Abstract
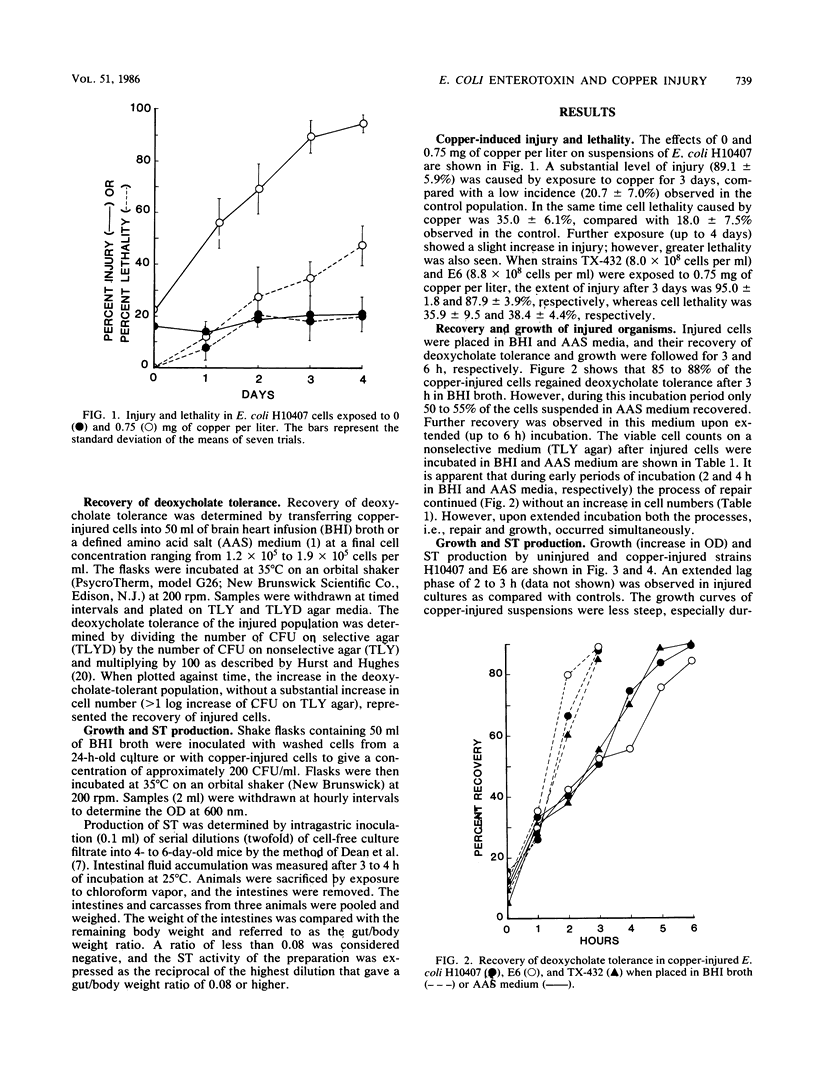
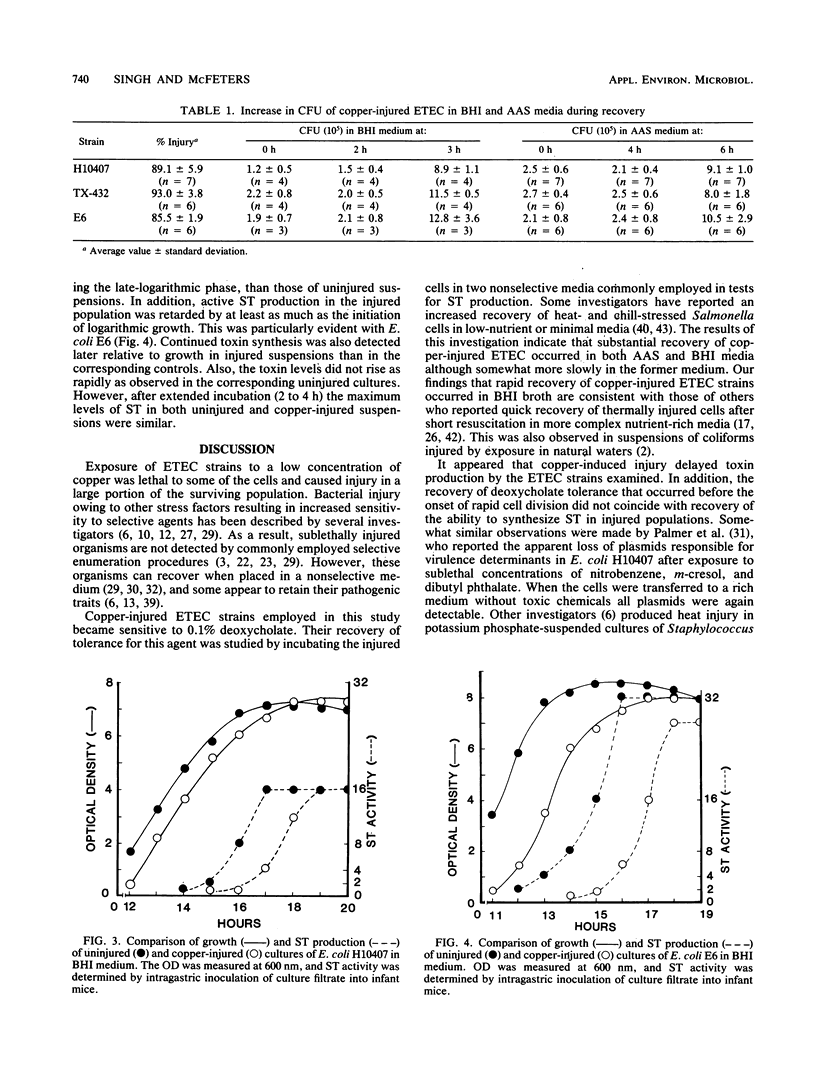
Exposure of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains to a sublethal concentration (0.75 mg/liter) of copper for 3 days at 4 degrees C induced sensitivity to deoxycholate (0.1%). When placed in a complex (brain heart infusion) or a defined amino acid salt medium, the copper-injured cells recovered their tolerance to deoxycholate in 3 and 6 h, respectively, and commenced active growth. Growth and heat-stable enterotoxin production of uninjured and copper-injured cells were studied in brain heart infusion medium. A slightly altered growth curve and an initial slow rate of toxin production were observed in injured cells when compared with those corresponding uninjured controls. However, maximum heat-stable enterotoxin levels in injured cultures were comparable to those produced by uninjured cells, suggesting that the enterotoxigenic potential of copper-injured cells was fully retained.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Nutrition and enterotoxin synthesis by enterotoxigenic strains of Escherichia coli: defined medium for production of heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):781–788. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.781-788.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette G. K., Jezeski J. J., McFeters G. A., Stuart D. G. Influence of environmental stress on enumeration of indicator bacteria from natural waters. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):186–194. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.186-194.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camper A. K., McFeters G. A. Chlorine injury and the enumeration of waterborne coliform bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):633–641. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.633-641.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins-Thompson D. L., Hurst A., Kruse H. Synthesis of enterotoxin B by Staphylococcus aureus strain S6 after recovery from heat injury. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Dec;19(12):1463–1468. doi: 10.1139/m73-238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domek M. J., LeChevallier M. W., Cameron S. C., McFeters G. A. Evidence for the role of copper in the injury process of coliform bacteria in drinking water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.289-293.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan A. F. Enumeration of stressed cells of Escherichia coli. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Jan;25(1):116–118. doi: 10.1139/m79-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka R. S., Hashimoto H. H., Siwak E. B., Young R. H. Effect of sunlight on survival of indicator bacteria in seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Mar;41(3):690–696. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.3.690-696.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Kean B. H., Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr, Bessudo D. Travelers' diarrhea and toxigenic Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 1;292(18):933–936. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505012921801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. J. Escherichia coli diarrhoea. J Infect. 1983 Nov;7(3):177–192. