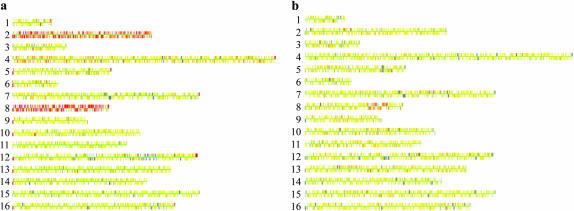
Figure 1.—
Microarray analysis (CGH) of two tel1 mec1-21 haploid strains derived from diploids MV24 and MV56. Diploids heterozygous for the tel1 and mec1-21 mutations were sporulated and dissected. Cultures derived from spores with the double-mutant genotype were examined before or after vegetative subculturing. DNA was isolated from each subcultured strain, labeled with a Cy5-fluorescent nucleotide, and mixed with DNA from a control strain that was labeled with a Cy3-fluorescent nucleotide. This mixture was hybridized to a microarray containing all of the yeast ORFs, and the ratio of hybridization of the two different samples to each ORF was determined (Dunham et al. 2002). In the Gene Spring 5.1 images used, each chromosome is shown by a series of adjacent very small rectangles representing the ORFs. In the image, yellow indicates the same dosage in the experimental and the control strain; red and blue indicate a duplication and a deletion, respectively, in the experimental strain relative to the control. The large gray region on chromosome XII is an uninformative signal on the microarray. (a) MV24-15. This strain (which was examined prior to subculturing) is disomic for chromosomes II and VIII. (b) MV56-5-2. This strain was vegetatively subcultured 10 times before the DNA was analyzed. The strain has a duplication of a 120-kb region of chromosome VIII that includes the DNA2 gene.