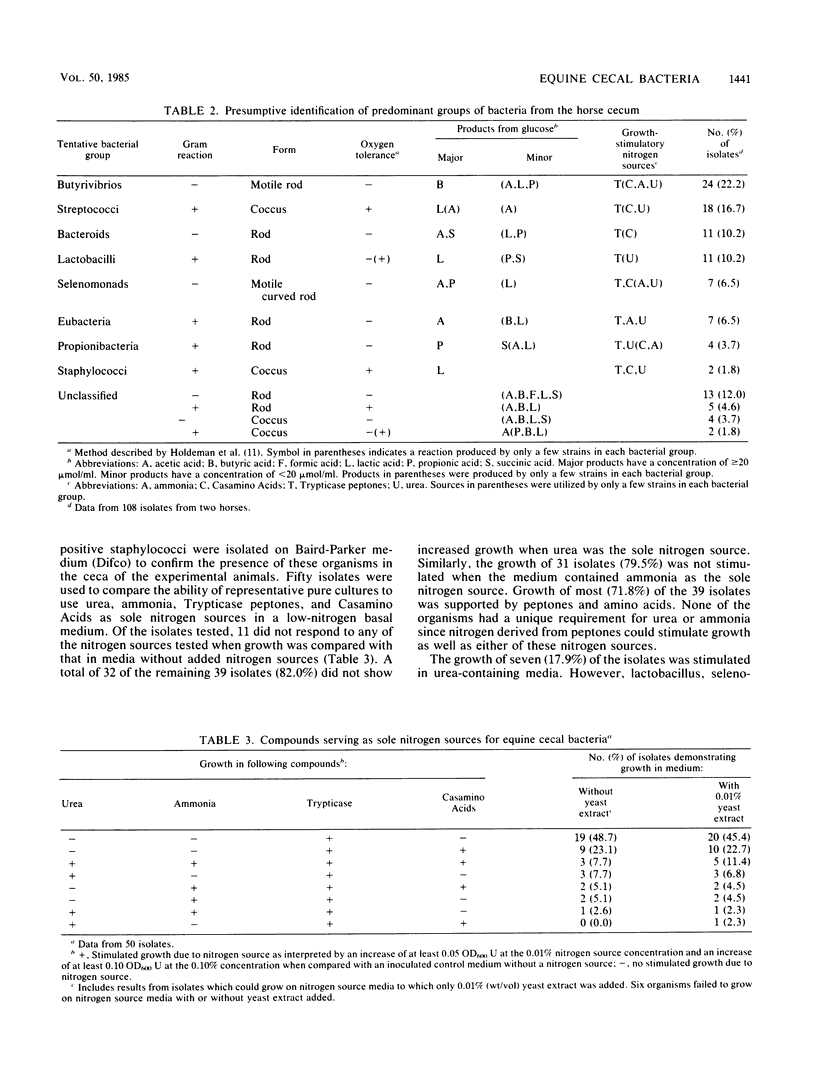
A total of 114 bacterial isolates were obtained from the cecal contents of two mature cecally fistulated horses on a habitat-simulating medium containing 40% energy-depleted cecal fluid. Of these isolates, 108 were maintained in pure cultures and were tentatively grouped on the basis of cell morphology and physiological characteristics. Gram-negative rods (50.9%), gram-positive rods (22.8%), and gram-positive cocci (21.9%) represented the largest groups isolated from these animals. Fifty isolates were tested for their ability to grow in media containing urea, ammonia, peptones, or amino acids as sole nitrogen sources. None of the isolates had a unique requirement for urea or ammonia since nitrogen derived from peptones, amino acids, or both supported growth as well as did ammonia or urea in a low nitrogen medium. Of the cecal isolates, 18% were able to use urea for growth, and 20.5% were able to grow with ammonia as the sole nitrogen source. All organisms grew in the experimental media containing peptones as the sole nitrogen source. Urease activity was detected in only 2 of 114 isolates tested. The inability of isolates to use urea or ammonia as nitrogen sources may have been a reflection of growth conditions in the habitat-stimulating medium used for isolation, but it could also suggest that many cecal bacteria require nitrogen sources other then ammonia or urea for growth.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER F., DAVIES M. E. Production and fermentation of lactate by bacteria in the alimentary canal of the horse and pig. J Comp Pathol. 1963 Jan;73:1–8. doi: 10.1016/s0368-1742(63)80001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison M. J., Robinson I. M., Bucklin J. A., Booth G. D. Comparison of bacterial populations of the pig cecum and colon based upon enumeration with specific energy sources. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1142–1151. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1142-1151.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., ROBINSON I. M. Some nutritional characteristics of predominant culturable ruminal bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:605–614. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.605-614.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P. Commentary on the Hungate technique for culture of anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1324–1328. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Wallace R. J. The mechanism of passage of endogenous urea through the rumen wall and the role of ureolytic epithelial bacteria in the urea flux. Br J Nutr. 1979 Nov;42(3):553–557. doi: 10.1079/bjn19790147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook A. R. Urease activity in the rumen of sheep and the isolation of ureolytic bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Jan;92(1):32–48. doi: 10.1099/00221287-92-1-32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A., Grubb J. A. Basal medium for the selective enumeration of rumen bacteria utilizing specific energy sources. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Nov;32(5):703–710. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.5.703-710.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houpt T. R., Houpt K. A. Nitrogen conservation by ponies fed a low -protein ration. Am J Vet Res. 1971 Apr;32(4):579–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houpt T. R., Houpt K. A. Transfer of urea nitrogen across the rumen wall. