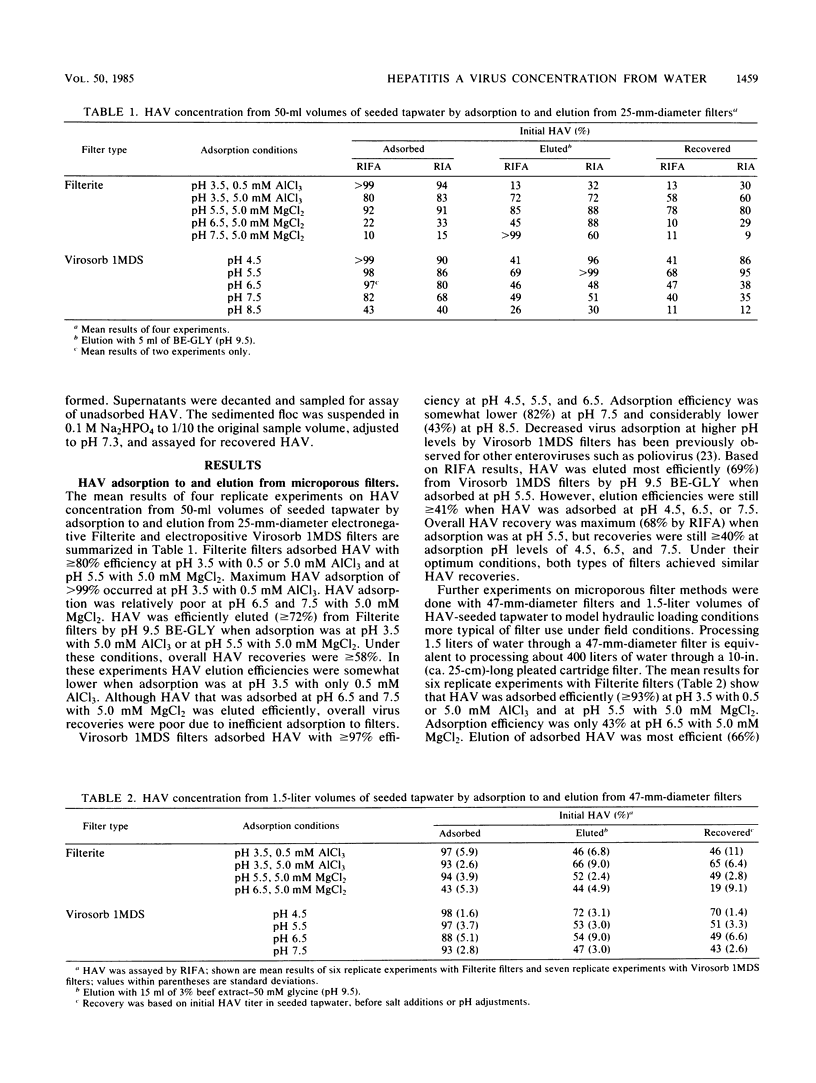
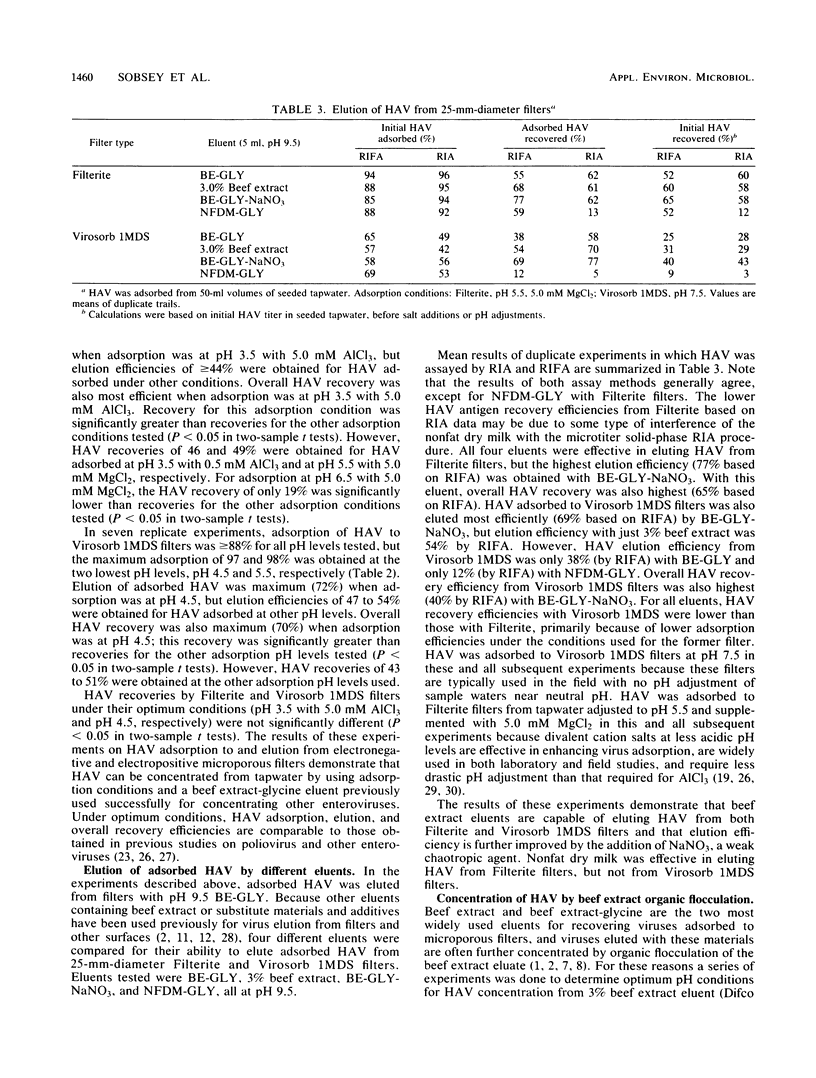
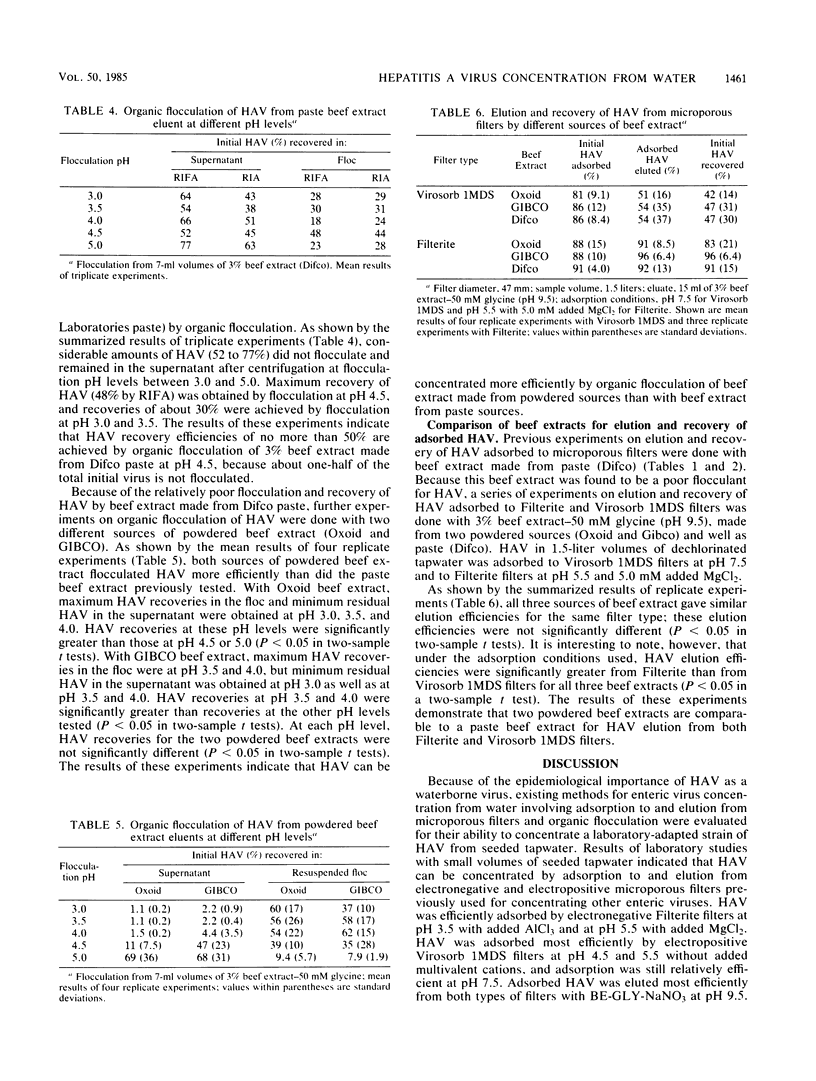
Abstract
By using recently developed cultivation and assay systems, currently available methods for concentrating enteric viruses from drinking water by adsorption to and subsequent elution from microporous filters followed by organic flocculation were evaluated for their ability to recover hepatitis A virus (HAV). Cell culture-adapted HAV (strain HM-175) in seeded tapwater was efficiently adsorbed by both electronegative (Filterite) and electropositive (Virosorb 1MDS) filters at pH and ionic conditions previously used for other enteric viruses. Adsorbed HAV was efficiently eluted from these filters by beef extract eluents at pH 9.5. Eluted HAV was further concentrated efficiently by acid precipitation (organic flocculation) of eluents containing beef extract made from powdered, but not paste, sources. By using optimum adsorption conditions for each type of filter, HAV was concentrated greater than 100-fold from samples of seeded tapwater, with about 50% recovery of the initial infectious virus added to the samples. The ability to recover and quantify HAV in contaminated drinking water with currently available methods should prove useful in further studies to determine the role of drinking water in HAV transmission.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Daemer R. J., Feinstone S. M., Gust I. D., Purcell R. H. Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in African green monkey kidney cell culture: primary isolation and serial passage. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):388–393. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.388-393.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrah S. R., Gerba C. P., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Concentration of viruses from large volumes of tap water using pleated membrane filters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):221–226. