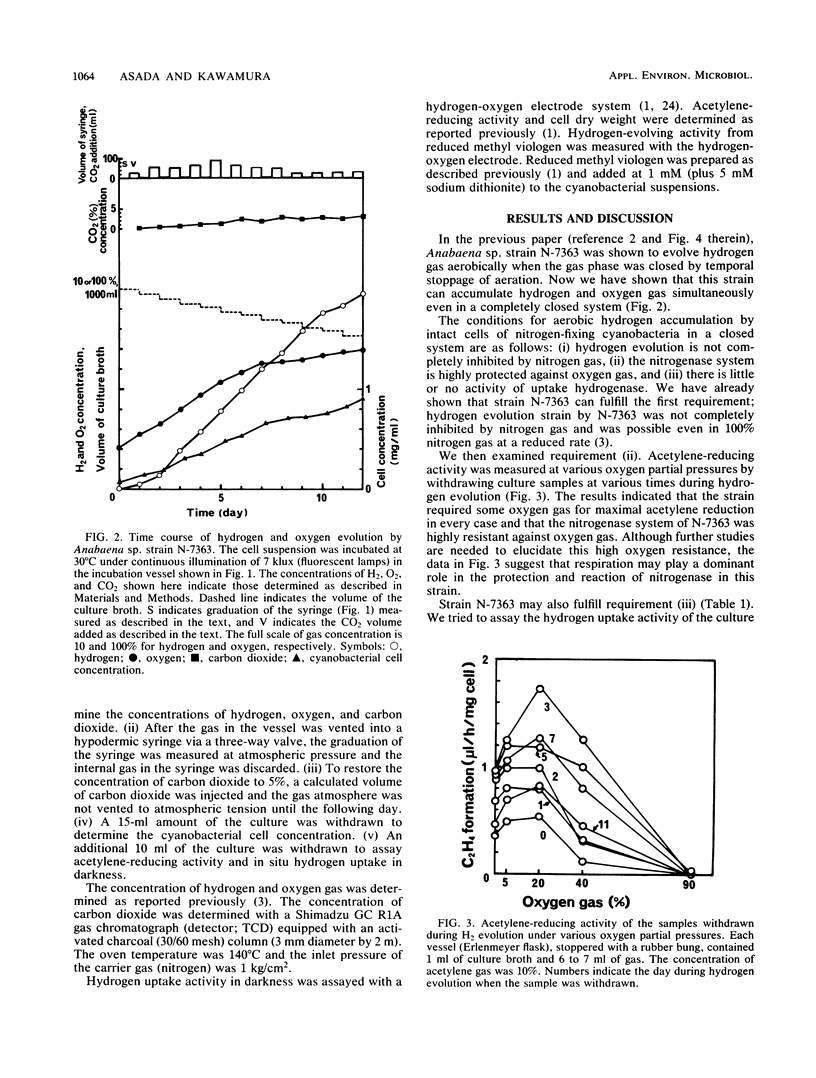
Abstract
Hydrogen evolution by a nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium, Anabaena sp. strain N-7363, was tested in order to develop a water biophotolysis system under aerobic conditions. A culture of the strain supplemented with carbon dioxide under an air atmosphere evolved hydrogen and oxygen gas, which reached final concentrations of 9.7 and 69.8%, respectively, after 12 days of incubation. Hydrogen uptake activity was not observed during incubation, and nitrogenase was thought to be the sole enzyme responsible for the hydrogen evolution.
