Abstract
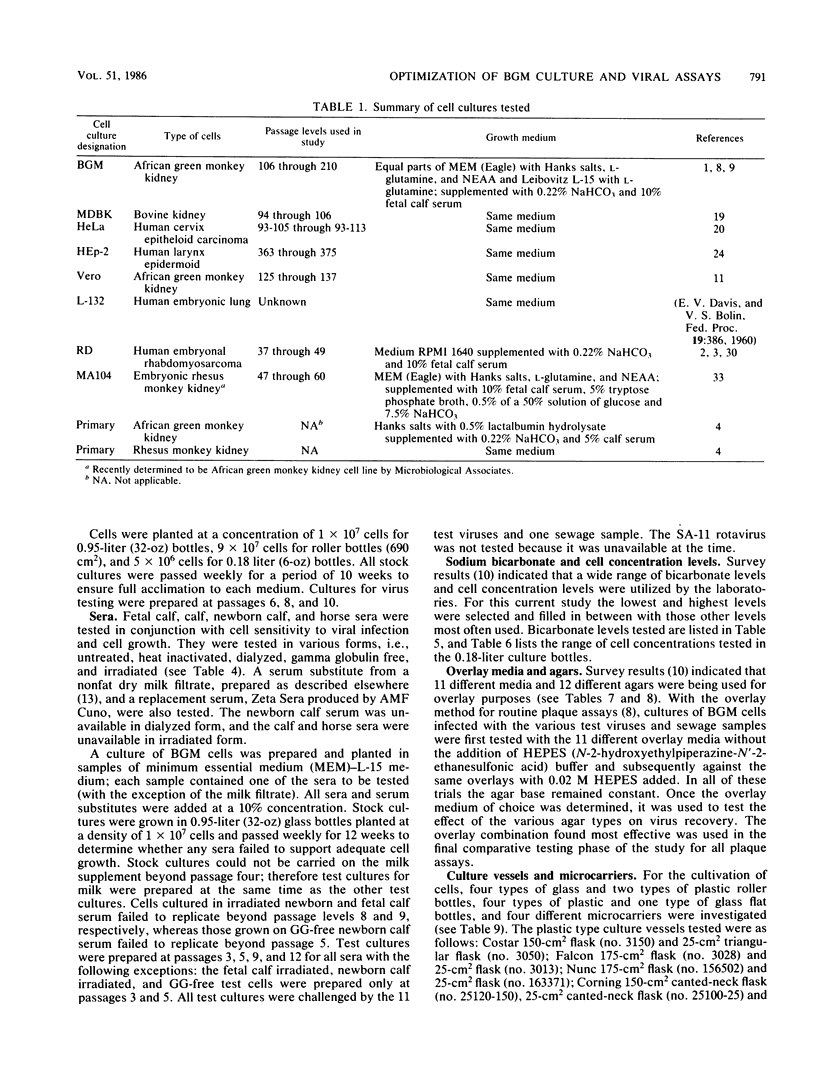
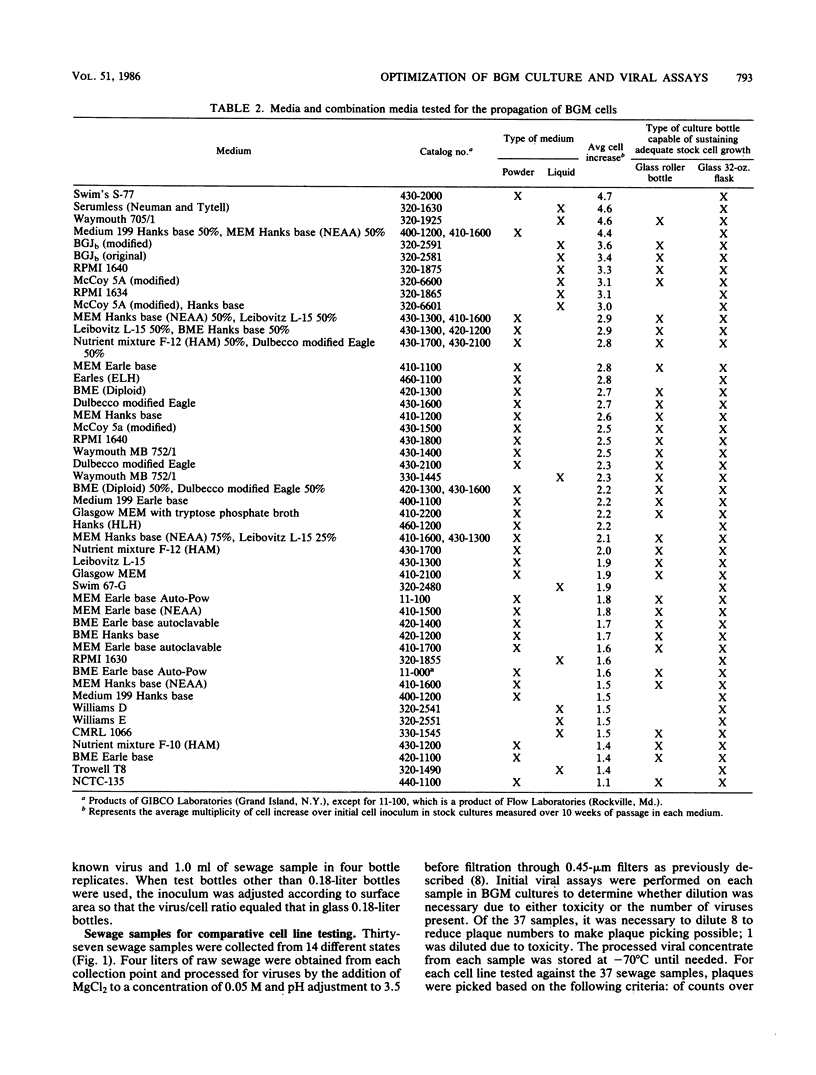
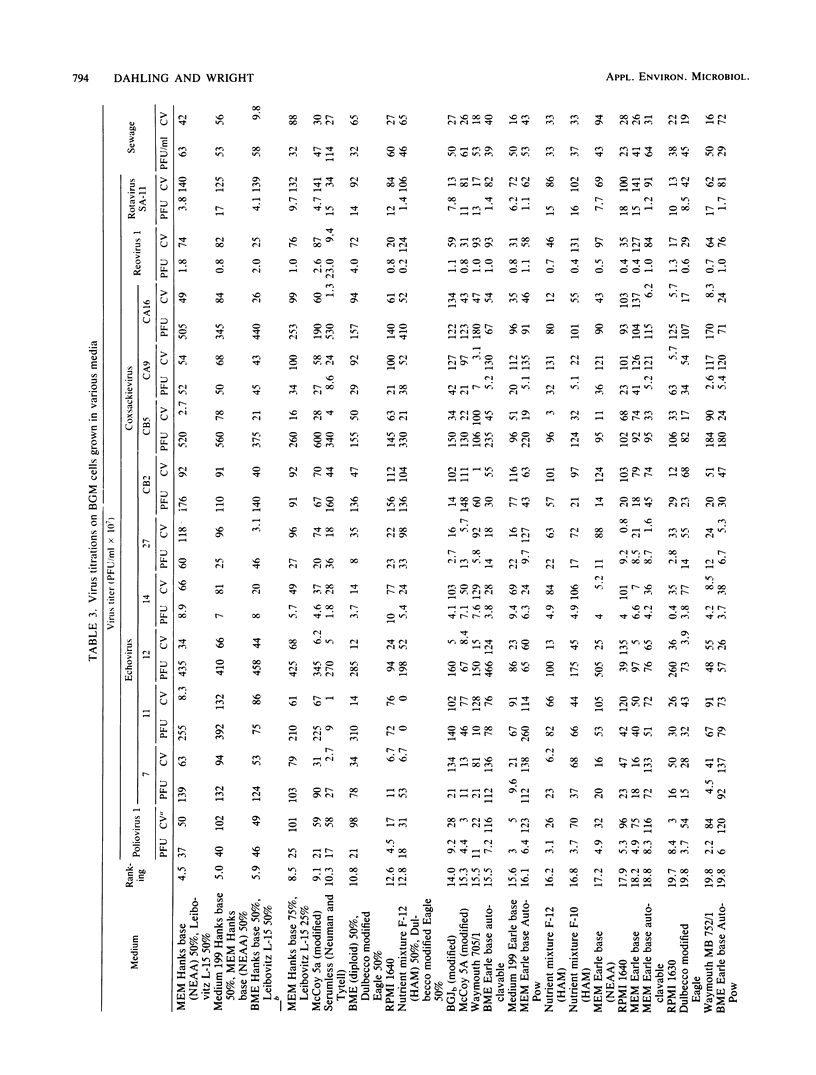
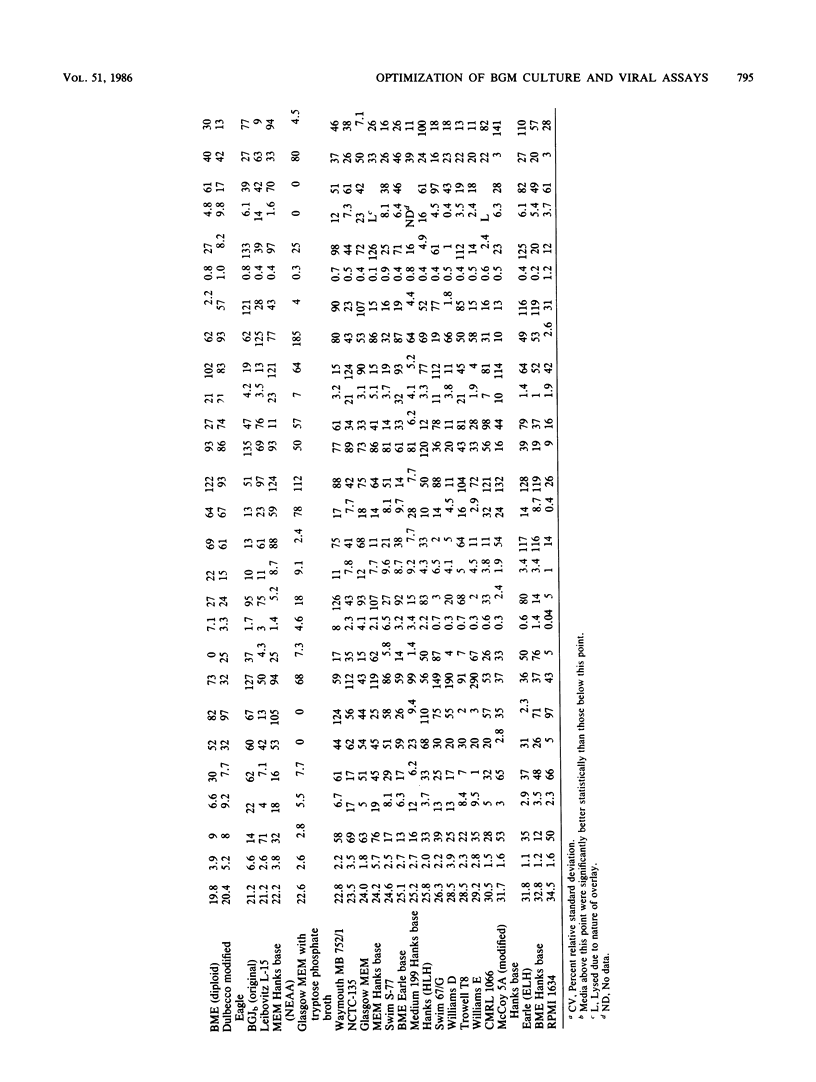
An in-depth study of the continuous cell line designated BGM is described herein, and recommendations are made for standardizing cell culture and viral assay procedures. Based on data gathered from a survey of 58 laboratories using this cell line, a research plan was developed that included the study of growth media, sera, NaHCO3 levels, culture bottles, cell concentration, overlay media, agar, virus infection conditions, and cell-dissociating agents. Additionally, a comparative virus isolation study with BGM cells and nine other cell types was conducted with 37 sewage samples collected from nine different geographic areas. The results of the study indicated that the BGM cell line is superior for virus isolation when compared with the other cell types and that certain media and additives tend to increase BGM cell sensitivity to a specific group of viruses. A standardized procedure for cultivation of BGM cells is described which provides a more effective enterovirus assay system.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERG G., CHANG S. L., HARRIS E. K. DEVITALIZATION OF MICROORGANISMS BY IODINE. I. DYNAMICS OF THE DEVITALIZATION OF ENTEROVIRUSES BY ELEMENTAL IODINE. Virology. 1964 Apr;22:461–481. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barron A. L., Olshevsky C., Cohen M. M. Characteristics of the BGM line of cells from African green monkey kidney. Brief report. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;32(4):389–392. doi: 10.1007/BF01250067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell E. J., Cosgrove B. P. Routine enterovirus diagnosis in a human rhabdomyosarcoma cell line. Bull World Health Organ. 1980;58(3):423–428. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. H., Ward R. L. Induction of cytopathogenicity in mammalian cell lines challenged with culturable enteric viruses and its enhancement by 5-iododeoxyuridine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Apr;43(4):861–868. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.4.861-868.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahling D. R., Berg G., Berman D. BGM, a continuous cell line more sensitive than primary rhesus and African green kidney cells for the recovery of viruses from water. Health Lab Sci. 1974 Oct;11(4):275–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahling D. R., Safferman R. S. Survival of enteric viruses under natural conditions in a subarctic river. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Dec;38(6):1103–1110. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.6.1103-1110.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. M., Phillpotts R. J. Susceptibility of the VERO line of African green monkey kidney cells to human enteroviruses. J Hyg (Lond) 1974 Feb;72(1):23–30. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400023160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagle H. Buffer combinations for mammalian cell culture. Science. 1971 Oct 29;174(4008):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4008.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fassolitis A. C., Novelli R. M., Larkin E. P. Serum substitute in epithelial cell culture media: nonfat dry milk filtrate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):200–203. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.200-203.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebb C., Clark J. M., Hirtenstein M. D., Lindgren G., Lindskog U., Lundgren B., Vretblad P. Alternative surfaces for microcarrier culture of animal cells. Dev Biol Stand. 1981;50:93–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ham R. G., McKeehan W. L. Media and growth requirements. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:44–93. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. W., Thilly W. G., Wang D. I. Parameters affecting cell growth on reduced charge microcarriers. Dev Biol Stand. 1979;42:159–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. H., Volkers S. A. Use of a new bead microcarrier for the culture of anchorage dependent cells in pseudo suspension. Dev Biol Stand. 