Abstract
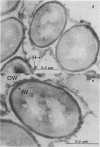
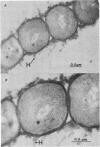
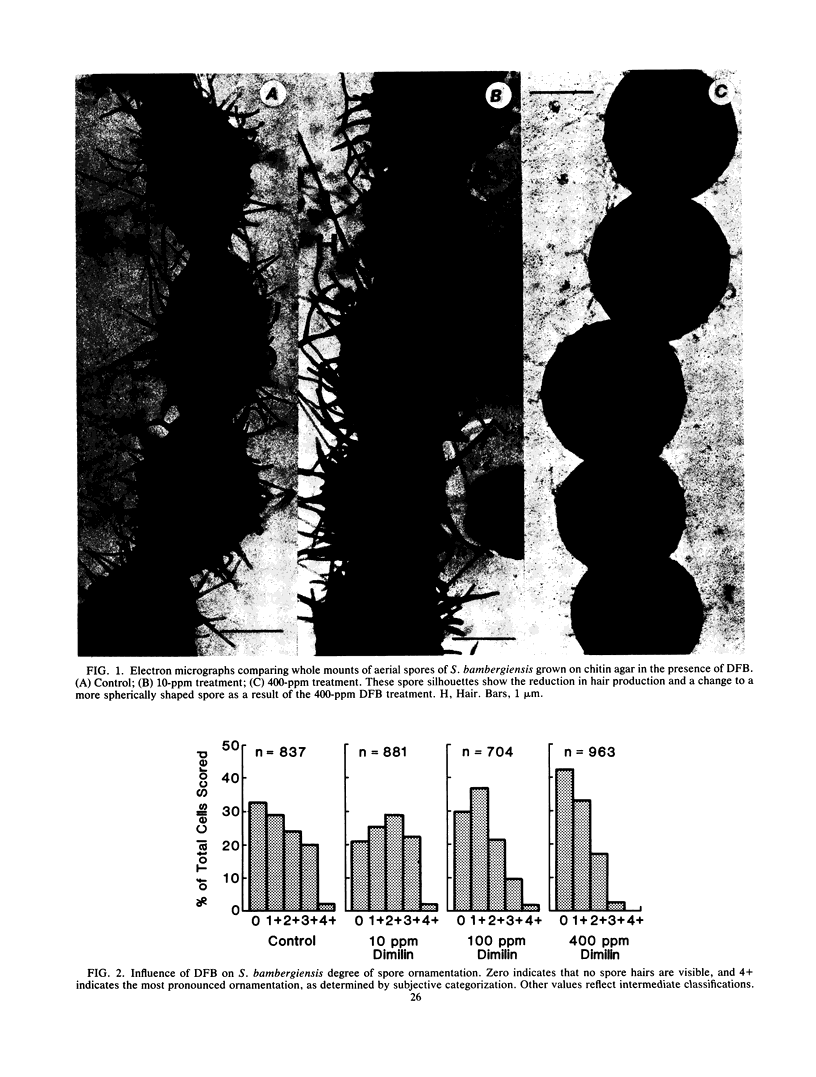
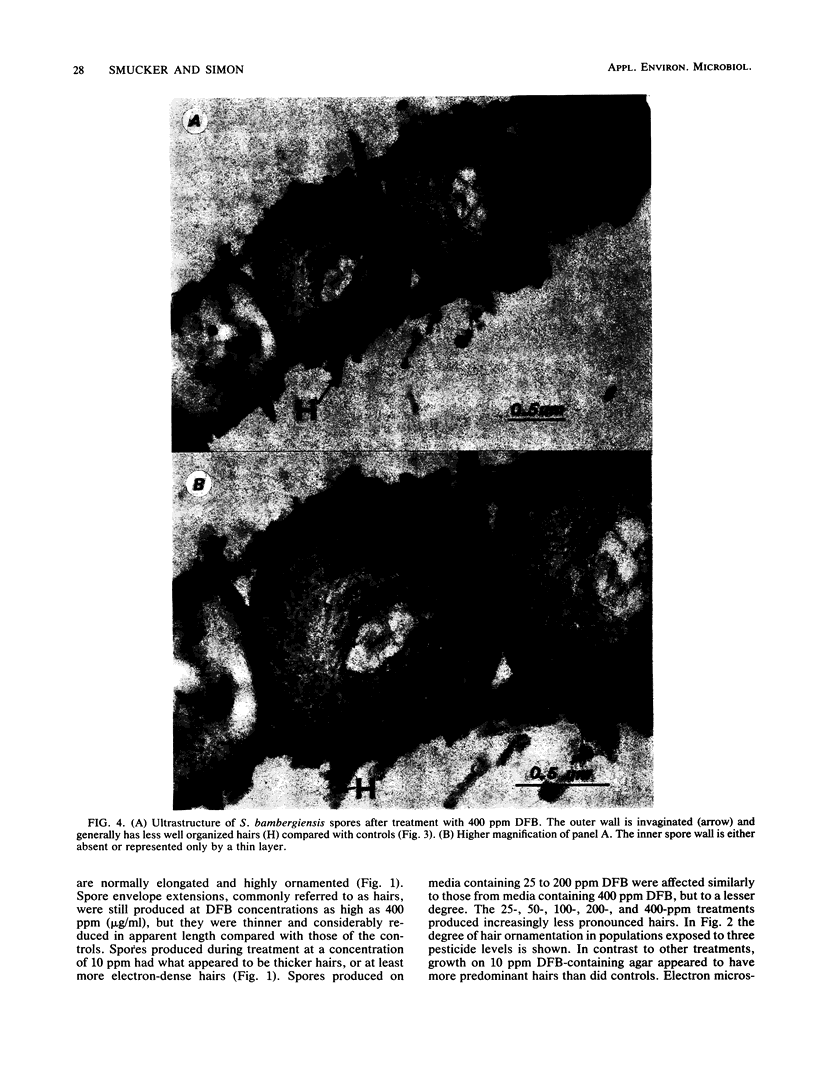
Diflubenzuron, an insect growth regulator that blocks chitin deposition in insect cuticles, was tested for its effects on morphogenesis of Streptomyces spp. Use of diflubenzuron resulted in reduced dominance of spore hairs, reduced the width of the outer wall, and prevented formation of the inner spore wall in S. bambergiensis. In S. coelicolor, diflubenzuron altered the structure of the fibrillar pattern of spore envelopes. Exposure to diflubenzuron resulted in small increases in exported protein and in a ca. 20% increase in chitinase in both Streptomyces spp.
Full text
PDF

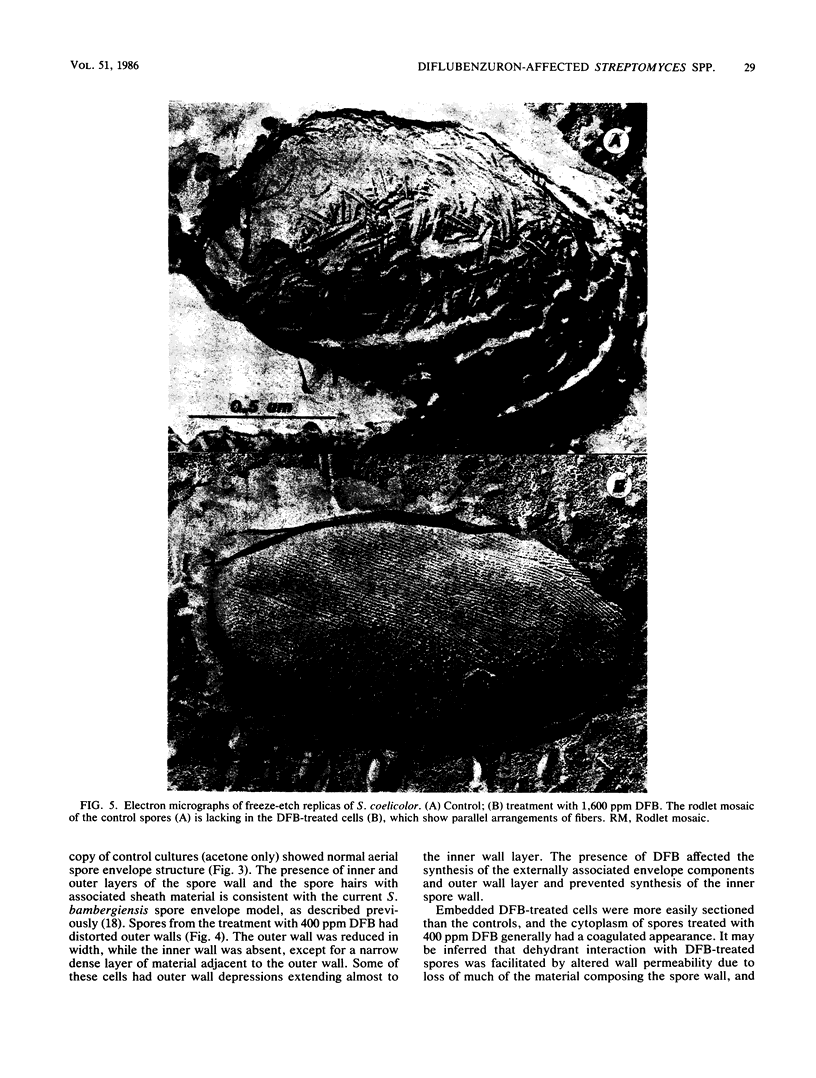
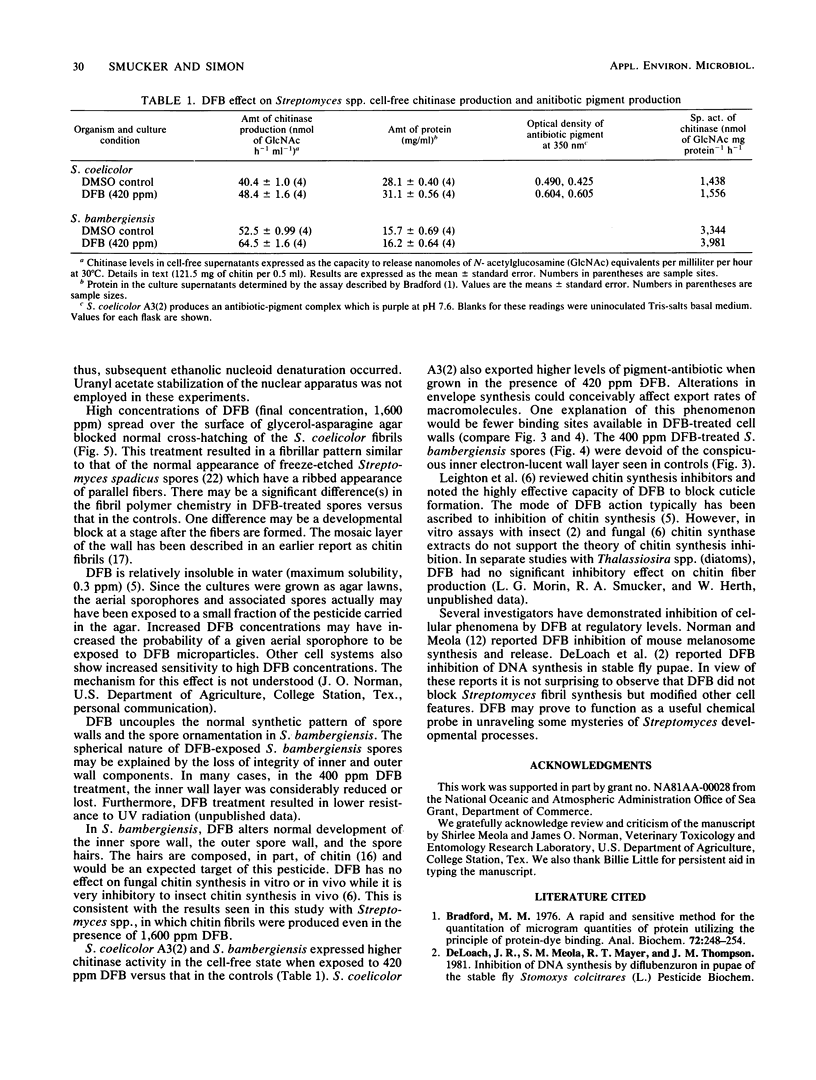

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. C., Lockwood J. L. Powdered chitin agar as a selective medium for enumeration of actinomycetes in water and soil. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Mar;29(3):422–426. doi: 10.1128/am.29.3.422-426.