Abstract
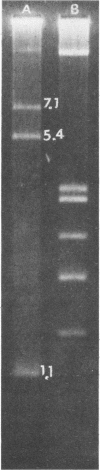
Two rapid methods were evaluated for their extraction of plasmids from Clostridium perfringens. The first method involved lysis of 1 to 2 ml of C. perfringens culture by treatment with hyaluronidase, lysozyme, and sarcosyl. DNA, extracted with phenol-chloroform, was treated with RNase, boiled, and electrophoresed in a 1.2% agarose gel. The second method involved lysis of 2 ml of culture by lysozyme treatment and extraction with alkaline sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). Extracted DNA was treated with RNase, boiled, and electrophoresed in a 0.7% agarose gel. Of 57 strains of C. perfringens analyzed by both extraction procedures, 11 were shown to have plasmids by the alkaline SDS method which were missed by the phenol-chloroform extraction method. These new plasmids were of higher molecular mass and ranged up to 68 megadaltons. Use of the DNase inhibitor diethyl pyrocarbonate did not further improve the yield of plasmid DNA. An additional 159 isolates of C. perfringens screened by the alkaline SDS method revealed plasmids up to 80 megadaltons in mass and an overall plasmid carriage rate of 69%.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaschek H. P., Klacik M. A. Role of DNase in recovery of plasmid DNA from Clostridium perfringens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):178–181. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.178-181.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brefort G., Magot M., Ionesco H., Sebald M. Characterization and transferability of Clostridium perfringens plasmids. Plasmid. 1977 Nov;1(1):52–66. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(77)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionesco H., Bieth G., Dauguet C., Bouanchaud D. Isolement et identification de deux plasmides d'une souche bactériocinogène de Clostridium perfringens. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1976 Oct;127B(3):283–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionesco H., Bouanchaud D. H. Production de bactériocine liée à présence d'un plasmide chez Clostridium perfringens type. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1973 May 14;276(20):2855–2857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li A. W., Krell P. J., Mahony D. E. Plasmid detection in a bacteriocinogenic strain of Clostridium perfringens. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Aug;26(8):1018–1022. doi: 10.1139/m80-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom M. S., Eklund M. W., Poysky F. T. Plasmids in Clostridium botulinum and related Clostridium species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):956–963. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.956-963.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]