Abstract
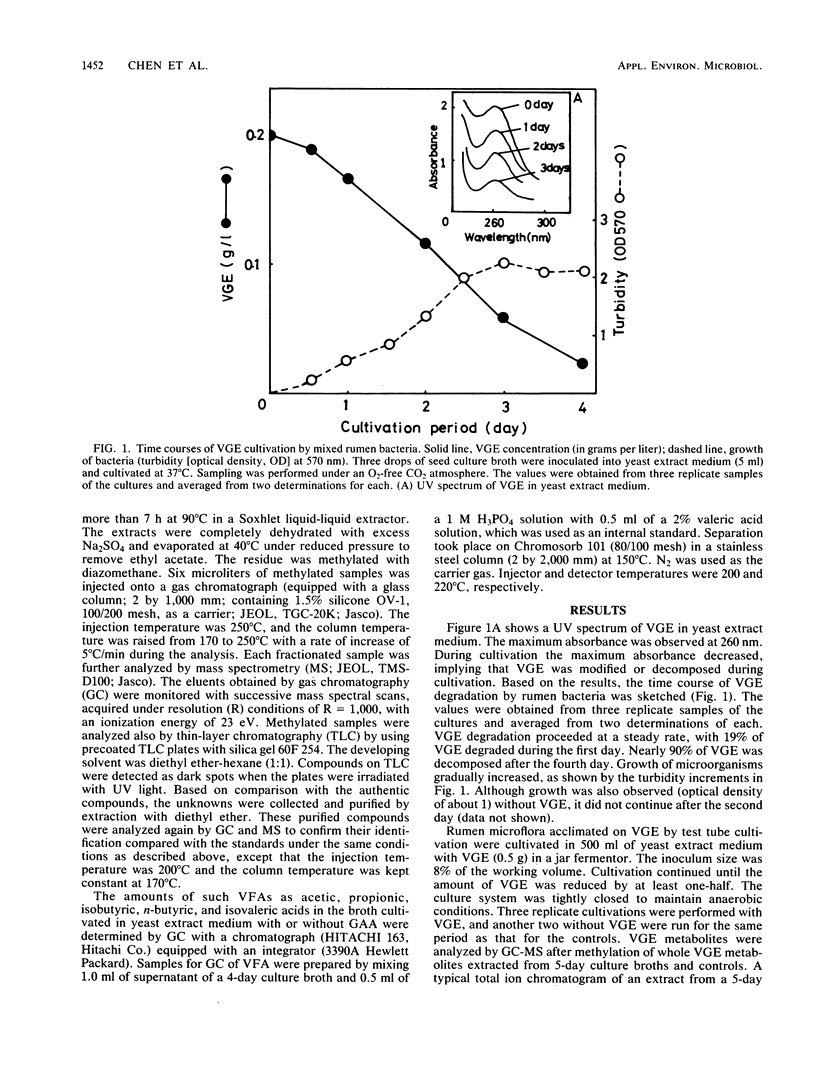
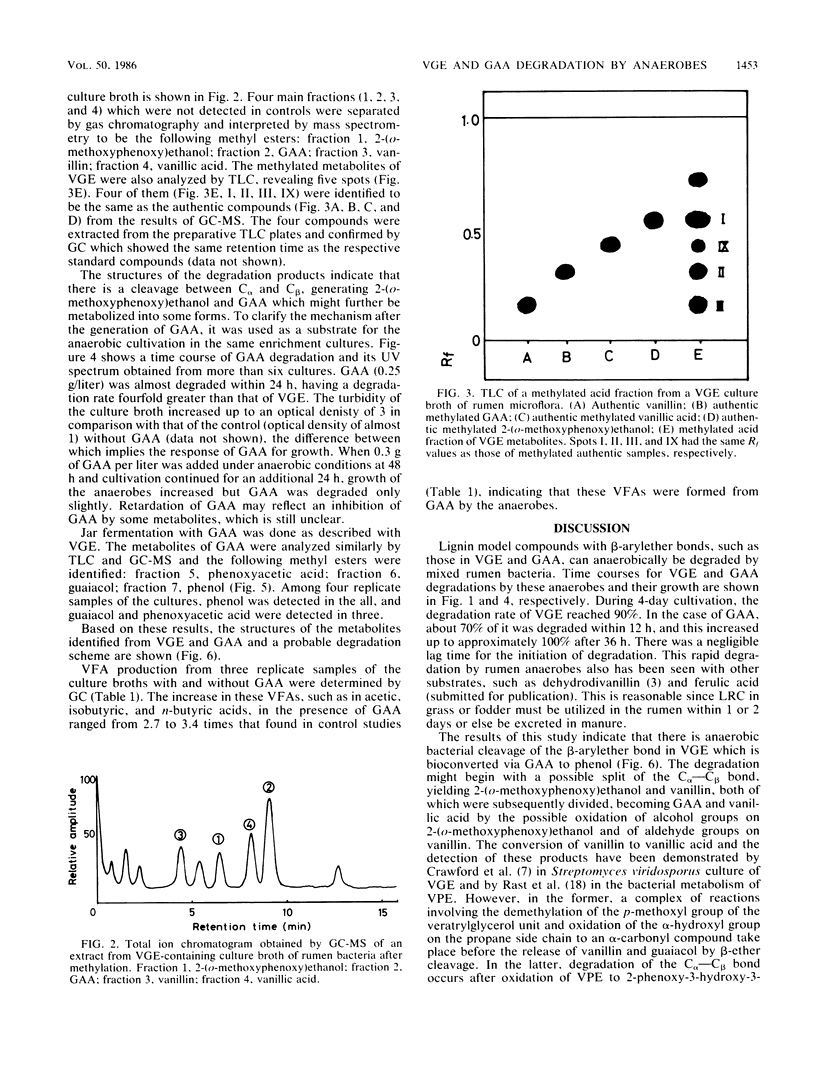
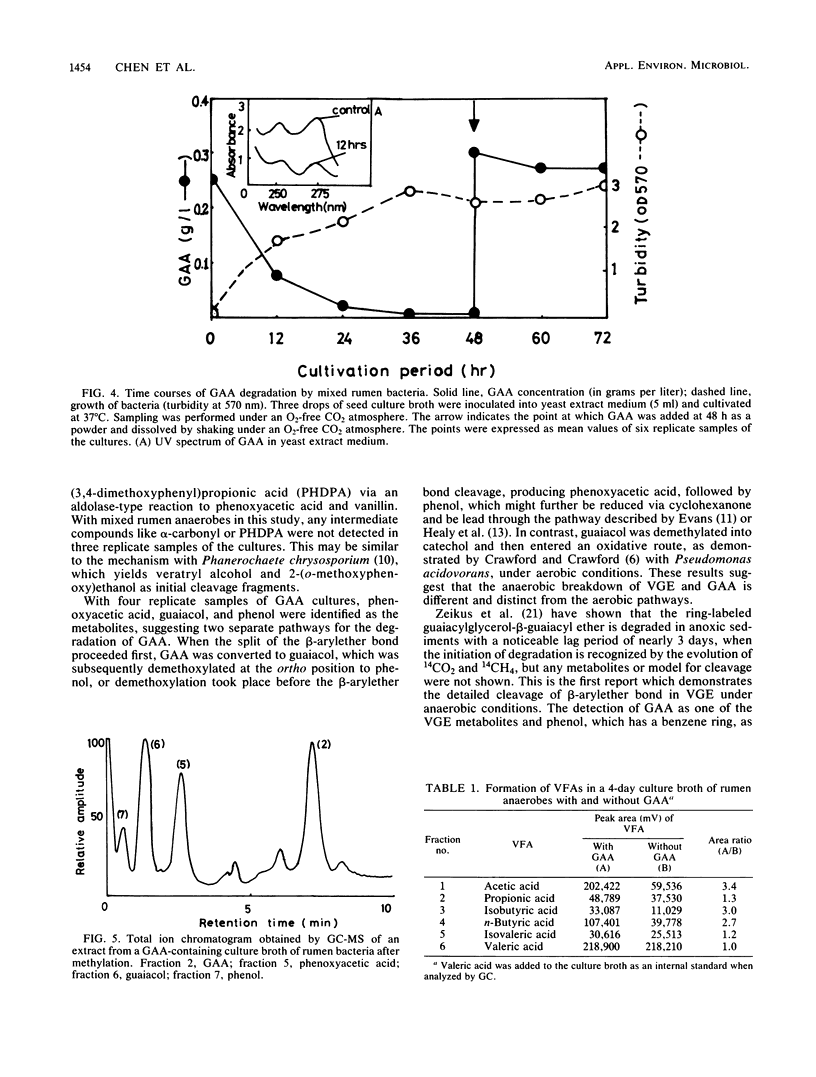
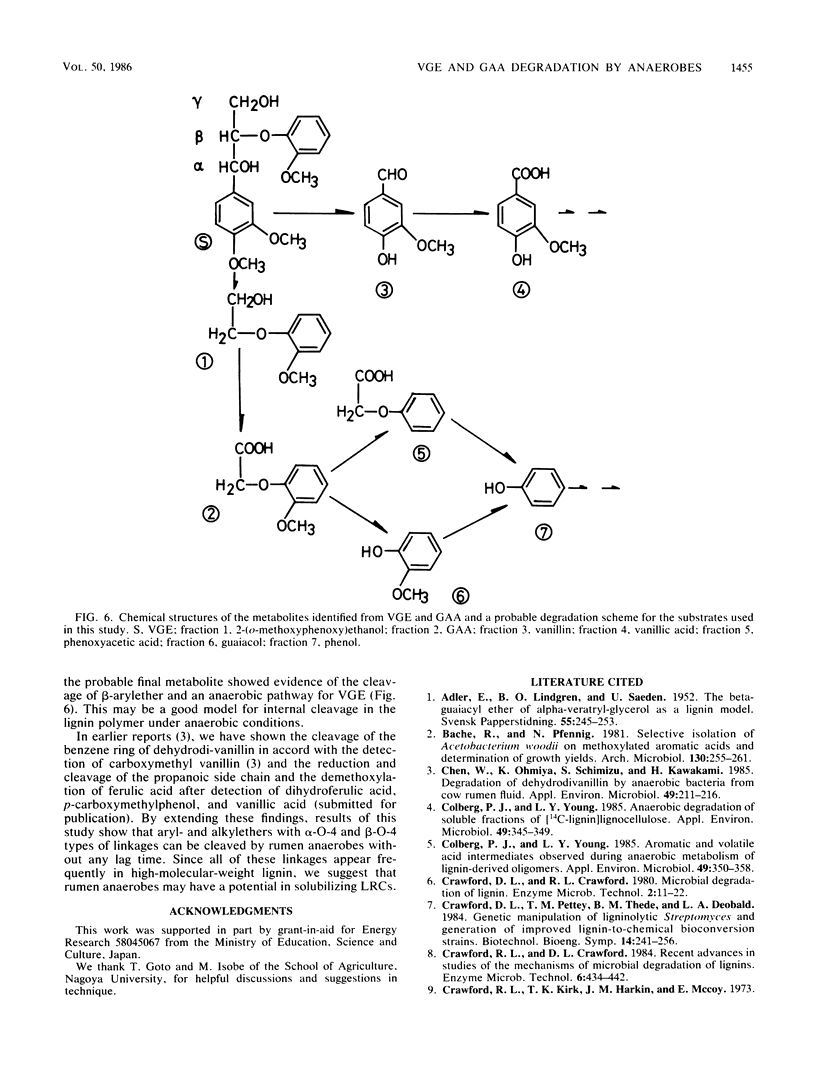
Veratrylglycerol-beta-guaiacyl ether (0.2 g/liter), a lignin model compound, was found to be degraded by mixed rumen bacteria in a yeast extract medium under strictly anaerobic conditions to the extent of 19% within 24 h. Guaiacoxyacetic acid, 2-(o-methoxyphenoxy)ethanol, vanillic acid, and vanillin were detected as degradation products of veratrylglycerol-beta-guaiacyl ether by thin-layer chromatography, gas chromatography, and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Guaiacoxyacetic acid (0.25 g/liter), when added into the medium as a substrate, was entirely degraded within 36 h, resulting in the formation of phenoxyacetic acid, guaiacol, and phenol. These results suggest that the beta-arylether bond, an important intermonomer linkage in lignin, can be cleaved completely by these rumen anaerobes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen W., Ohmiya K., Shimizu S., Kawakami H. Degradation of dehydrodivanillin by anaerobic bacteria from cow rumen fluid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):211–216. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.211-216.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg P. J., Young L. Y. Anaerobic degradation of soluble fractions of [C-lignin]lignocellulose. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):345–349. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.345-349.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg P. J., Young L. Y. Aromatic and Volatile Acid Intermediates Observed during Anaerobic Metabolism of Lignin-Derived Oligomers. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):350–358. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.350-358.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C. Biochemistry of the bacterial catabolism of aromatic compounds in anaerobic environments. Nature. 1977 Nov 3;270(5632):17–22. doi: 10.1038/270017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINA L. R., FISKIN A. M. The anaerobic decomposition of benzoic acid during methane fermentation. II. Fate of carbons one and seven. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Dec;91:163–165. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy J. B., Young L. Y., Reinhard M. Methanogenic decomposition of ferulic Acid, a model lignin derivative. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):436–444. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.436-444.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janshekar H., Fiechter A. Lignin: biosynthesis, application, and biodegradation. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 1983;27:119–178. doi: 10.1007/BFb0009107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleat R., Robinson J. P. The bacteriology of anaerobic degradation of aromatic compounds. J Appl Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;57(3):381–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1984.tb01404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein D. A., Krisnangkura K., Mayfield M. B., Gold M. H. Metabolism of Radiolabeled beta-Guaiacyl Ether-Linked Lignin Dimeric Compounds by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Mar;39(3):535–540. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.3.535-540.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