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(83)96953-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Moore R. A., Kirschenfeld P. M., Sande M. A. Role of toxigenic and invasive bacteria in acute diarrhea of childhood. N Engl J Med. 1975 Sep 18;293(12):567–572. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197509182931201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney T. R., Quesnel L. B. Thermal activation and dry-heat inactivation of spores of Bacillus subtilis MD2 and Bacillus subtilis var. niger. J Appl Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;48(2):231–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1980.tb01222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTSELL S. E. The longevity and behavior of pathogenic bacteria in frozen foods; the influence of plating media. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1951 Sep;41(9):1072–1077. doi: 10.2105/ajph.41.9.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst A., Hughes A. Repair of salt tolerance and recovery of lost D-alanine and magnesium following sublethal heating of Staphylococcus aureus are independent events. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Jun;27(6):627–632. doi: 10.1139/m81-095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudoh Y., Zen-Yoji H., Matsushita S., Sakai S., Maruyama T. Outbreaks of acute enteritis due to heat-stable enterotoxin-producing strains of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(3):175–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1977.tb00278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeChevallier M. W., Singh A., Schiemann D. A., McFeters G. A. Changes in virulence of waterborne enteropathogens with chlorine injury. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):412–419. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.412-419.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Caplan E. S., Waterman D., Cash R. A., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J. Diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli that produce only heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):78–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.78-82.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod R. A., Kuo S. C., Gelinas R. Metabolic injury to bacteria. II. Metabolic injury induced by distilled water or Cu++ in the plating diluent. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):961–969. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.961-969.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackey B. M., Derrick C. M. A comparison of solid and liquid media for measuring the sensitivity of heat-injured Salmonella typhimurium to selenite and tetrathionate media, and the time needed to recover resistance. J Appl Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;53(2):233–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1982.tb04682.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFeters G. A., Cameron S. C., LeChevallier M. W. Influence of diluents, media, and membrane filters on detection fo injured waterborne coliform bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):97–103. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.97-103.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFeters G. A., Camper A. K. Enumeration of indicator bacteria exposed to chlorine. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1983;29:177–193. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70357-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAMURA M., DAWSON D. A. Role of suspending and recovery media in the survival of frozen Shigella sonnei. Appl Microbiol. 1962 Jan;10:40–43. doi: 10.1128/am.10.1.40-43.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przybylski K. S., Witter L. D. Injury and recovery of Escherichia coli after sublethal acidification. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Feb;37(2):261–265. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.2.261-265.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. L., Koplan J. P., Wachsmuth I. K., Wells J. G., Gangarosa E. J., Guerrant R. L., Sack D. A. Epidemic diarrhea at Crater Lake from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. A large waterborne outbreak. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):714–718. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. W., Wachsmuth I. K., Buxton A. E., Evans D. G., DuPont H. L., Mason E., Barrett F. F. Infantile diarrhea produced by heat-stable enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 14;295(16):849–853. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610142951601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Hirschhorn N., Brownlee I., Cash R. A., Woodward W. E., Sack D. A. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia-coli-associated diarrheal disease in Apache children. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 15;292(20):1041–1045. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505152922001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A., LeChevallier M. W., McFeters G. A. Reduced virulence of Yersinia enterocolitica by copper-induced injury. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):406–411. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.406-411.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Halls S. Observations by the ligated intestinal segment and oral inoculation methods on Escherichia coli infections in pigs, calves, lambs and rabbits. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):499–529. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobota A. E. Effect of sublethal heat injury on tumour induction and RNA synthesis in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Microbios. 1978;23(92):115–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrells K. M., Speck M. L., Warren J. A. Pathogenicity of Salmonella gallinarum after metabolic injury by freezing. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jan;19(1):39–43. doi: 10.1128/am.19.1.39-43.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh S. M., Bissonnette G. K. Chlorine-induced damage to surface adhesions during sublethal injury of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1060–1065. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.1060-1065.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. M., Davies R. Minimal medium recovery of thermally injured Salmonella senftenberg 4969. J Appl Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;40(3):365–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1976.tb04185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