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ker R. F. Investigation of locust cuticle using the insecticide diflubenzuron. J Insect Physiol. 1977;23(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(77)90107-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. A., Maibach H. I., Strauss W. G., Fisher J. L. Increased attractiveness of man to mosquitoes with induced eccrine sweating. Nature. 1969 Aug 23;223(5208):859–860. doi: 10.1038/223859a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton T., Marks E., Leighton F. Pesticides: insecticides and fungicides are chitin synthesis inhibitors. Science. 1981 Aug 21;213(4510):905–907. doi: 10.1126/science.213.4510.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):347–368. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf R. L., Lu P. Y., Bowlus S. Degradation and environmental fate of 1-(2,6-difluorobenzoly)-3-(4-chlorophenyl) urea. J Agric Food Chem. 1975 May-Jun;23(3):359–364. doi: 10.1021/jf60199a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molano J., Durán A., Cabib E. A rapid and sensitive assay for chitinase using tritiated chitin. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):648–656. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman J. O., Meola S. M. Inhibition of melanogenesis in B16-F1 melanoma cells after exposure to diflubenzuron. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Feb;23(2):313–316. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer C. H., Dupras E. F. Factors affecting the stability of dimilin in water and the persistence of dimilin in field waters. J Agric Food Chem. 1976 Jul-Aug;24(4):733–738. doi: 10.1021/jf60206a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smucker R. A., Pfister R. M. Characteristics of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) aerial spore rodlet mosaic. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Apr;24(4):397–408. doi: 10.1139/m78-066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildermuth H. Surface structure of streptomycete spores as revealed by negative staining and freeze-etching. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):318–322. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.318-322.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]