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.221-226.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrah S. R., Shah D. O., Ingram L. O. Effects of chaotropic and antichaotropic agents on elution of poliovirus adsorbed on membrane filters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1229–1232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frösner G. G., Deinhardt F., Scheid R., Gauss-Müller V., Holmes N., Messelberger V., Siegl G., Alexander J. J. Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in a hepatoma cell line. Infection. 1979;7(6):303–305. doi: 10.1007/BF01642154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst C. J., Dahling D. R., Safferman R. S., Goyke T. Comparison of commercial beef extracts and similar materials for recovering viruses from environmental samples. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Oct;30(10):1253–1263. doi: 10.1139/m84-198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenelson E., Fattal B., Hostovesky T. Organic flocculation: an efficient second-step concentration method for the detection of viruses in tap water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):638–639. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.638-639.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemon S. M., Binn L. N., Marchwicki R. H. Radioimmunofocus assay for quantitation of hepatitis A virus in cell cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):834–839. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.834-839.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen L. R., Feinstone S. M., Purcell R. H., Wagner J. A. Detection of hepatitis A antigen by immunofluorescence. Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):524–530. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.524-530.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost P. J., Hilleman M. R. Propagation of human hepatitis A virus in cell culture in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Feb;160(2):213–221. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Moritsugu Y., Dienstag J. L., Routenberg J. A., Boggs J. D. A microtiter solid-phase radioimmunoassay for hepatitis A antigen and antibody. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):349–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao N. U., Labzoffsky N. A. A simple method for the detection of low concentration of viruses in large volumes of water by the membrane filter technique. Can J Microbiol. 1969 May;15(5):399–403. doi: 10.1139/m69-071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields P. A., Farrah S. R. Influence of salts on electrostatic interactions between poliovirus and membrane filters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.526-531.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds R. S., Szücs G., Metcalf T. G., Melnick J. L. Persistently infected cultures as a source of hepatitis A virus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Apr;49(4):749–755. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.4.749-755.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D., Glass J. S. Influence of water quality on enteric virus concentration by microporous filter methods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):956–960. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.956-960.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D., Glass J. S. Poliovirus concentration from tap water with electropositive adsorbent filters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug;40(2):201–210. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.2.201-210.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wait D. A., Sobsey M. D. Method for recovery of enteric viruses from estuarine sediments with chaotropic agents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):379–385. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.379-385.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



