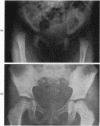
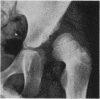
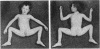
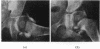
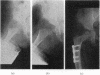
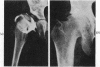
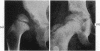
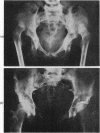
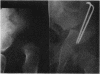
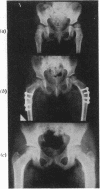
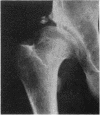
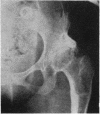
Full text
PDF
























Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDREN L., BORGLIN N. E. Disturbed urinary excretion pattern of oestrogens in newborns with congenital dislocation of the hip. I. The excretion of oestrogen during the first few days of life. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1961 Jul;37:423–426. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0370423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C. O., Wilkinson J. A. Genetic and environmental factors in the etiology of congenital dislocation of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1964 Mar-Apr;33:119–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOMERVILLE E. W. Open reduction in congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1953 Aug;35-B(3):363–371. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.35B3.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thieme W. T., Wynne-Davies R. Clinical examination and urinary oestrogen assays in newborn children with congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1968 Aug;50(3):546–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevor D. The place of the Hey Groves-Colonna operation in the treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1968 Nov;43(5):241–258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynne-Davies R. Acetabular dysplasia and familial joint laxity: two etiological factors in congenital dislocation of the hip. A review of 589 patients and their families. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1970 Nov;52(4):704–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von ROSEN Diagnosis and treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip hoint in the new-born. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1962 May;44-B:284–291. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.44B2.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]