Abstract
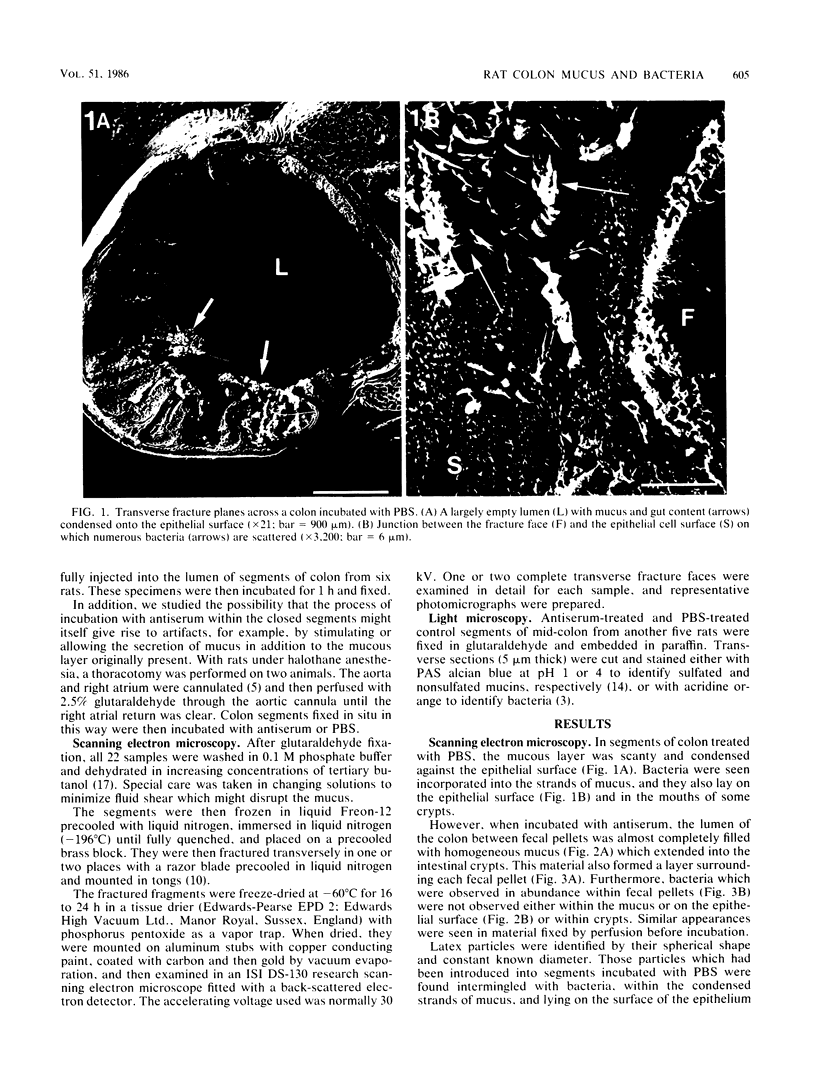
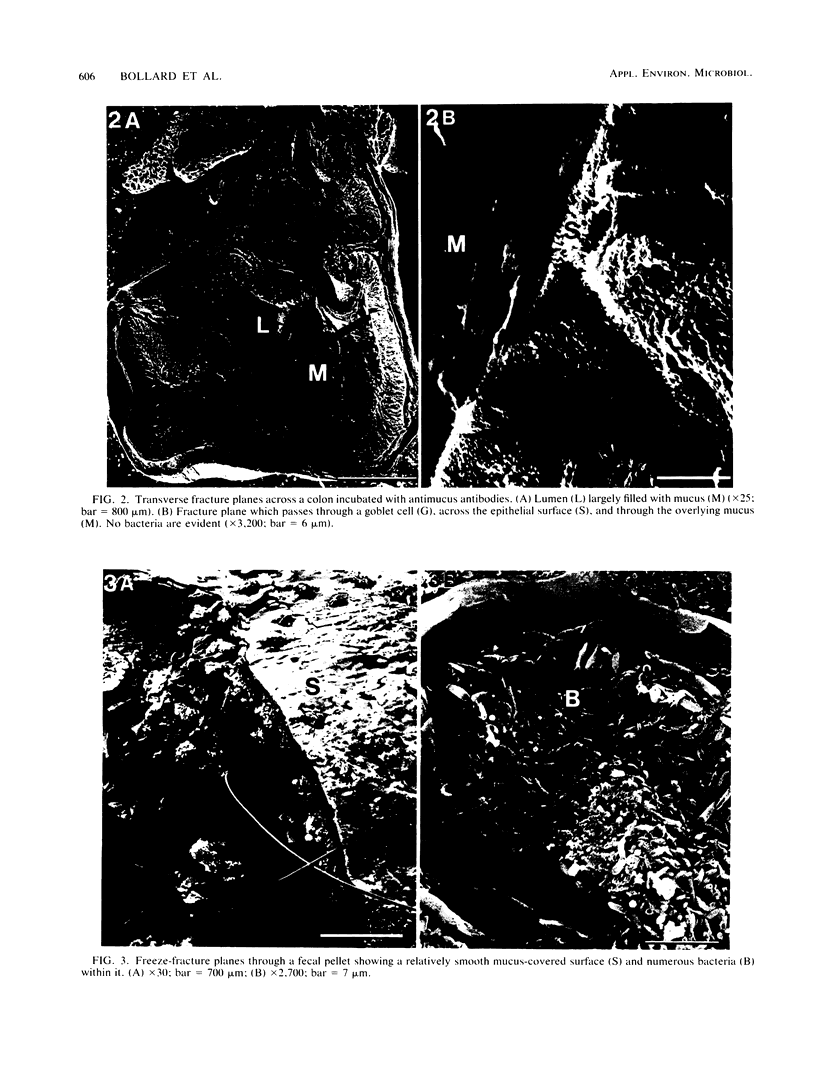
The distribution of microorganisms in the mid-colon of the rat was studied by light and scanning electron microscopy. An antiserum against rat colon mucus was used to stabilize the mucus in situ. In samples not incubated with antiserum, the mucus disintegrated and contracted into patchy strands only partly covering the luminal surface of the colon. Bacteria were seen within fecal pellets, tangled among the strands of mucus, and scattered on the epithelial surface. However, when incubated with antiserum, mucus almost completely filled the lumen and coated the fecal pellets. Bacteria in these stabilized preparations were limited mainly to the fecal pellets, and there were small numbers scattered in the luminal mucus, but none were observed on the epithelial surface or within the crypts. Latex particles introduced into the lumen with the antiserum or with phosphate-buffered saline showed the same distribution as the bacteria. These findings are at variance with previous reports that organisms occur in abundance in the mucous layer, adjacent to cell surfaces, and inside crypts. Our results suggest that conventional preparation for microscopy without prior stabilization of the mucus in situ may lead to artifactual redistribution of microorganisms and emphasize the importance of mucus in maintaining mucosal-floral homeostasis in the colon.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davis C. P., McAllister J. S., Savage D. C. Microbial colonization of the intestinal epithelium in suckling mice. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):666–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.666-672.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurn B. A., Chantler S. M. Production of reagent antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):104–142. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Myhre E. Differential staining of bacteria in clinical specimens using acridine orange buffered at low pH. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Aug;85(4):249–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach W. D., Lee A., Stubbs R. P. Localization of bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract: a possible explanation of intestinal spirochaetosis. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):961–972. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.961-972.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. P., Lim T. H., Pybus J., Clarke A. C. Tissue distribution of orally administered bismuth in the rat. