Abstract
A simple method for detection of radiation-inducible radiation resistance was developed by irradiating aliquots (0.01 ml) of cell suspension on agar plates. Part of each experimental plate was subjected to an induction treatment, and subsequent radiation resistance was compared with that of untreated cells on the same plate. The UV radiation resistance of a Micrococcus sp. was increased approximately 1.6 times by an induction treatment. This simple procedure of irradiating cells in a "fixed" position on agar avoided washing, centrifugation, and cell enumeration required in traditional methods.
Full text
PDF
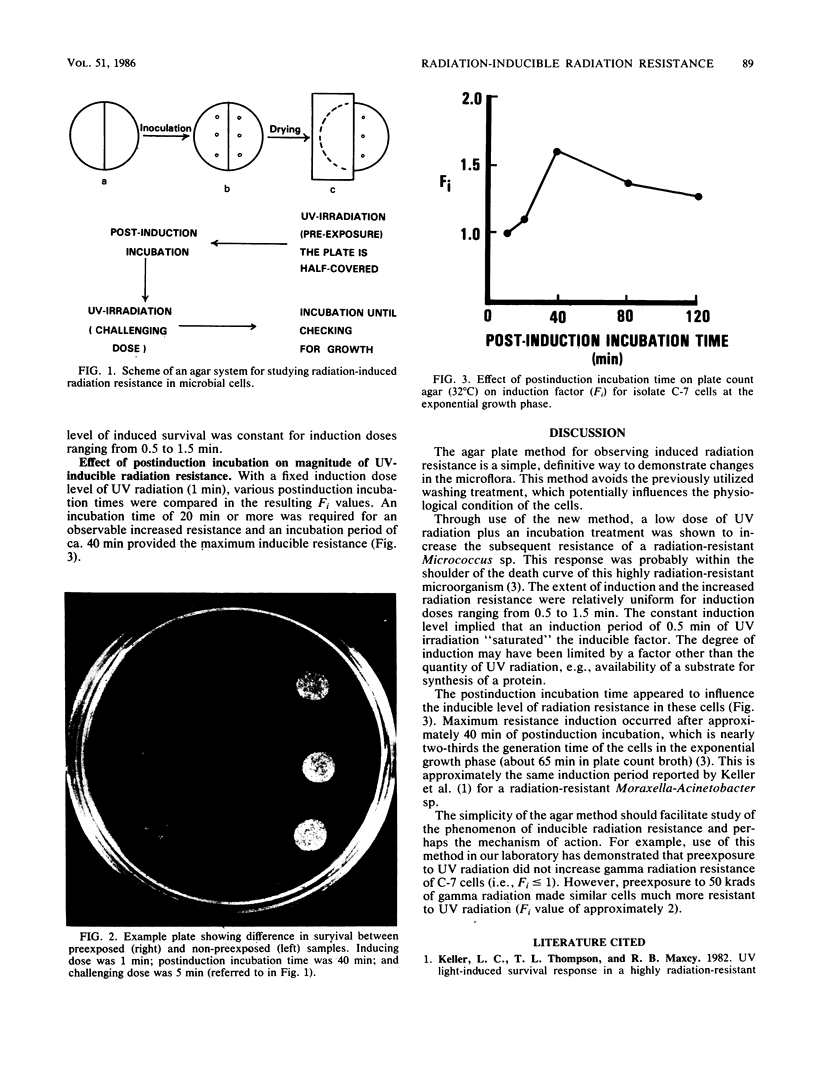

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Pollard E. C., Achey P. M. Induction of radioresistance in Escherichia coli. Biophys J. 1975 Nov;15(11):1141–1154. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85890-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. T., Maxcy R. B., Thompson T. L. Paper replication method for isolation of radiation-sensitive mutants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):233–236. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.233-236.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]