1979;42:147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADIN S. H., DARBY N. B., Jr Established kidney cell lines of normal adult bovine and ovine origin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Jul;98(3):574–576. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE A. E., SABACHEWSKY L., TOOLAN H. W. Culture characteristics of four permanent lines of human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1955 Oct;15(9):598–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto M., Mukai M., Tagaya I. Variation in susceptibility of HeLa cell lines to coxsackievirus A9. Arch Virol. 1979;59(3):213–222. doi: 10.1007/BF01317416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick J. L., Safferman R., Rao V. C., Goyal S., Berg G., Dahling D. R., Wright B. A., Akin E., Stetler R., Sorber C. Round robin investigation of methods for the recovery of poliovirus from drinking water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):144–150. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.144-150.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menegus M. A., Hollick G. E. Increased Efficiency of Group B Coxsackievirus Isolation from Clinical Specimens by Use of BGM Cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):945–948. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.945-948.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monahan J. J., Hall R. H. Magnesium acetate treatment of roller bottles for the preparation of uniform cell monolayers. Prep Biochem. 1974;4(4):353–358. doi: 10.1080/00327487408068210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton H. J. A survey of commercially available tissue culture media. In Vitro. 1970 Sep-Oct;6(2):89–108. doi: 10.1007/BF02616112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payment P., Ayache R., Trudel M. A survey of enteric viruses in domestic sewage. Can J Microbiol. 1983 Jan;29(1):111–119. doi: 10.1139/m83-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. J., Gregory E. A. Relationship between in vitro growth promotion and biophysical and biochemical properties of the serum supplement. In Vitro. 1982 Jun;18(6):576–584. doi: 10.1007/BF02810081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridinger D. N., Spendlove R. S., Barnett B. B., George D. B., Roth J. C. Evaluation of cell lines and immunofluorescence and plaque assay procedures for quantifying reoviruses in sewage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Apr;43(4):740–746. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.4.740-746.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Ho H. H., Lennette E. H. Propagation and isolation of group A coxsackieviruses in RD cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Sep;2(3):183–185. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.3.183-185.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Ho H. H., Riggs J. L., Lennette E. H. Comparative sensitivity of various cell culture systems for isolation of viruses from wastewater and fecal samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Sep;36(3):480–486. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.3.480-486.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellwood J., Dadswell J. V., Slade J. S. Viruses in sewage as an indicator of their presence in the community. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Apr;86(2):217–225. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400068947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. M., Estes M. K., Graham D. Y., Gerba C. P. A plaque assay for the simian rotavirus SAII. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jun;43(3):513–519. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-3-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. M., Gerba C. P. Development of a method for detection of human rotavirus in water and sewage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1440–1450. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1440-1450.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis C., Melnick J. L., Rapp F. Effects of pancreatin on the growth of reovirus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):155–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.1.155-160.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



