Abstract
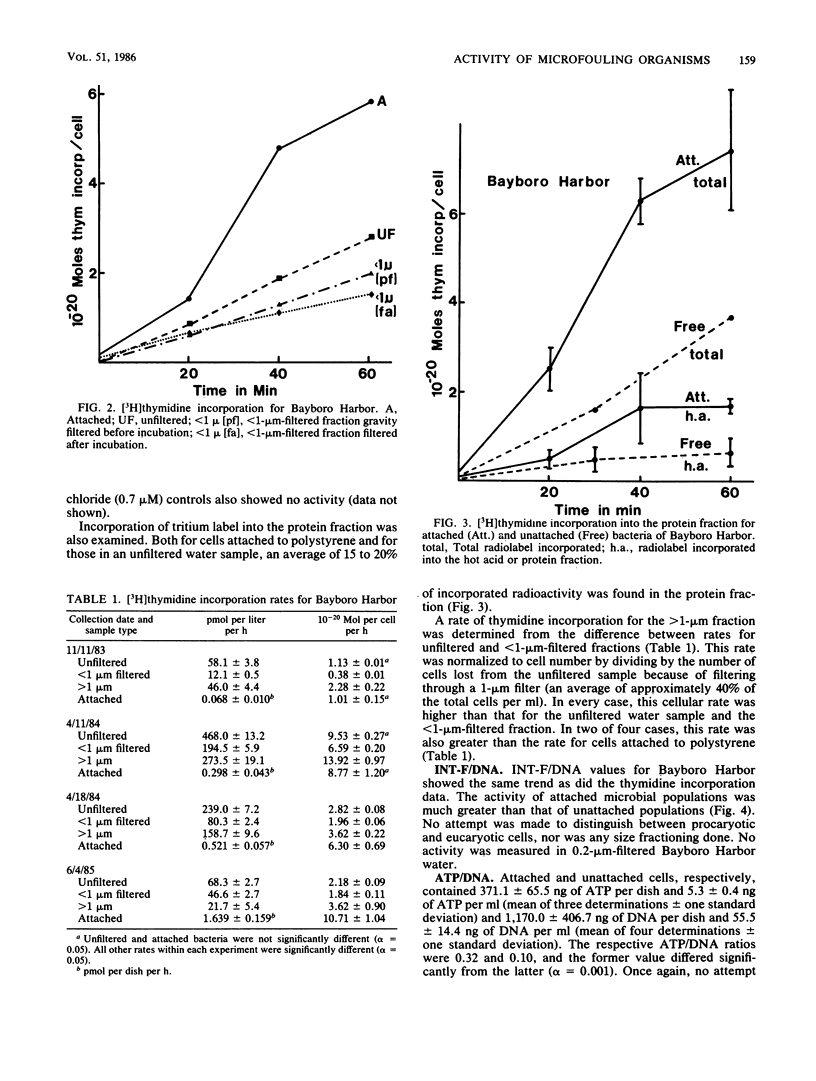
[3H]thymidine incorporation, the rate of reduction of iodonitrotetrazolium violet (INT) to INT formazan normalized to DNA, and the ratio of ATP to DNA were adapted to measure the activity of attached and unattached microbial assemblages of Bayboro Harbor, Fla. Activity measurements by [3H]thymidine incorporation were made of cells attached to polystyrene culture dishes, in unfiltered water samples, and in the <1-μm-filtered fraction. In most cases, the activity of attached cells was greater than that of unattached cells either in unfiltered water samples or in the <1-μm fraction. The calculated thymidine incorporation rates for cells in the >1-μm fraction were higher than those for cells either in unfiltered water or in the <1-μm-filtered fraction. By the rate of reduction of INT to INT formazan normalized to DNA and by ATP-to-DNA ratios, attached cells were also more active than cells in unfiltered water samples. These results indicate that the microenvironment afforded by attachment is a more beneficial habitat for microbial growth. Reasons for greater activity by natural populations of attached bacteria are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bobbie R. J., Morrison S. J., White D. C. Effects of substrate biodegradability on the mass and activity of the associated estuarine microbiota. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jan;35(1):179–184. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.1.179-184.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. W., Young L. Y. Enumeration of particle-bound and unattached respiring bacteria in the salt marsh environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):156–160. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.156-160.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Hattori R. The physical environment in soil microbiology: an attempt to extend principles of microbiology to soil microoganisms. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1976 May;4(4):423–461. doi: 10.3109/10408417609102305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey W. H., Paul J. H. Activity of an Attached and Free-Living Vibrio sp. as Measured by Thymidine Incorporation, p-Iodonitrotetrazolium Reduction, and ATP/DNA Ratios. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jan;51(1):150–156. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.1.150-156.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karl D. M. Selected nucleic Acid precursors in studies of aquatic microbial ecology. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):891–902. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.891-902.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchman D., Mitchell R. Contribution of particle-bound bacteria to total microheterotrophic activity in five ponds and two marshes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):200–209. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.200-209.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeChevallier M. W., Hassenauer T. S., Camper A. K., McFeters G. A. Disinfection of bacteria attached to granular activated carbon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):918–923. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.918-923.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. H., Loeb G. I. Improved Microfouling Assay Employing a DNA-Specific Fluorochrome and Polystyrene as Substratum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Aug;46(2):338–343. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.2.338-343.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard P. C., Moriarty D. J. Validity of the tritiated thymidine method for estimating bacterial growth rates: measurement of isotope dilution during DNA synthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1076–1083. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1076-1083.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevors J. T. Electron transport system activity in soil, sediment, and pure cultures. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1984;11(2):83–100. doi: 10.3109/10408418409105473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R., Iturriaga R., Becker-Birck J. Simultaneous determination of the total number of aquatic bacteria and the number thereof involved in respiration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):926–935. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.926-935.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


