Abstract
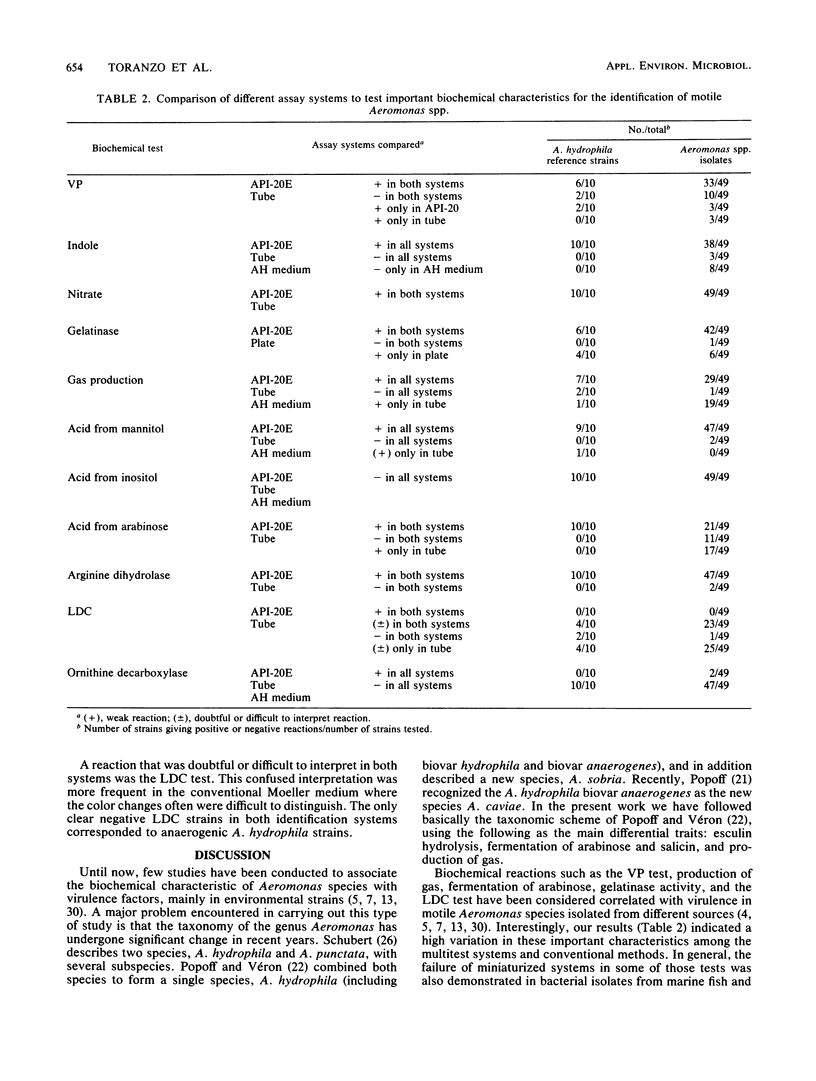
Important biochemical reactions in conventional tests were compared with counterpart reactions in two multiple test systems, API-20E (Analytab Products, Plainview, N.Y.) and Aeromonas hydrophila medium, to evaluate their accuracy for the identification of motile Aeromonas spp. isolated from fish. In a total of 49 Aeromonas spp. isolates and 10 A. hydrophila reference strains, false-negative or -positive reactions were detected in the Voges-Proskauer test, indole production, gelatinase activity, production of gas, fermentation of arabinose, and lysine decarboxylase reaction. A good correlation was found, among the three identification systems, for the fermentation of mannitol and inositol as well as for the arginine dihydrolase and ornithine decarboxylase tests. The failure of A. hydrophila medium in the detection of gas indicates that this medium is not entirely suitable for defining aerogenic or anaerogenic strains. From the results of the present study, we consider that of the identification method and taxonomic scheme to be adopted for environmental Aeromonas spp. must be standardized.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan B. J., Stevenson R. M. Extracellular virulence factors of Aeromonas hydrophila in fish infections. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Oct;27(10):1114–1122. doi: 10.1139/m81-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asao T., Kinoshita Y., Kozaki S., Uemura T., Sakaguchi G. Purification and some properties of Aeromonas hydrophila hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):122–127. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.122-127.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger Y., Lallier R., Cousineau G. Isolation of enterotoxigenic Aeromonas from fish. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1161–1164. doi: 10.1139/m77-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Atkinson H. M., Gracey M. Biochemical characteristics of enterotoxigenic Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):48–52. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.48-52.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Cooper M., Beaman J., Partridge K., Peterson D., Gracey M. Biotyping and virulence factors in clinical and environmental isolates of Aeromonas species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):1146–1149. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.1146-1149.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumberbatch N., Gurwith M. J., Langston C., Sack R. B., Brunton J. L. Cytotoxic enterotoxin produced by Aeromonas hydrophila: relationship of toxigenic isolates to diarrheal disease. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):829–837. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.829-837.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. A., 2nd, Kane J. G., Garagusi V. F. Human aeromonas infections: a review of the literature and a case report of endocarditis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 May;57(3):267–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen T. C., Fliermans C. B., Hirsch R. P., Esch G. W. Prevalence and distribution of Aeromonas hydrophila in the United States. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Nov;36(5):731–738. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.5.731-738.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. W., Daily O. P., Hunt W. S., Seidler R. J., Allen D. A., Colwell R. R. Aeromonas primary wound infection of a diver in polluted waters. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):46–49. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.46-49.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W. Aeromonas hydrophila: ecology and toxigenicity of isolates from an estuary. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;50(2):359–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb00900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J., Seidler R. J., Lockman H., Colwell R. R. Medium for the presumptive identification of Aeromonas hydrophila and Enterobacteriaceae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):1023–1026. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.1023-1026.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lallier R., Bernard F., Lalonde G. Difference in the extracellular products of two strains of Aeromonas hydrophila virulent and weakly virulent for fish. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Jul;30(7):900–904. doi: 10.1139/m84-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. L., Jensen N. J. An Aeromonas species implicated in ulcer-disease of the cod (Gadus morhua). Nord Vet Med. 1977 Apr-May;29(4-5):199–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. L., Willeberg P. The impact of terrestrial and estuarial factors on the density of environmental bacterial (Vibrionaceae) and faecal coliforms in coastal water. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1984 Aug;179(4):308–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivier G., Lallier R., Larivière S. A toxigenic profile of Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas sobria isolated from fish. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Mar;27(3):330–333. doi: 10.1139/m81-050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M., Véron M. A taxonomic study of the Aeromonas hydrophila-Aeromonas punctata group. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):11–22. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahim Z., Sanyal S. C., Aziz K. M., Huq M. I., Chowdhury A. A. Isolation of enterotoxigenic, hemolytic, and antibiotic-resistant Aeromonas hydrophila strains from infected fish in Bangladesh. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):865–867. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.865-867.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotts E. B., Jr, Gaines J. L., Jr, Martin L., Prestwood A. K. Aeromonas-induced deaths among fish and reptiles in an eutrophic inland lake. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Sep 15;161(6):603–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toranzo A. E., Barja J. L., Potter S. A., Colwell R. R., Hetrick F. M., Crosa J. H. Molecular factors associated with virulence of marine vibrios isolated from striped bass in Chesapeake Bay. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1220–1227. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1220-1227.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



