Abstract
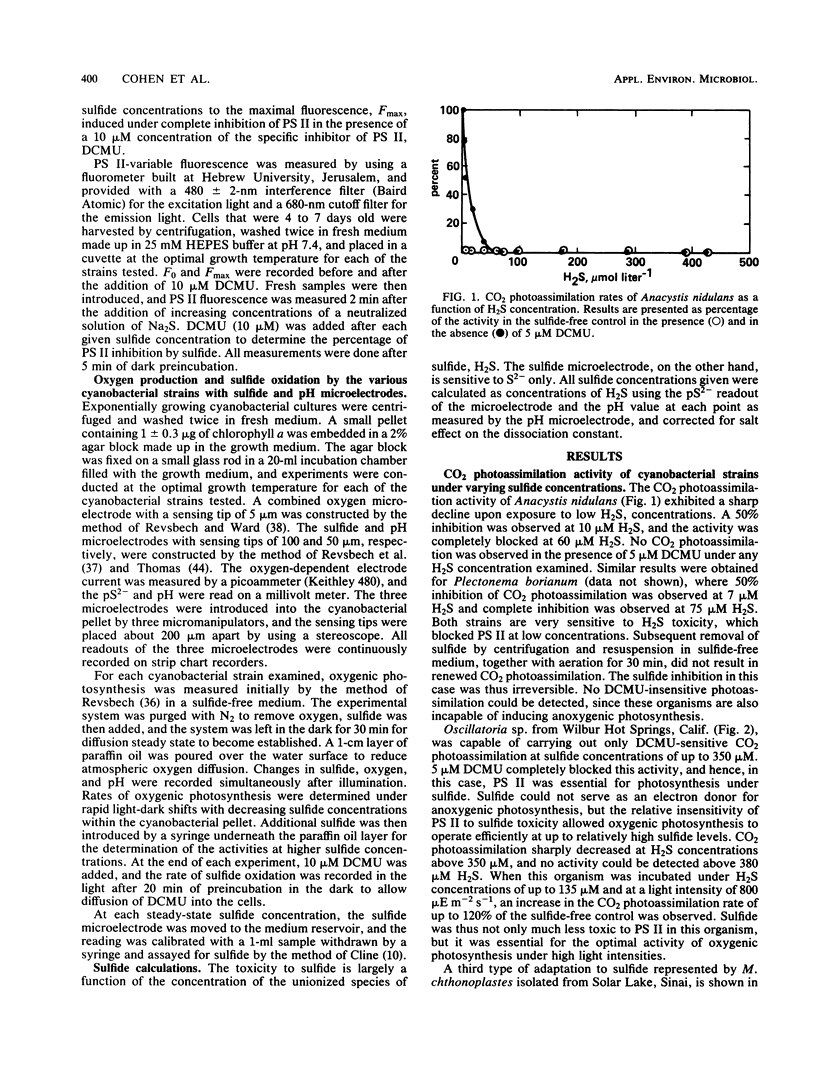
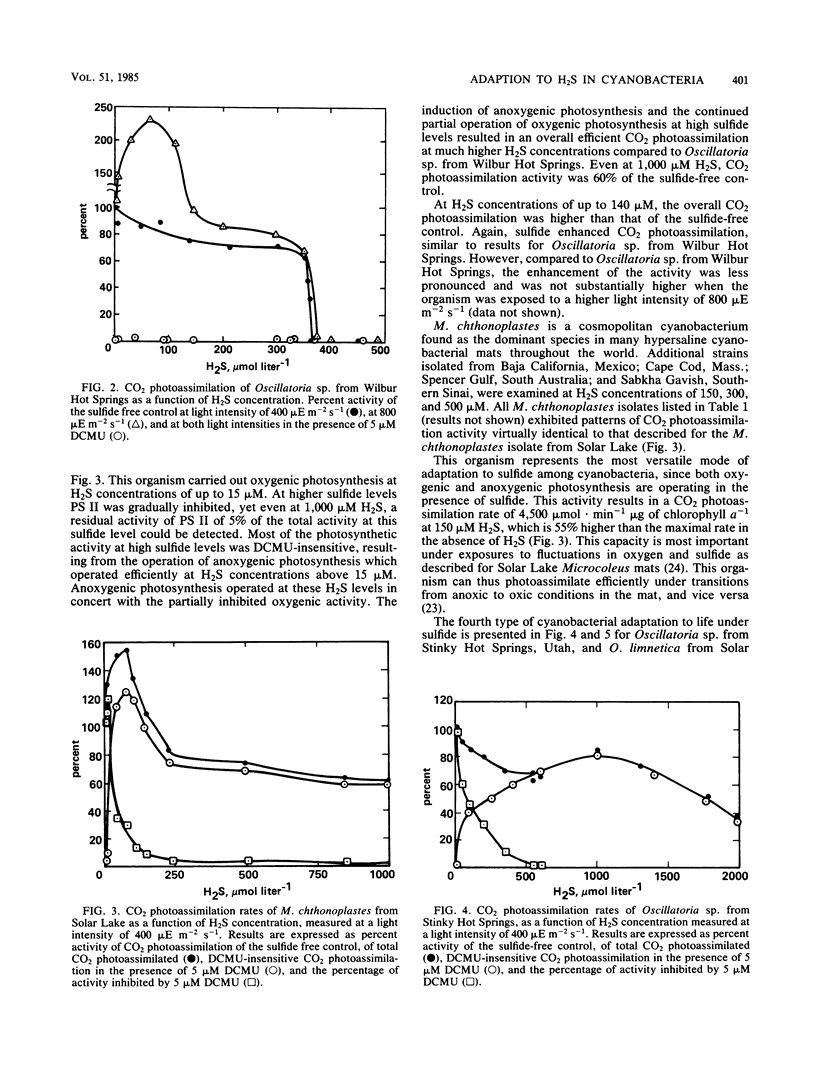
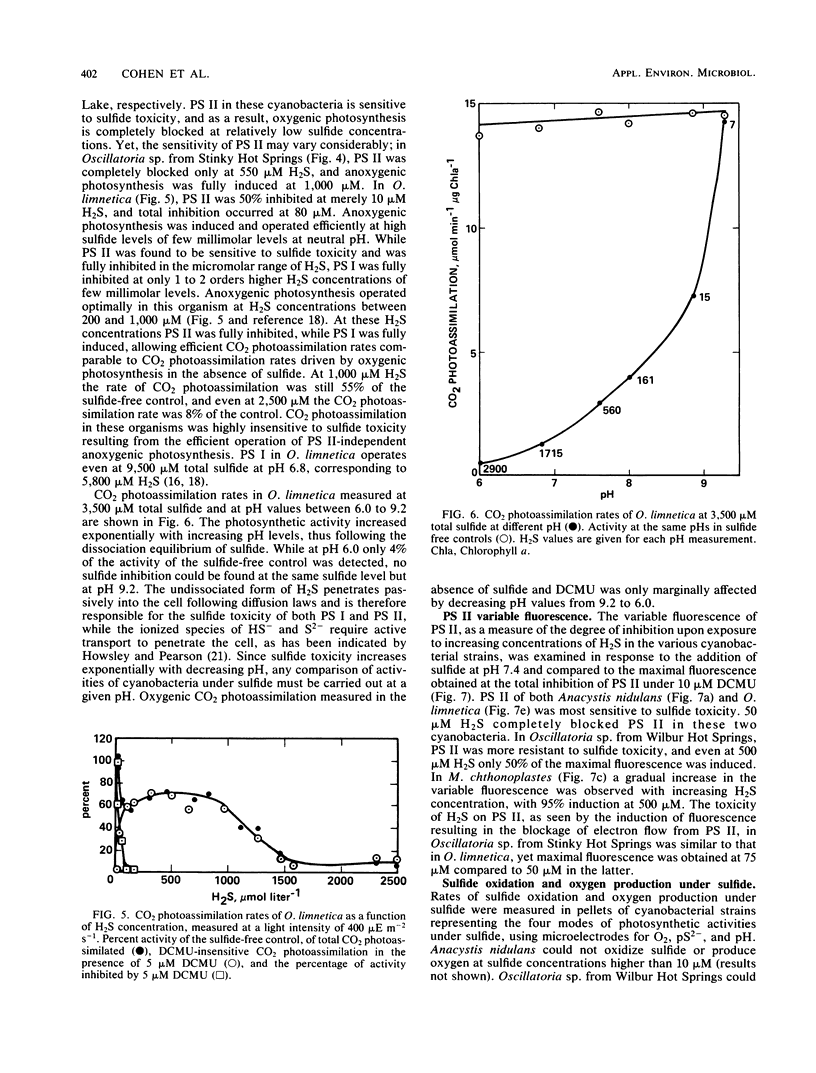
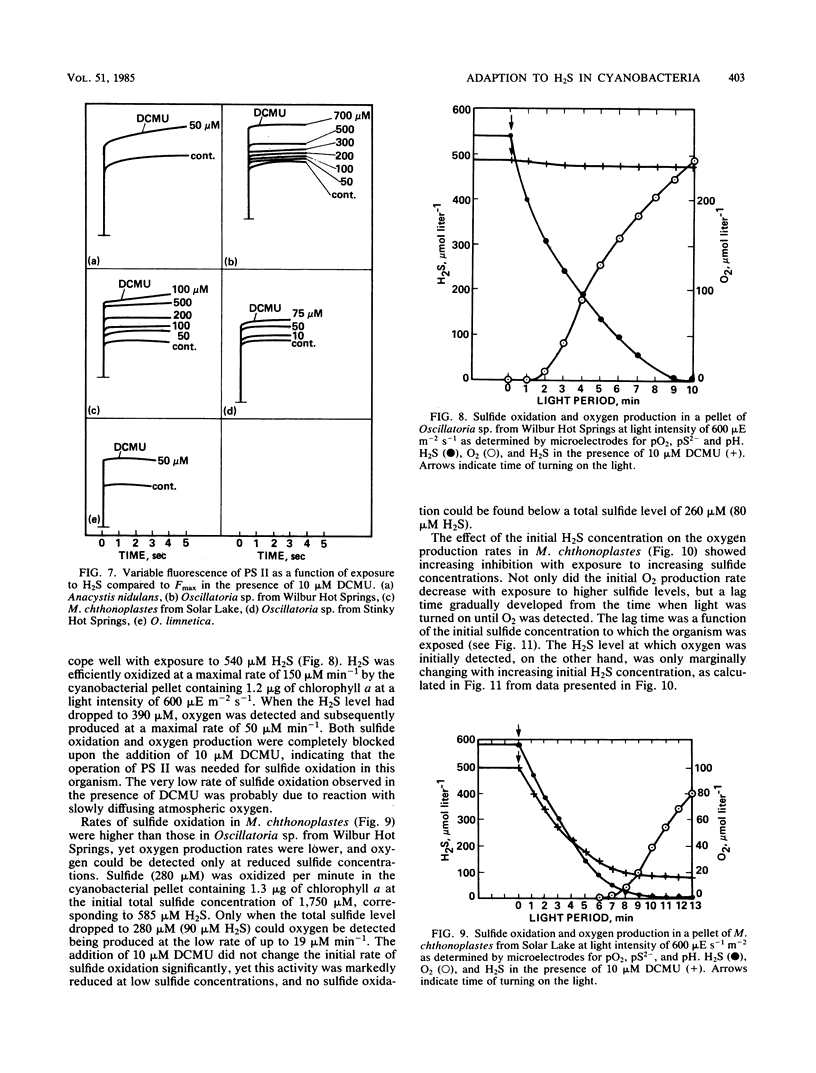
Four different types of adaptation to sulfide among cyanobacteria are described based on the differential toxicity to sulfide of photosystems I and II and the capacity for the induction of anoxygenic photosynthesis. Most cyanobacteria are highly sensitive to sulfide toxicity, and brief exposures to low concentrations cause complete and irreversible cessation of CO2 photoassimilation. Resistance of photosystem II to sulfide toxicity, allowing for oxygenic photosynthesis under sulfide, is found in cyanobacteria exposed to low H2S concentrations in various hot springs. When H2S levels exceed 200 μM another type of adaptation involving partial induction of anoxygenic photosynthesis, operating in concert with partially inhibited oxygenic photosynthesis, is found in cyanobacterial strains isolated from both hot springs and hypersaline cyanobacterial mats. The fourth type of adaptation to sulfide is found at H2S concentrations higher than 1 mM and involves a complete replacement of oxygenic photosynthesis by an effective sulfide-dependent, photosystem II-independent anoxygenic photosynthesis. The ecophysiology of the various sulfide-adapted cyanobacteria may point to their uniqueness within the division of cyanobacteria.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belkin S., Padan E. Hydrogen metabolism in the facultative anoxygenic cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) Oscillatoria limnetica and Aphanothece halophytica. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Jan 23;116(1):109–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00408741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen Y., Padan E., Shilo M. Facultative anoxygenic photosynthesis in the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria limnetica. J Bacteriol. 1975 Sep;123(3):855–861. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.3.855-861.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick S., Oren A., Padan E. Occurrence of facultative anoxygenic photosynthesis among filamentous and unicellular cyanobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):623–629. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.623-629.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen B. B., Cohen Y., Revsbech N. P. Transition from Anoxygenic to Oxygenic Photosynthesis in a Microcoleus chthonoplastes Cyanobacterial Mat. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Feb;51(2):408–417. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.2.408-417.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen B. B., Revsbech N. P., Blackburn T. H., Cohen Y. Diurnal cycle of oxygen and sulfide microgradients and microbial photosynthesis in a cyanobacterial mat sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):46–58. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.46-58.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren A., Padan E., Avron M. Quantum yields for oxygenic and anoxygenic photosynthesis in the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria limnetica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2152–2156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren A., Padan E. Induction of anaerobic, photoautotrophic growth in the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria limnetica. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):558–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.558-563.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren A., Padan E., Malkin S. Sulfide inhibition of photosystem II in cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) and tobacco chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 9;546(2):270–279. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfennig N. Phototrophic green and purple bacteria: a comparative, systematic survey. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:275–290. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utkilen H. C. Thiosulphate as electron donor in the blue-green alga Anacystis nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Jul;95(1):177–180. doi: 10.1099/00221287-95-1-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller D., Doemel W., Brock T. D. Requirement of low oxidation-reduction potential for photosynthesis in a blue-green alga (Phormidium sp.). Arch Microbiol. 1975 Jun 20;104(1):7–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00447293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


