Abstract
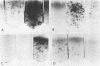
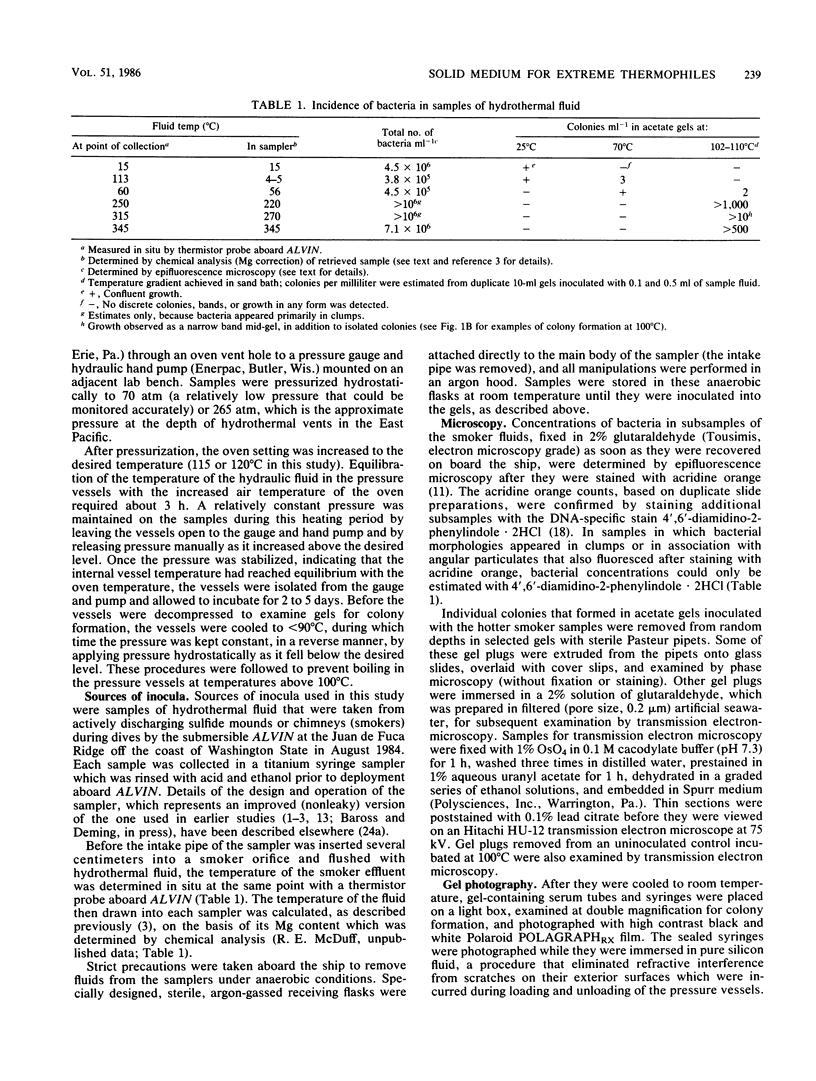
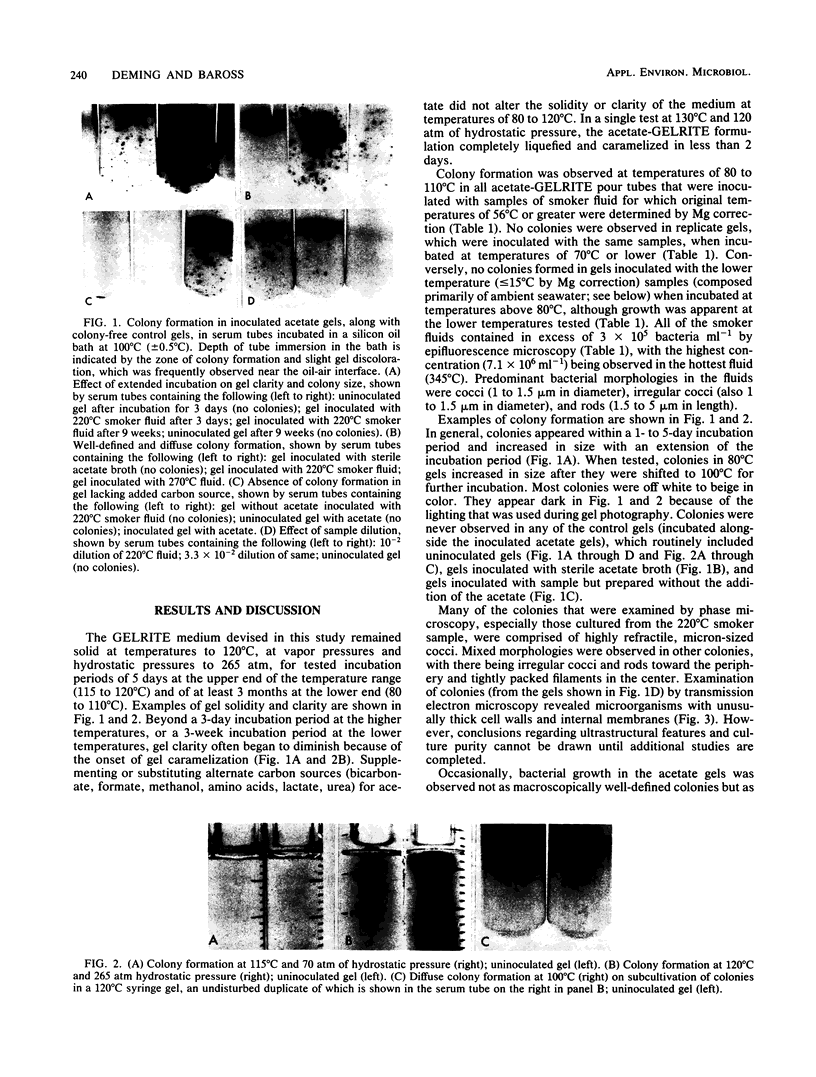
A solid, highly thermostable medium, based on the new gelling agent GELRITE, was devised to facilitate the culturing of extremely thermophilic microorganisms from submarine hydrothermal vents. The medium remained solid at temperatures to 120°C at vapor pressures and hydrostatic pressures to 265 atm. It proved useful to its maximum tested limits in isolating colonies of black smoker bacteria from hydrothermal fluids recently collected at the Juan de Fuca Ridge in the Pacific Ocean.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dietz A. S., Yayanos A. A. Silica gel media for isolating and studying bacteria under hydrostatic pressure. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):966–968. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.966-968.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbie J. E., Daley R. J., Jasper S. Use of nuclepore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1225–1228. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1225-1228.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang K. S., Veeder G. T., Mirrasoul P. J., Kaneko T., Cottrell I. W. Agar-like polysaccharide produced by a pseudomonas species: production and basic properties. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1086–1091. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1086-1091.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. C., Casida L. E. GELRITE as a Gelling Agent in Media for the Growth of Thermophilic Microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Feb;47(2):427–429. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.2.427-429.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungdahl L. G. Physiology of thermophilic bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol. 1979;19:149–243. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]