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jun;214(6):1296–1303. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.6.1296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John A., Isaacson H. R., Bryant M. P. Isolation and characteristics of a ureolytic strain of Selenomonas ruminatium. J Dairy Sci. 1974 Sep;57(9):1003–1014. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(74)85001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern D. L., Slyter L. L., Leffel E. C., Weaver J. M., Oltjen R. R. Ponies vs. steers: microbial and chemical characteristics of intestinal ingesta. J Anim Sci. 1974 Mar;38(3):559–564. doi: 10.2527/jas1974.383559x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern D. L., Slyter L. L., Weaver J. M., Leffel E. C., Samuelson G. Pony cecum vs. steer rumen: the effect of oats and hay on the microbial ecosystem. J Anim Sci. 1973 Aug;37(2):463–469. doi: 10.2527/jas1973.372463x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior R. L., Hintz H. F., Lowe J. E., Visek W. J. Urea recycling and metabolism of ponies. J Anim Sci. 1974 Mar;38(3):565–571. doi: 10.2527/jas1974.383565x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitnour C. M., Treece J. M. Relationship of nitrogen source to certain blood compents and nitrogen balance in the equine. J Anim Sci. 1971 Mar;32(3):487–490. doi: 10.2527/jas1971.323487x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson I. M., Allison M. J., Bucklin J. A. Characterization of the cecal bacteria of normal pigs. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):950–955. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.950-955.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slade L. M., Robinson D. W., Casey K. E. Nitrogen metabolism in nonruminant herbivores. I. The influence of nonprotein nitrogen and protein quality on the nitrogen retention of adult mares. J Anim Sci. 1970 May;30(5):753–760. doi: 10.2527/jas1970.305753x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillman A. D., Sidhu K. S. Nitrogen metabolism in ruminants: rate of ruminal ammonia production and nitrogen utilization by ruminants--a review. J Anim Sci. 1969 May;28(5):689–697. doi: 10.2527/jas1969.285689x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varel V. H., Bryant M. P., Holdeman L. V., Moore W. E. Isolation of ureolytic Peptostreptococcus productus from feces using defined medium; failure of common urease tests. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):594–599. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.594-599.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Cheng K. J., Dinsdale D., Orskov E. R. An independent microbial flora of the epithelium and its role in the ecomicrobiology of the rumen. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):424–426. doi: 10.1038/279424a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wootton J. F., Argenzio R. A. Nitrogen utilization within equine large intestine. Am J Physiol. 1975 Oct;229(4):1062–1067. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.4.1062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozny M. A., Bryant M. P., Holdeman L. V., Moore W. E. Urease assay and urease-producing species of anaerobes in the bovine rumen and human feces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1097–1104. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1097-1104.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