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1980 May-Jun;7(3):319–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1980.tb00076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudin J. Immunochemical analysis by antigen-antibody precipitation in gels. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):166–198. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M., Lee A., Leach W. D. The mucosa-associated microflora of the rat intestine: a study of normal distribution and magnesium sulphate induced diarrhoea. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1978 Dec;56(6):649–662. doi: 10.1038/icb.1978.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozee K. R., Cooper D., Lam K., Costerton J. W. Microbial flora of the mouse ileum mucous layer and epithelial surface. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1451–1463. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1451-1463.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Associations and physiological interactions of indigenous microorganisms and gastrointestinal epithelia. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1372–1379. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Blumershine R. V. Surface-surface associations in microbial communities populating epithelial habitats in the murine gastrointestinal ecosystem: scanning electron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):240–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.240-250.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., McAllister J. S., Davis C. P. Anaerobic bacteria on the mucosal epithelium of the murine large bowel. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):492–502. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.492-502.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. W., Tasman-Jones C., Wiggins P. M., Lee S. P. Pig gastric mucus: a one-way barrier for H+. Gastroenterology. 1985 Dec;89(6):1313–1318. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90648-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Jervis H. R., Nakazawa H., Robinson D. M. Spiral-shaped organisms on the surface colonic epithelium of the monkey and man. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Nov;27(11):1287–1296. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.11.1287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler E. E., Gavin J. B., Seelye R. N. Freeze-drying from tertiary butanol in the preparation of endocardium for scanning electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 1975 Sep;50(5):331–337. doi: 10.3109/10520297509117083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]