Full text
PDF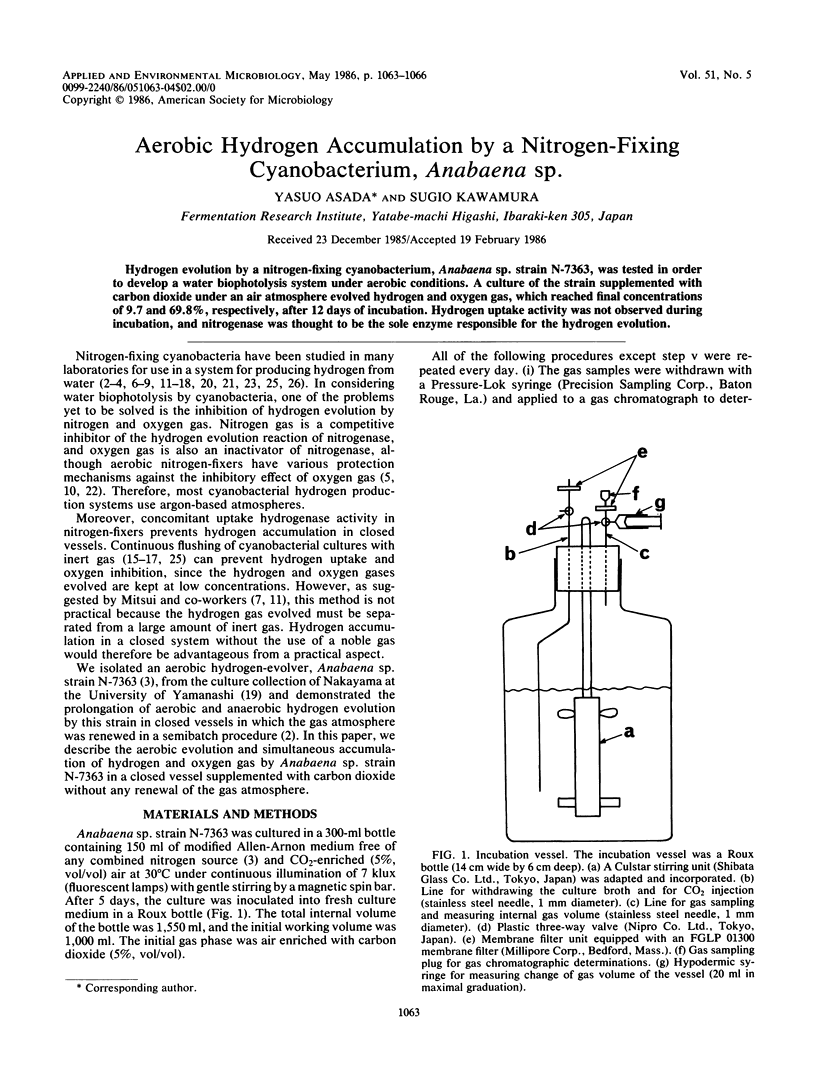


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Daday A., Platz R. A., Smith G. D. Anaerobic and aerobic hydrogen gas formation by the blue-green alga Anabaena cylindrica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Nov;34(5):478–483. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.5.478-483.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumazawa S., Mitsui A. Comparative Amperometric Study of Uptake Hydrogenase and Hydrogen Photoproduction Activities between Heterocystous Cyanobacterium Anabaena cylindrica B629 and Nonheterocystous Cyanobacterium Oscillatoria sp. Strain Miami BG7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):287–291. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.287-291.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert G. R., Daday A., Smith G. D. Duration of Hydrogen Formation by Anabaena cylindrica B629 in Atmospheres of Argon, Air, and Nitrogen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Sep;38(3):530–536. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.3.530-536.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert G. R., Daday A., Smith G. D. Effects of Ammonium Ions, Oxygen, Carbon Monoxide, and Acetylene on Anaerobic and Aerobic Hydrogen Formation by Anabaena cylindrica B629. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Sep;38(3):521–529. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.3.521-529.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto K., Hallenbeck P. C., Benemann J. R. Hydrogen Production by the Thermophilic Alga Mastigocladus laminosus: Effects of Nitrogen, Temperature, and Inhibition of Photosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Sep;38(3):440–446. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.3.440-446.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto K., Hallenbeck P. C., Benemann J. R. Nitrogen fixation by thermophilic blue-green algae (cyanobacteria): temperature characteristics and potential use in biophotolysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):454–458. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.454-458.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phlips E. J., Mitsui A. Role of Light Intensity and Temperature in the Regulation of Hydrogen Photoproduction by the Marine Cyanobacterium Oscillatoria sp. Strain Miami BG7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1212–1220. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1212-1220.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. D. Some aspects of structure and function in N2-fixing cyanobacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:497–536. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman J. C., Benemann J. R. Hydrogen production by nitrogen-starved cultures of Anabaena cylindrica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):123–131. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.123-131.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. K., Haskell J. B., Tabita F. R., Van Baalen C. Aerobic hydrogen production by the heterocystous cyanobacteria Anabaena spp. strains CA and 1F. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1118–1122. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1118-1122.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


