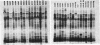Abstract
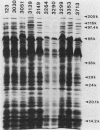
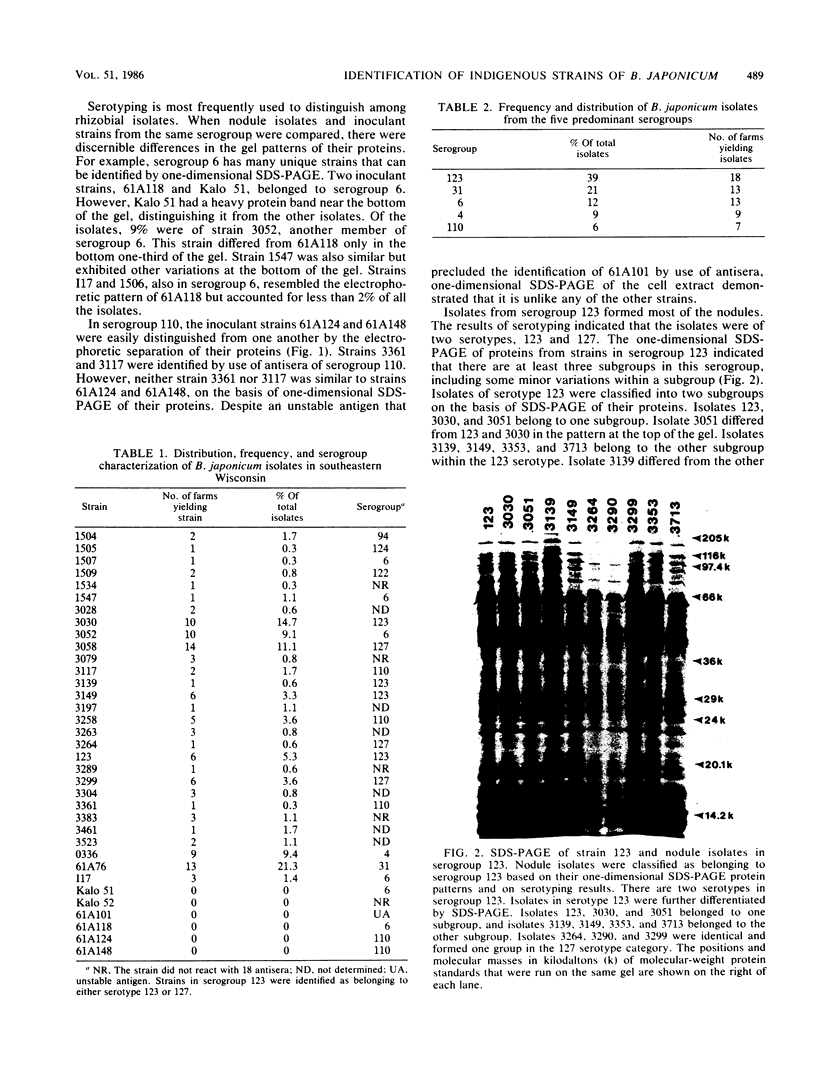
One-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis was a more discriminating method than serotyping for identifying strains of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Analysis of 543 nodule isolates from southeastern Wisconsin soybean farms revealed that none of the isolates were formed by any of the inoculant strains supplied by either of two inoculant companies. Twenty-nine indigenous strains and six inoculant strains were identified. Strain 61A76, the most competitive indigenous strain, formed 21% of the nodules. Indigenous strains 3030, 3058, 0336, and 3052 formed 15, 11, 9, and 9% of the nodules, respectively. These predominant strains were not associated with a particular soybean cultivar, soil type, or farm location.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jackman P. J. Classification of Corynebacterium species from axillary skin by numerical analysis of electrophoretic protein patterns. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Nov;15(4):485–492. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-4-485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersters K., De Ley J. Identification and grouping of bacteria by numerical analysis of their electrophoretic protein patterns. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Apr;87(2):333–342. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-2-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyser H. H., Weber D. F., Uratsu S. L. Rhizobium japonicum Serogroup and Hydrogenase Phenotype Distribution in 12 States. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Apr;47(4):613–615. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.4.613-615.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall K. C. Interaction between colloidal montmorillonite and cells of Rhizobium species with different inogenic surfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 1;156(1):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Materon L. A., Weaver R. W. Inoculant maturity influences survival of rhizobia on seed. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Feb;49(2):465–467. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.2.465-467.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil D. L. Variations in Ability of Rhizobium japonicum Strains To Nodulate Soybeans and Maintain Fixation in the Presence of Nitrate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):647–652. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.647-652.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Brill W. J. Diversity and Dynamics of Indigenous Rhizobium japonicum Populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Nov;40(5):931–938. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.5.931-938.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Carneol M., Brill W. J. Nodule protein synthesis and nitrogenase activity of soybeans exposed to fixed nitrogen. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1236–1241. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. L., Bakole R. O., Bohlool B. B. Fluorescent-antibody approach to study of rhizobia in soil. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):1987–1992. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.1987-1992.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rensburg H. J., Strijdom B. W. Effectiveness of Rhizobium strains used in inoculants after their introduction into soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):127–131. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.127-131.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]