Abstract
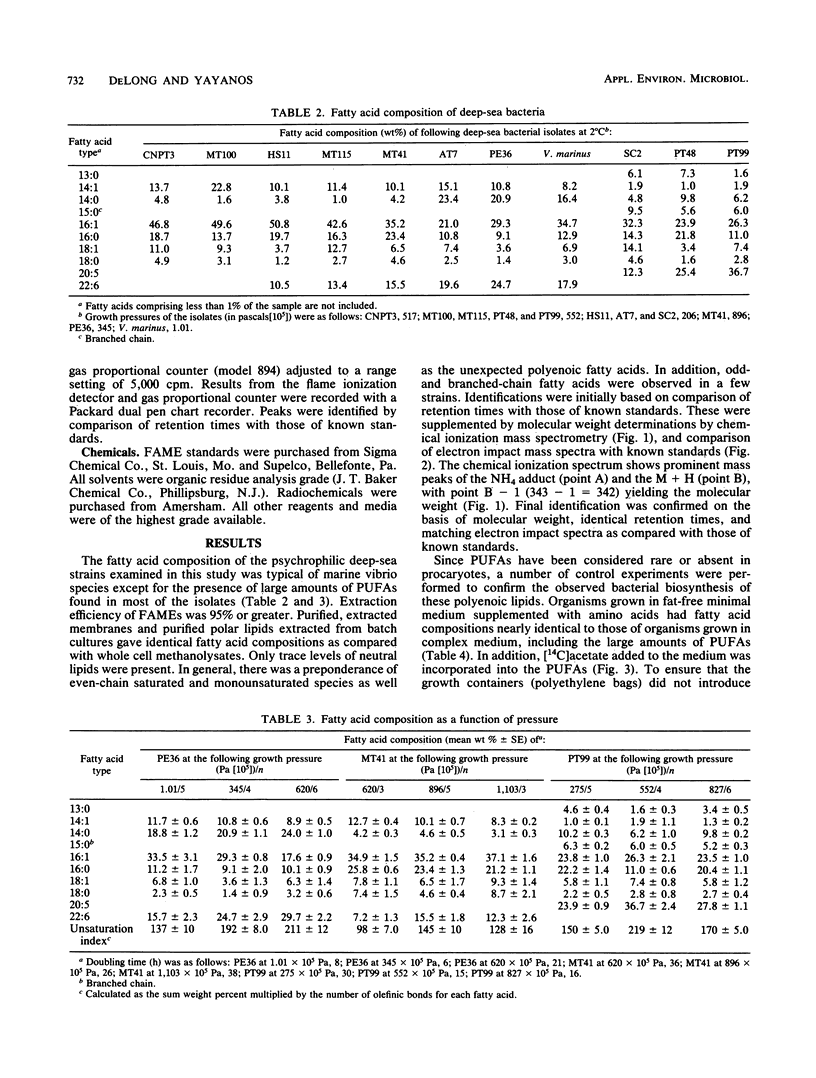
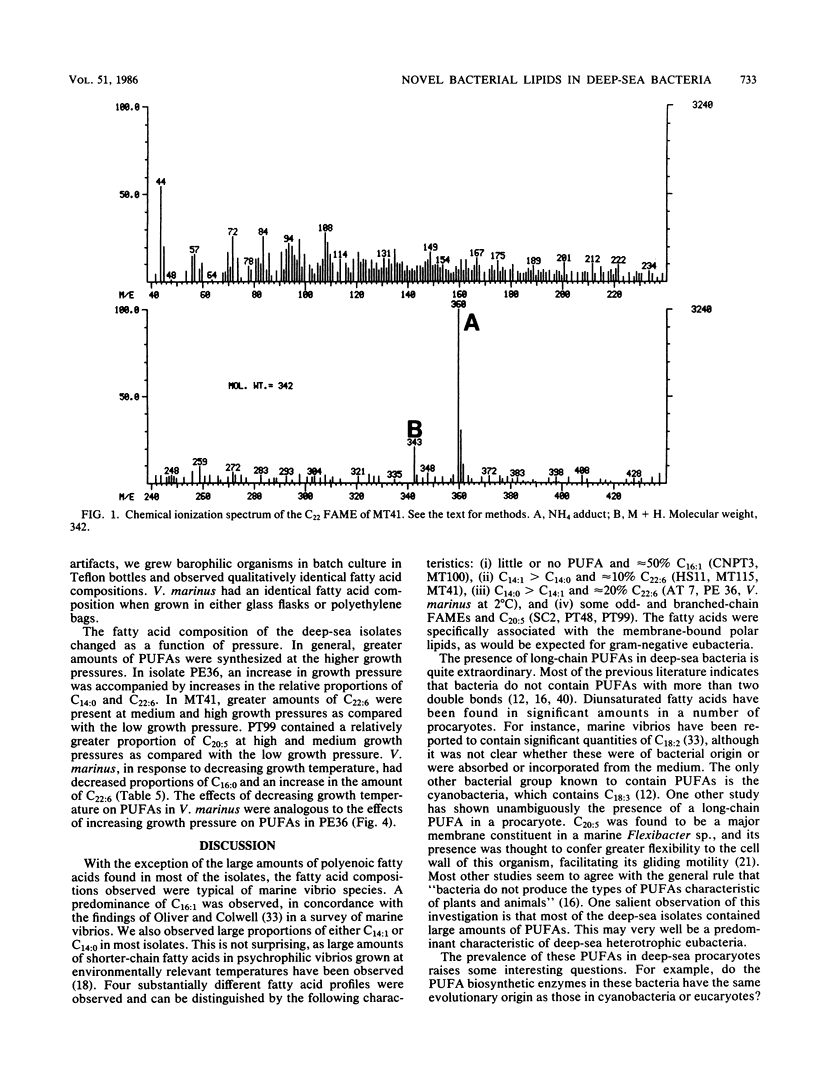
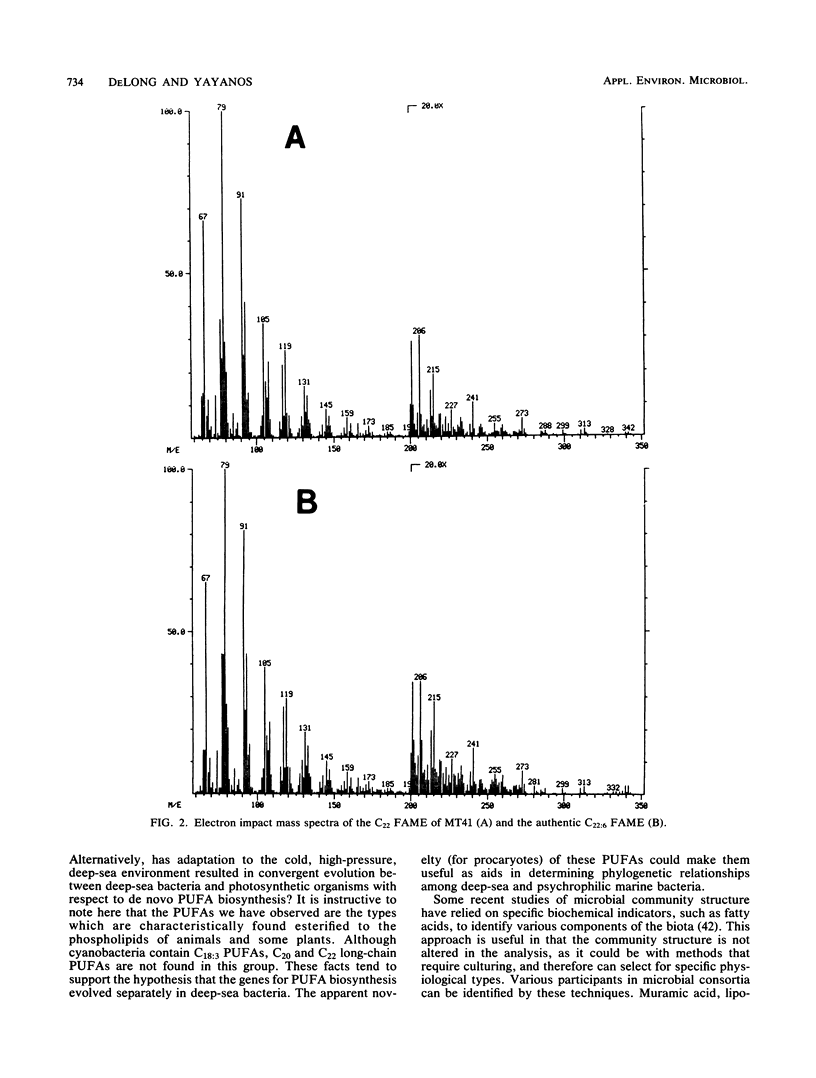
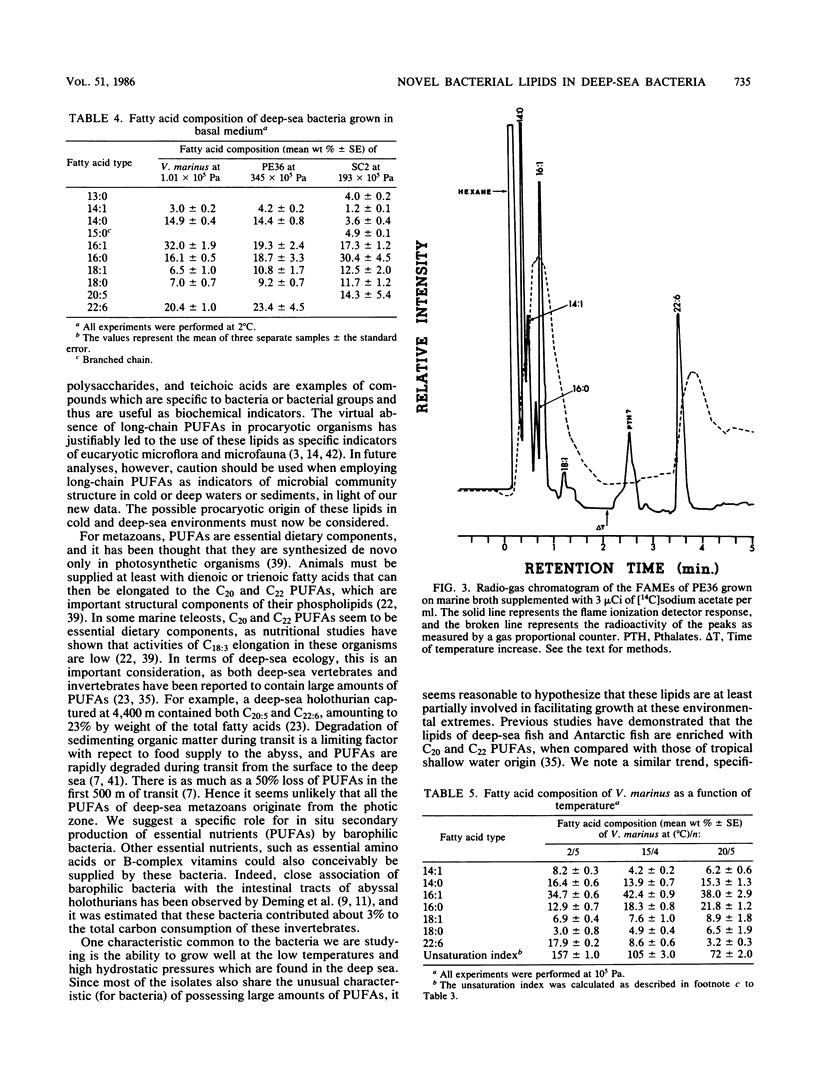
The fatty acid composition of the membrane lipids in 11 deep-sea bacterial isolates was determined. The fatty acids observed were typical of marine vibrios except for the presence of large amounts of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). These long-chain PUFAs were previously thought to be absent in procaryotes, with the notable exception of a single marine Flexibacter sp. In three barophilic strains tested at 2°C, there was a general increase in the relative amount of PUFAs as pressure was increased from a low growth pressure towards the optimal growth pressure. In Vibrio marinus MP-1, a psychrophilic strain, PUFAs were found to increase as a function of decreasing temperature at constant atmospheric pressure. These results suggest the involvement of PUFAs in the maintenance of optimal membrane fluidity and function over environmentally relevant temperatures and pressures. Furthermore, since these lipids are essential nutrients for higher taxa and are found in large amounts in the lipids of deep-sea vertebrates and invertebrates, an important, specific role for deep-sea bacteria in abyssal food webs is implicated.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F. Lipids of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: structure and metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):833–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.833-843.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobbie R. J., White D. C. Characterization of benthic microbial community structure by high-resolution gas chromatography of Fatty Acid methyl esters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jun;39(6):1212–1222. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.6.1212-1222.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. J., Katznel A., Razin S., Rottem S. Spiroplasma membrane lipids. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):118–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.118-122.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong E. F., Yayanos A. A. Adaptation of the membrane lipids of a deep-sea bacterium to changes in hydrostatic pressure. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1101–1103. doi: 10.1126/science.3992247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deming J. W., Colwell R. R. Barophilic bacteria associated with digestive tracts of abyssal holothurians. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Nov;44(5):1222–1230. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.5.1222-1230.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deming J. W., Colwell R. R. Observations of barophilic microbial activity in samples of sediment and intercepted particulates from the demerara abyssal plain. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):1002–1006. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.1002-1006.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERWIN J., BLOCH K. BIOSYNTHESIS OF UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS IN MICROORGANISMS. Science. 1964 Mar 6;143(3610):1006–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3610.1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas T., Herodek S. The effect of environmental temperature on the fatty acid composition of crustacean plankton. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jul;5(3):369–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federle T. W., Hullar M. A., Livingston R. J., Meeter D. A., White D. C. Spatial distribution of biochemical parameters indicating biomass and community composition of microbial assemblies in estuarine mud flat sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):58–63. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.58-63.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine H. Comparative aspects of bacterial lipids. Adv Microb Physiol. 1972;8:1–58. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannasch H. W., Taylor C. D. Deep-sea microbiology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:487–514. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald A. G. The effects of pressure on the molecular structure and physiological functions of cell membranes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Jan 7;304(1118):47–68. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquis R. E. High-pressure microbial physiology. Adv Microb Physiol. 1976;14(11):159–241. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr A. G., Ingraham J. L. EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON THE COMPOSITION OF FATTY ACIDS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84(6):1260–1267. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1260-1267.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita R. Y. Psychrophilic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Jun;39(2):144–167. doi: 10.1128/br.39.2.144-167.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Lambert M. A., Merwin W. H. Comparison of rapid methods for analysis of bacterial fatty acids. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jul;28(1):80–85. doi: 10.1128/am.28.1.80-85.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Munson R. Separation of the inner (cytoplasmic) and outer membranes of Gram-negative bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:642–653. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders H. L., Hessler R. R. Ecology of the deep-sea benthos. Science. 1969 Mar 28;163(3874):1419–1424. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3874.1419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. The polyunsaturated fatty acids of microorganisms. Adv Lipid Res. 1966;4:107–174. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9940-5.50011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayanos A. A., Dietz A. S. Thermal Inactivation of a Deep-Sea Barophilic Bacterium, Isolate CNPT-3. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1481–1489. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1481-1489.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayanos A. A., Dietz A. S., VAN Boxtel R. Isolation of a deep-sea barophilic bacterium and some of its growth characteristics. Science. 1979 Aug 24;205(4408):808–810. doi: 10.1126/science.205.4408.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayanos A. A., Dietz A. S., Van Boxtel R. Dependence of reproduction rate on pressure as a hallmark of deep-sea bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1356–1361. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1356-1361.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yayanos A. A., Pollard E. C. A study of the effects of hydrostatic pressure on macromolecular synthesis in Escherichia coli. Biophys J. 1969 Dec;9(12):1464–1482. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86466-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



